28 KiB
| comments |
|---|
| true |
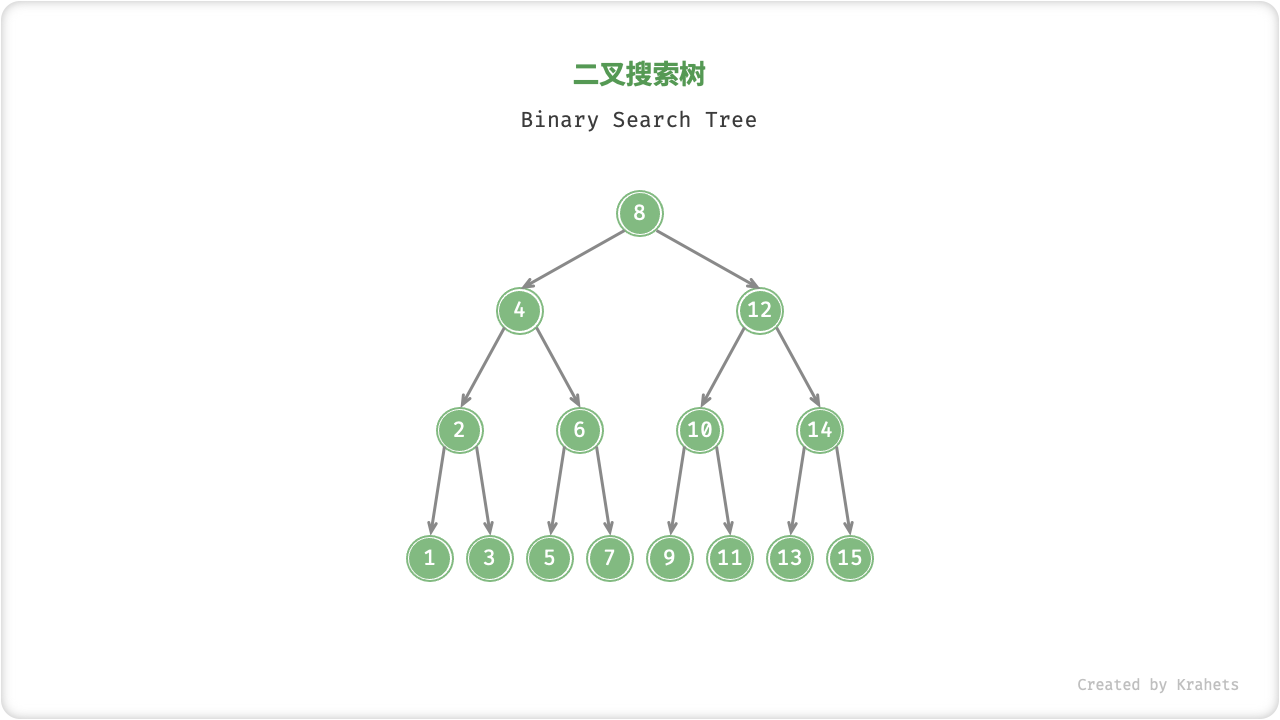
二叉搜索树
「二叉搜索树 Binary Search Tree」满足以下条件:
- 对于根结点,左子树中所有结点的值
<根结点的值<右子树中所有结点的值; - 任意结点的左子树和右子树也是二叉搜索树,即也满足条件
1.;
二叉搜索树的操作
查找结点
给定目标结点值 num ,可以根据二叉搜索树的性质来查找。我们声明一个结点 cur ,从二叉树的根结点 root 出发,循环比较结点值 cur.val 和 num 之间的大小关系
- 若
cur.val < val,说明目标结点在cur的右子树中,因此执行cur = cur.right; - 若
cur.val > val,说明目标结点在cur的左子树中,因此执行cur = cur.left; - 若
cur.val = val,说明找到目标结点,跳出循环并返回该结点即可;
=== "Step 1"

=== "Step 2"

=== "Step 3"

=== "Step 4"

二叉搜索树的查找操作和二分查找算法如出一辙,也是在每轮排除一半情况。循环次数最多为二叉树的高度,当二叉树平衡时,使用 O(\log n) 时间。
=== "Java"
```java title="binary_search_tree.java"
/* 查找结点 */
TreeNode search(int num) {
TreeNode cur = root;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur != null) {
// 目标结点在 root 的右子树中
if (cur.val < num) cur = cur.right;
// 目标结点在 root 的左子树中
else if (cur.val > num) cur = cur.left;
// 找到目标结点,跳出循环
else break;
}
// 返回目标结点
return cur;
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="binary_search_tree.cpp"
/* 查找结点 */
TreeNode* search(int num) {
TreeNode* cur = root;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur != nullptr) {
// 目标结点在 root 的右子树中
if (cur->val < num) cur = cur->right;
// 目标结点在 root 的左子树中
else if (cur->val > num) cur = cur->left;
// 找到目标结点,跳出循环
else break;
}
// 返回目标结点
return cur;
}
```
=== "Python"
```python title="binary_search_tree.py"
""" 查找结点 """
def search(self, num: int) -> typing.Optional[TreeNode]:
cur = self.root
# 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while cur is not None:
# 目标结点在 root 的右子树中
if cur.val < num:
cur = cur.right
# 目标结点在 root 的左子树中
elif cur.val > num:
cur = cur.left
# 找到目标结点,跳出循环
else:
break
return cur
```
=== "Go"
```go title="binary_search_tree.go"
/* 查找结点 */
func (bst *BinarySearchTree) Search(num int) *TreeNode {
node := bst.root
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
for node != nil {
if node.Val < num {
// 目标结点在 root 的右子树中
node = node.Right
} else if node.Val > num {
// 目标结点在 root 的左子树中
node = node.Left
} else {
// 找到目标结点,跳出循环
break
}
}
// 返回目标结点
return node
}
```
=== "JavaScript"
```js title="binary_search_tree.js"
/* 查找结点 */
function search(num) {
let cur = root;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur !== null) {
// 目标结点在 root 的右子树中
if (cur.val < num) cur = cur.right;
// 目标结点在 root 的左子树中
else if (cur.val > num) cur = cur.left;
// 找到目标结点,跳出循环
else break;
}
// 返回目标结点
return cur;
}
```
=== "TypeScript"
```typescript title="binary_search_tree.ts"
/* 查找结点 */
function search(num: number): TreeNode | null {
let cur = root;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur !== null) {
if (cur.val < num) {
cur = cur.right; // 目标结点在 root 的右子树中
} else if (cur.val > num) {
cur = cur.left; // 目标结点在 root 的左子树中
} else {
break; // 找到目标结点,跳出循环
}
}
// 返回目标结点
return cur;
}
```
=== "C"
```c title="binary_search_tree.c"
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title="binary_search_tree.cs"
/* 查找结点 */
TreeNode? search(int num)
{
TreeNode? cur = root;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur != null)
{
// 目标结点在 root 的右子树中
if (cur.val < num) cur = cur.right;
// 目标结点在 root 的左子树中
else if (cur.val > num) cur = cur.left;
// 找到目标结点,跳出循环
else break;
}
// 返回目标结点
return cur;
}
```
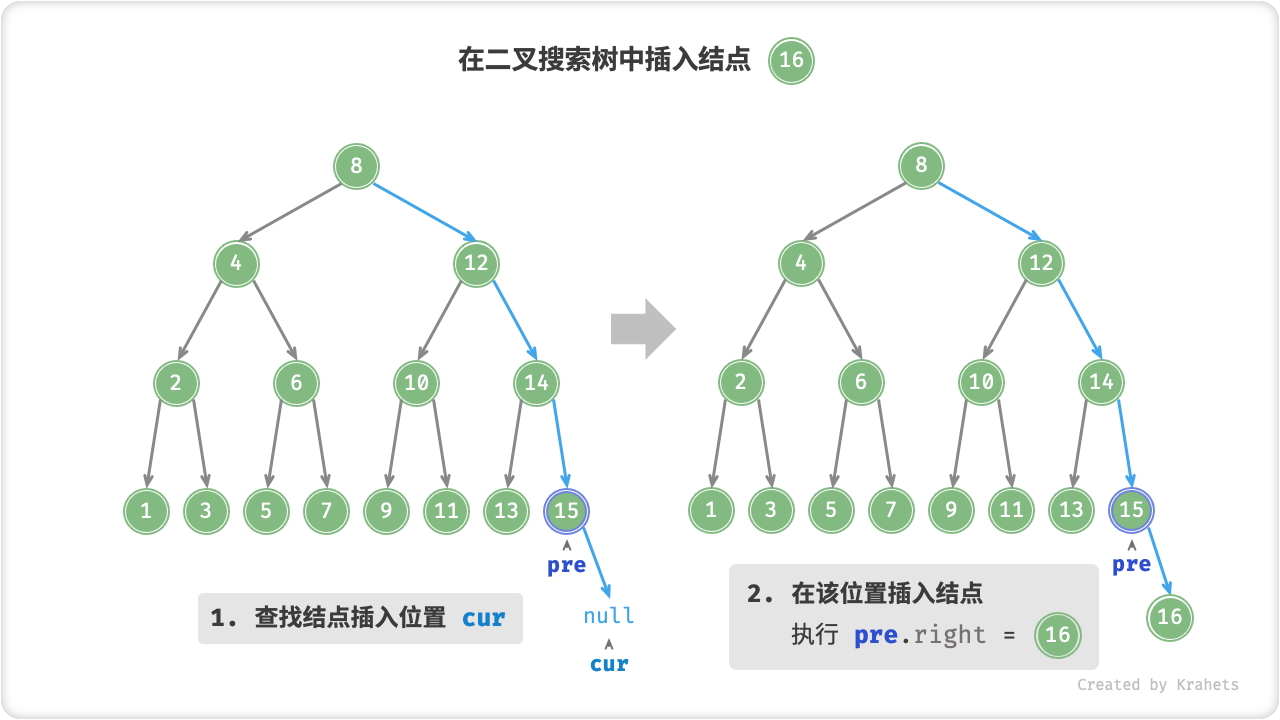
插入结点
给定一个待插入元素 num ,为了保持二叉搜索树“左子树 < 根结点 < 右子树”的性质,插入操作分为两步:
- 查找插入位置: 与查找操作类似,我们从根结点出发,根据当前结点值和
num的大小关系循环向下搜索,直到越过叶结点(遍历到\text{null})时跳出循环; - 在该位置插入结点: 初始化结点
num,将该结点放到\text{null}的位置 ;
二叉搜索树不允许存在重复结点,否则将会违背其定义。因此若待插入结点在树中已经存在,则不执行插入,直接返回即可。
=== "Java"
```java title="binary_search_tree.java"
/* 插入结点 */
TreeNode insert(int num) {
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if (root == null) return null;
TreeNode cur = root, pre = null;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur != null) {
// 找到重复结点,直接返回
if (cur.val == num) return null;
pre = cur;
// 插入位置在 root 的右子树中
if (cur.val < num) cur = cur.right;
// 插入位置在 root 的左子树中
else cur = cur.left;
}
// 插入结点 val
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(num);
if (pre.val < num) pre.right = node;
else pre.left = node;
return node;
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="binary_search_tree.cpp"
/* 插入结点 */
TreeNode* insert(int num) {
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
TreeNode *cur = root, *pre = nullptr;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur != nullptr) {
// 找到重复结点,直接返回
if (cur->val == num) return nullptr;
pre = cur;
// 插入位置在 root 的右子树中
if (cur->val < num) cur = cur->right;
// 插入位置在 root 的左子树中
else cur = cur->left;
}
// 插入结点 val
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(num);
if (pre->val < num) pre->right = node;
else pre->left = node;
return node;
}
```
=== "Python"
```python title="binary_search_tree.py"
""" 插入结点 """
def insert(self, num: int) -> typing.Optional[TreeNode]:
root = self.root
# 若树为空,直接提前返回
if root is None:
return None
cur = root
pre = None
# 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while cur is not None:
# 找到重复结点,直接返回
if cur.val == num:
return None
pre = cur
if cur.val < num: # 插入位置在 root 的右子树中
cur = cur.right
else: # 插入位置在 root 的左子树中
cur = cur.left
# 插入结点 val
node = TreeNode(num)
if pre.val < num:
pre.right = node
else:
pre.left = node
return node
```
=== "Go"
```go title="binary_search_tree.go"
/* 插入结点 */
func (bst *BinarySearchTree) Insert(num int) *TreeNode {
cur := bst.root
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if cur == nil {
return nil
}
// 待插入结点之前的结点位置
var prev *TreeNode = nil
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
for cur != nil {
if cur.Val == num {
return nil
}
prev = cur
if cur.Val < num {
cur = cur.Right
} else {
cur = cur.Left
}
}
// 插入结点
node := NewTreeNode(num)
if prev.Val < num {
prev.Right = node
} else {
prev.Left = node
}
return cur
}
```
=== "JavaScript"
```js title="binary_search_tree.js"
/* 插入结点 */
function insert(num) {
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if (root === null) return null;
let cur = root, pre = null;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur !== null) {
// 找到重复结点,直接返回
if (cur.val === num) return null;
pre = cur;
// 插入位置在 root 的右子树中
if (cur.val < num) cur = cur.right;
// 插入位置在 root 的左子树中
else cur = cur.left;
}
// 插入结点 val
let node = new Tree.TreeNode(num);
if (pre.val < num) pre.right = node;
else pre.left = node;
return node;
}
```
=== "TypeScript"
```typescript title="binary_search_tree.ts"
/* 插入结点 */
function insert(num: number): TreeNode | null {
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if (root === null) {
return null;
}
let cur = root,
pre: TreeNode | null = null;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur !== null) {
if (cur.val === num) {
return null; // 找到重复结点,直接返回
}
pre = cur;
if (cur.val < num) {
cur = cur.right as TreeNode; // 插入位置在 root 的右子树中
} else {
cur = cur.left as TreeNode; // 插入位置在 root 的左子树中
}
}
// 插入结点 val
let node = new TreeNode(num);
if (pre!.val < num) {
pre!.right = node;
} else {
pre!.left = node;
}
return node;
}
```
=== "C"
```c title="binary_search_tree.c"
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title="binary_search_tree.cs"
/* 插入结点 */
TreeNode? insert(int num)
{
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if (root == null) return null;
TreeNode? cur = root, pre = null;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur != null)
{
// 找到重复结点,直接返回
if (cur.val == num) return null;
pre = cur;
// 插入位置在 root 的右子树中
if (cur.val < num) cur = cur.right;
// 插入位置在 root 的左子树中
else cur = cur.left;
}
// 插入结点 val
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(num);
if (pre != null)
{
if (pre.val < num) pre.right = node;
else pre.left = node;
}
return node;
}
```
为了插入结点,需要借助 辅助结点 prev 保存上一轮循环的结点,这样在遍历到 \text{null} 时,我们也可以获取到其父结点,从而完成结点插入操作。
与查找结点相同,插入结点使用 O(\log n) 时间。
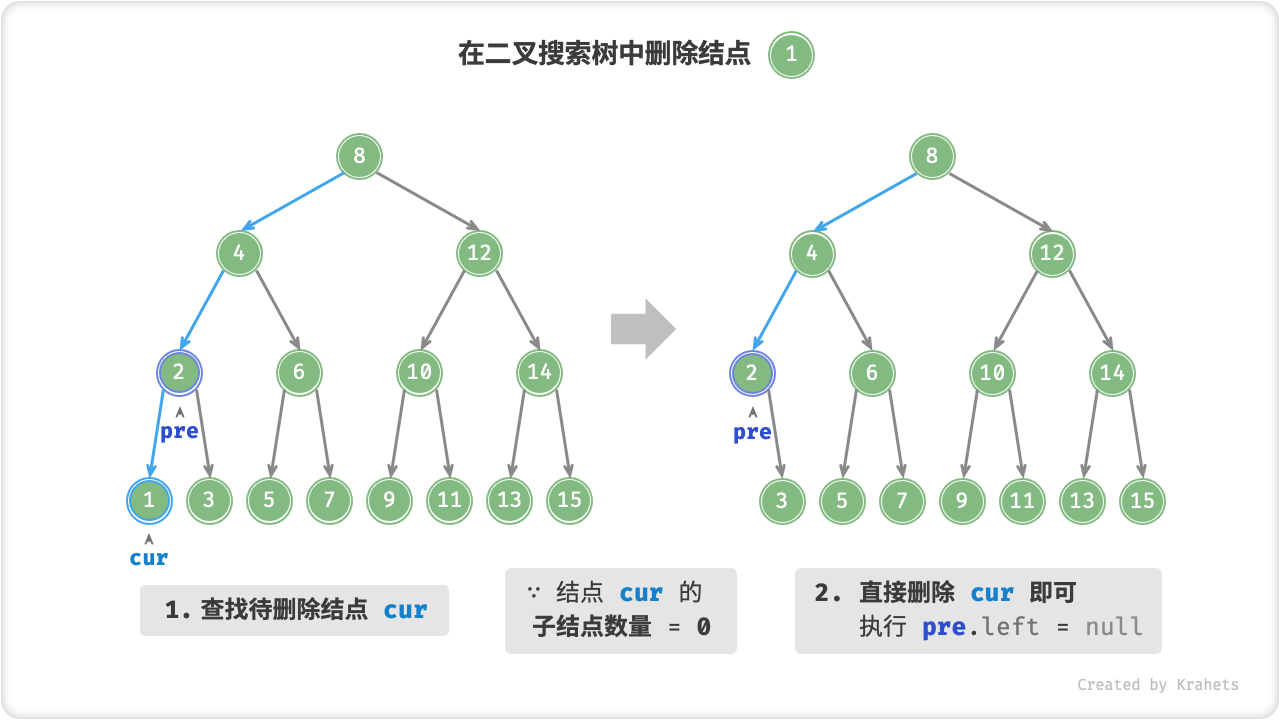
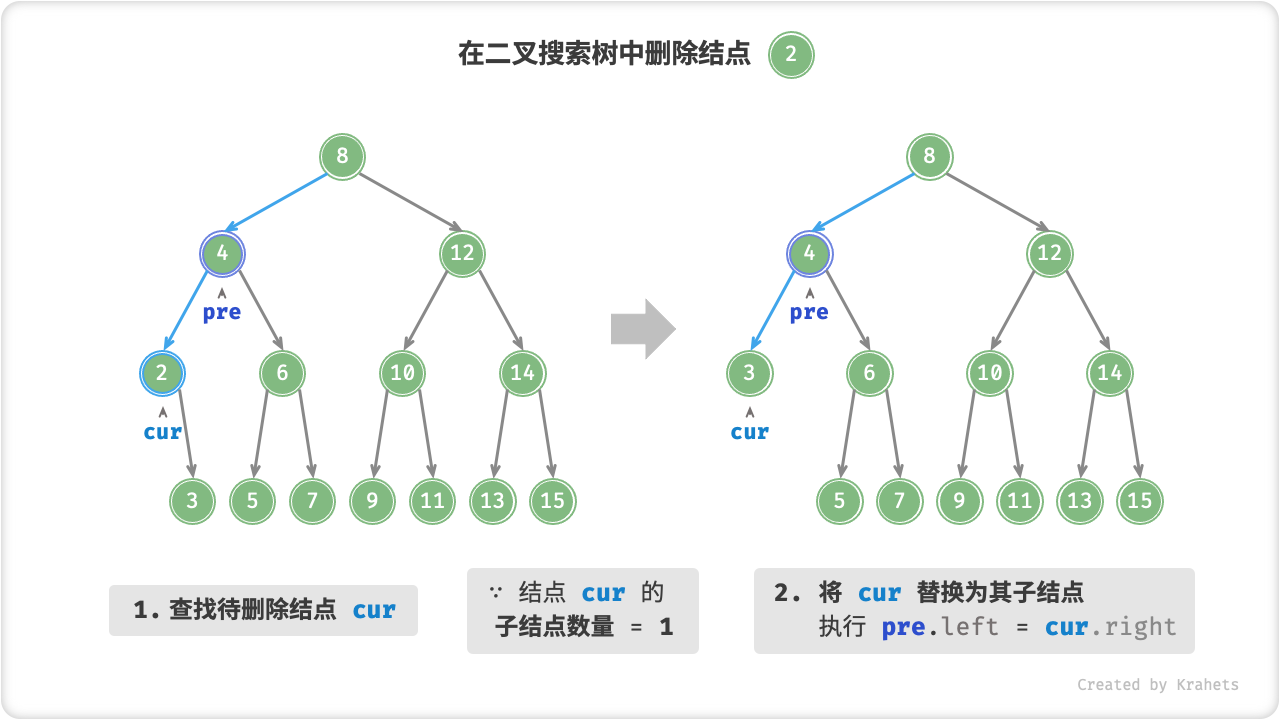
删除结点
与插入结点一样,我们需要在删除操作后维持二叉搜索树的“左子树 < 根结点 < 右子树”的性质。首先,我们需要在二叉树中执行查找操作,获取待删除结点。接下来,根据待删除结点的子结点数量,删除操作需要分为三种情况:
待删除结点的子结点数量 = 0 。 表明待删除结点是叶结点,直接删除即可。
待删除结点的子结点数量 = 1 。 将待删除结点替换为其子结点。
待删除结点的子结点数量 = 2 。 删除操作分为三步:
- 找到待删除结点在 中序遍历序列 中的下一个结点,记为
nex; - 在树中递归删除结点
nex; - 使用
nex替换待删除结点;
=== "Step 1"

=== "Step 2"

=== "Step 3"

=== "Step 4"

删除结点操作也使用 O(\log n) 时间,其中查找待删除结点 O(\log n) ,获取中序遍历后继结点 O(\log n) 。
=== "Java"
```java title="binary_search_tree.java"
/* 删除结点 */
TreeNode remove(int num) {
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if (root == null) return null;
TreeNode cur = root, pre = null;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur != null) {
// 找到待删除结点,跳出循环
if (cur.val == num) break;
pre = cur;
// 待删除结点在 root 的右子树中
if (cur.val < num) cur = cur.right;
// 待删除结点在 root 的左子树中
else cur = cur.left;
}
// 若无待删除结点,则直接返回
if (cur == null) return null;
// 子结点数量 = 0 or 1
if (cur.left == null || cur.right == null) {
// 当子结点数量 = 0 / 1 时, child = null / 该子结点
TreeNode child = cur.left != null ? cur.left : cur.right;
// 删除结点 cur
if (pre.left == cur) pre.left = child;
else pre.right = child;
}
// 子结点数量 = 2
else {
// 获取中序遍历中 cur 的下一个结点
TreeNode nex = min(cur.right);
int tmp = nex.val;
// 递归删除结点 nex
remove(nex.val);
// 将 nex 的值复制给 cur
cur.val = tmp;
}
return cur;
}
/* 获取最小结点 */
TreeNode min(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return root;
// 循环访问左子结点,直到叶结点时为最小结点,跳出
while (root.left != null) {
root = root.left;
}
return root;
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="binary_search_tree.cpp"
/* 删除结点 */
TreeNode* remove(int num) {
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
TreeNode *cur = root, *pre = nullptr;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur != nullptr) {
// 找到待删除结点,跳出循环
if (cur->val == num) break;
pre = cur;
// 待删除结点在 root 的右子树中
if (cur->val < num) cur = cur->right;
// 待删除结点在 root 的左子树中
else cur = cur->left;
}
// 若无待删除结点,则直接返回
if (cur == nullptr) return nullptr;
// 子结点数量 = 0 or 1
if (cur->left == nullptr || cur->right == nullptr) {
// 当子结点数量 = 0 / 1 时, child = nullptr / 该子结点
TreeNode* child = cur->left != nullptr ? cur->left : cur->right;
// 删除结点 cur
if (pre->left == cur) pre->left = child;
else pre->right = child;
}
// 子结点数量 = 2
else {
// 获取中序遍历中 cur 的下一个结点
TreeNode* nex = min(cur->right);
int tmp = nex->val;
// 递归删除结点 nex
remove(nex->val);
// 将 nex 的值复制给 cur
cur->val = tmp;
}
return cur;
}
/* 获取最小结点 */
TreeNode* min(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return root;
// 循环访问左子结点,直到叶结点时为最小结点,跳出
while (root->left != nullptr) {
root = root->left;
}
return root;
}
```
=== "Python"
```python title="binary_search_tree.py"
""" 删除结点 """
def remove(self, num: int) -> typing.Optional[TreeNode]:
root = self.root
# 若树为空,直接提前返回
if root is None:
return None
cur = root
pre = None
# 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while cur is not None:
# 找到待删除结点,跳出循环
if cur.val == num:
break
pre = cur
if cur.val < num: # 待删除结点在 root 的右子树中
cur = cur.right
else: # 待删除结点在 root 的左子树中
cur = cur.left
# 若无待删除结点,则直接返回
if cur is None:
return None
# 子结点数量 = 0 or 1
if cur.left is None or cur.right is None:
# 当子结点数量 = 0 / 1 时, child = null / 该子结点
child = cur.left or cur.right
# 删除结点 cur
if pre.left == cur:
pre.left = child
else:
pre.right = child
# 子结点数量 = 2
else:
# 获取中序遍历中 cur 的下一个结点
nex = self.min(cur.right)
tmp = nex.val
# 递归删除结点 nex
self.remove(nex.val)
# 将 nex 的值复制给 cur
cur.val = tmp
return cur
""" 获取最小结点 """
def min(self, root: typing.Optional[TreeNode]) -> typing.Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None:
return root
# 循环访问左子结点,直到叶结点时为最小结点,跳出
while root.left is not None:
root = root.left
return root
```
=== "Go"
```go title="binary_search_tree.go"
/* 删除结点 */
func (bst *BinarySearchTree) Remove(num int) *TreeNode {
cur := bst.root
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if cur == nil {
return nil
}
// 待删除结点之前的结点位置
var prev *TreeNode = nil
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
for cur != nil {
if cur.Val == num {
break
}
prev = cur
if cur.Val < num {
// 待删除结点在右子树中
cur = cur.Right
} else {
// 待删除结点在左子树中
cur = cur.Left
}
}
// 若无待删除结点,则直接返回
if cur == nil {
return nil
}
// 子结点数为 0 或 1
if cur.Left == nil || cur.Right == nil {
var child *TreeNode = nil
// 取出待删除结点的子结点
if cur.Left != nil {
child = cur.Left
} else {
child = cur.Right
}
// 将子结点替换为待删除结点
if prev.Left == cur {
prev.Left = child
} else {
prev.Right = child
}
// 子结点数为 2
} else {
// 获取中序遍历中待删除结点 cur 的下一个结点
next := bst.GetInorderNext(cur)
temp := next.Val
// 递归删除结点 next
bst.Remove(next.Val)
// 将 next 的值复制给 cur
cur.Val = temp
}
return cur
}
```
=== "JavaScript"
```js title="binary_search_tree.js"
/* 删除结点 */
function remove(num) {
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if (root === null) return null;
let cur = root, pre = null;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur !== null) {
// 找到待删除结点,跳出循环
if (cur.val === num) break;
pre = cur;
// 待删除结点在 root 的右子树中
if (cur.val < num) cur = cur.right;
// 待删除结点在 root 的左子树中
else cur = cur.left;
}
// 若无待删除结点,则直接返回
if (cur === null) return null;
// 子结点数量 = 0 or 1
if (cur.left === null || cur.right === null) {
// 当子结点数量 = 0 / 1 时, child = null / 该子结点
let child = cur.left !== null ? cur.left : cur.right;
// 删除结点 cur
if (pre.left === cur) pre.left = child;
else pre.right = child;
}
// 子结点数量 = 2
else {
// 获取中序遍历中 cur 的下一个结点
let nex = min(cur.right);
let tmp = nex.val;
// 递归删除结点 nex
remove(nex.val);
// 将 nex 的值复制给 cur
cur.val = tmp;
}
return cur;
}
```
=== "TypeScript"
```typescript title="binary_search_tree.ts"
/* 删除结点 */
function remove(num: number): TreeNode | null {
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if (root === null) {
return null;
}
let cur = root,
pre: TreeNode | null = null;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur !== null) {
// 找到待删除结点,跳出循环
if (cur.val === num) {
break;
}
pre = cur;
if (cur.val < num) {
cur = cur.right as TreeNode; // 待删除结点在 root 的右子树中
} else {
cur = cur.left as TreeNode; // 待删除结点在 root 的左子树中
}
}
// 若无待删除结点,则直接返回
if (cur === null) {
return null;
}
// 子结点数量 = 0 or 1
if (cur.left === null || cur.right === null) {
// 当子结点数量 = 0 / 1 时, child = null / 该子结点
let child = cur.left !== null ? cur.left : cur.right;
// 删除结点 cur
if (pre!.left === cur) {
pre!.left = child;
} else {
pre!.right = child;
}
}
// 子结点数量 = 2
else {
// 获取中序遍历中 cur 的下一个结点
let next = min(cur.right);
let tmp = next!.val;
// 递归删除结点 nex
remove(next!.val);
// 将 nex 的值复制给 cur
cur.val = tmp;
}
return cur;
}
```
=== "C"
```c title="binary_search_tree.c"
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title="binary_search_tree.cs"
/* 删除结点 */
TreeNode? remove(int num)
{
// 若树为空,直接提前返回
if (root == null) return null;
TreeNode? cur = root, pre = null;
// 循环查找,越过叶结点后跳出
while (cur != null)
{
// 找到待删除结点,跳出循环
if (cur.val == num) break;
pre = cur;
// 待删除结点在 root 的右子树中
if (cur.val < num) cur = cur.right;
// 待删除结点在 root 的左子树中
else cur = cur.left;
}
// 若无待删除结点,则直接返回
if (cur == null || pre == null) return null;
// 子结点数量 = 0 or 1
if (cur.left == null || cur.right == null)
{
// 当子结点数量 = 0 / 1 时, child = null / 该子结点
TreeNode? child = cur.left != null ? cur.left : cur.right;
// 删除结点 cur
if (pre.left == cur)
{
pre.left = child;
}
else
{
pre.right = child;
}
}
// 子结点数量 = 2
else
{
// 获取中序遍历中 cur 的下一个结点
TreeNode? nex = min(cur.right);
if (nex != null)
{
int tmp = nex.val;
// 递归删除结点 nex
remove(nex.val);
// 将 nex 的值复制给 cur
cur.val = tmp;
}
}
return cur;
}
/* 获取最小结点 */
TreeNode? min(TreeNode? root)
{
if (root == null) return root;
// 循环访问左子结点,直到叶结点时为最小结点,跳出
while (root.left != null)
{
root = root.left;
}
return root;
}
```
二叉搜索树的优势
假设给定 n 个数字,最常用的存储方式是「数组」,那么对于这串乱序的数字,常见操作的效率为:
- 查找元素: 由于数组是无序的,因此需要遍历数组来确定,使用
O(n)时间; - 插入元素: 只需将元素添加至数组尾部即可,使用
O(1)时间; - 删除元素: 先查找元素,使用
O(n)时间,再在数组中删除该元素,使用O(n)时间; - 获取最小 / 最大元素: 需要遍历数组来确定,使用
O(n)时间;
为了得到先验信息,我们也可以预先将数组元素进行排序,得到一个「排序数组」,此时操作效率为:
- 查找元素: 由于数组已排序,可以使用二分查找,平均使用
O(\log n)时间; - 插入元素: 先查找插入位置,使用
O(\log n)时间,再插入到指定位置,使用O(n)时间; - 删除元素: 先查找元素,使用
O(\log n)时间,再在数组中删除该元素,使用O(n)时间; - 获取最小 / 最大元素: 数组头部和尾部元素即是最小和最大元素,使用
O(1)时间;
观察发现,无序数组和有序数组中的各项操作的时间复杂度是“偏科”的,即有的快有的慢;而二叉搜索树的各项操作的时间复杂度都是对数阶,在数据量 n 很大时有巨大优势。
| 无序数组 | 有序数组 | 二叉搜索树 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 查找指定元素 | O(n) |
O(\log n) |
O(\log n) |
| 插入元素 | O(1) |
O(n) |
O(\log n) |
| 删除元素 | O(n) |
O(n) |
O(\log n) |
| 获取最小 / 最大元素 | O(n) |
O(1) |
O(\log n) |
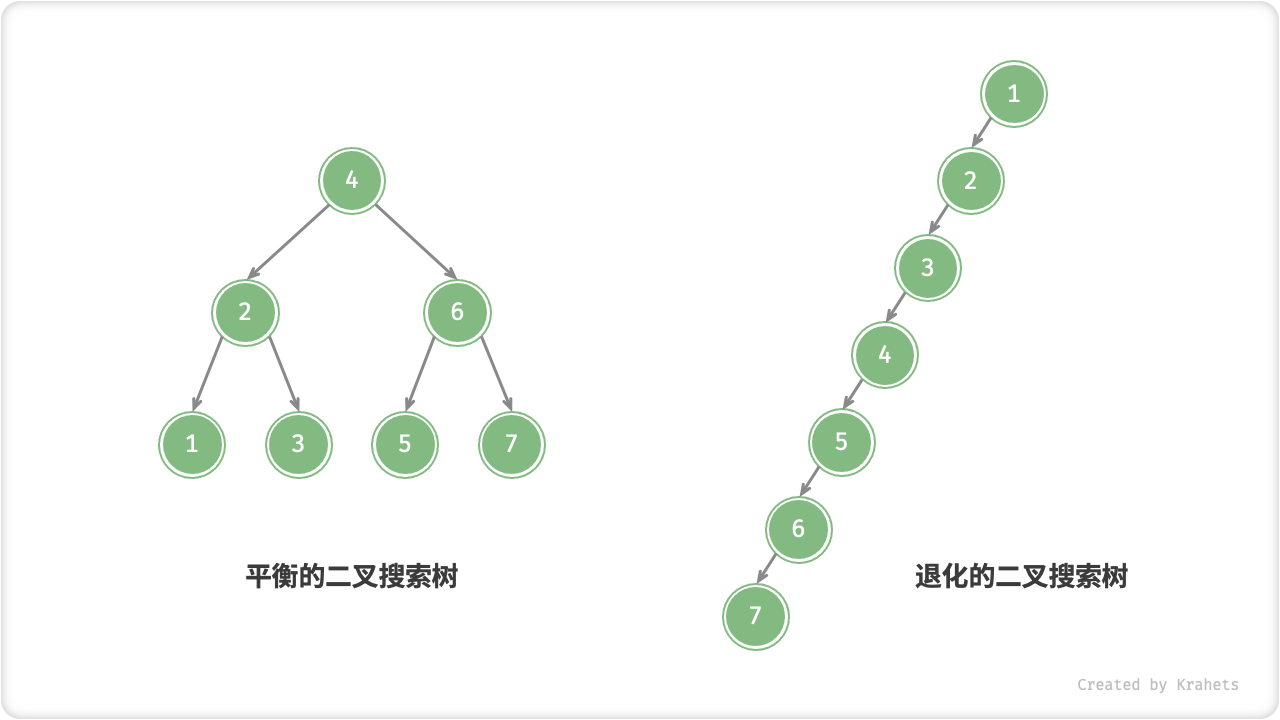
二叉搜索树的退化
理想情况下,我们希望二叉搜索树的是“左右平衡”的(详见「平衡二叉树」章节),此时可以在 \log n 轮循环内查找任意结点。
如果我们动态地在二叉搜索树中插入与删除结点,则可能导致二叉树退化为链表,此时各种操作的时间复杂度也退化之 O(n) 。
!!! note
在实际应用中,如何保持二叉搜索树的平衡,也是一个需要重要考虑的问题。
二叉搜索树常见应用
- 系统中的多级索引,高效查找、插入、删除操作。
- 各种搜索算法的底层数据结构。
- 存储数据流,保持其已排序。