mirror of
https://github.com/krahets/hello-algo.git
synced 2024-12-27 12:46:27 +08:00
10 KiB
10 KiB
| comments |
|---|
| true |
二叉树遍历
非线性数据结构的遍历操作比线性数据结构更加复杂,往往需要使用搜索算法来实现。常见的二叉树遍历方式有层序遍历、前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历。
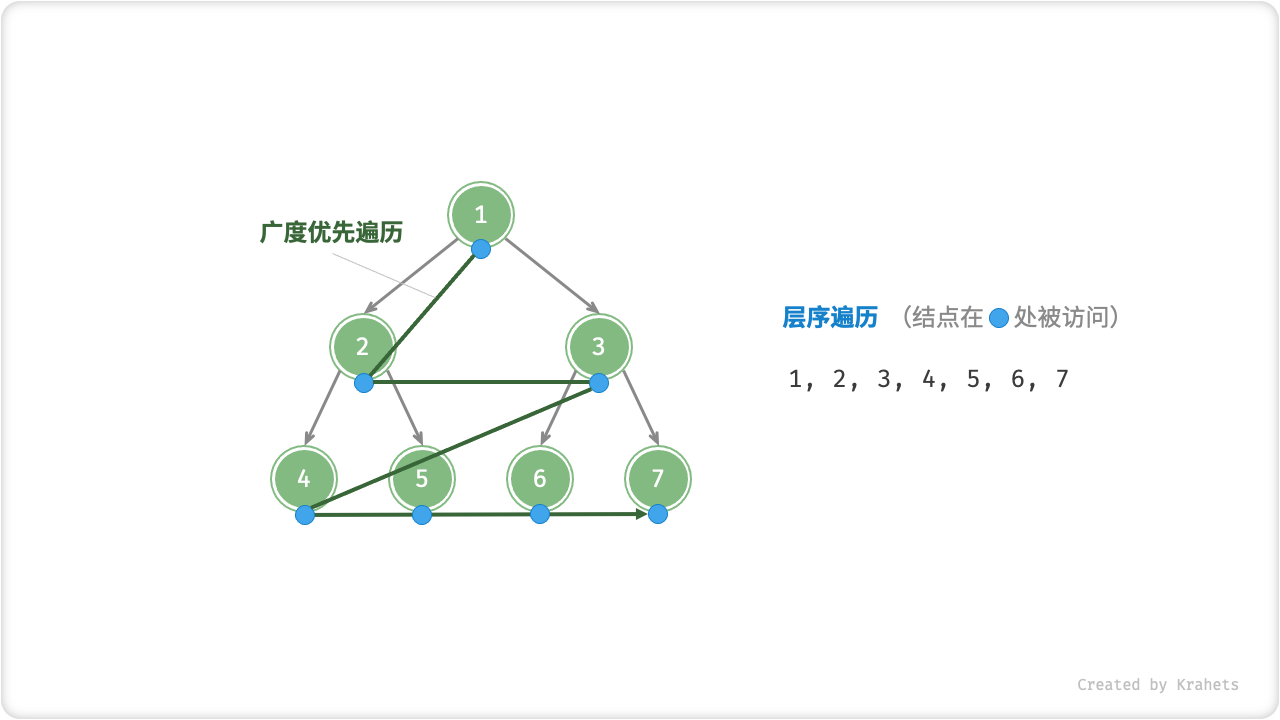
层序遍历
「层序遍历 Hierarchical-Order Traversal」从顶至底、一层一层地遍历二叉树,并在每层中按照从左到右的顺序访问结点。
层序遍历本质上是「广度优先搜索 Breadth-First Traversal」,其体现着一种“一圈一圈向外”的层进遍历方式。
Fig. 二叉树的层序遍历
广度优先遍历一般借助「队列」来实现。队列的规则是“先进先出”,广度优先遍历的规则是 ”一层层平推“ ,两者背后的思想是一致的。
=== "Java"
```java title="binary_tree_bfs.java"
/* 层序遍历 */
List<Integer> hierOrder(TreeNode root) {
// 初始化队列,加入根结点
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>() {{ add(root); }};
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll(); // 队列出队
list.add(node.val); // 保存结点值
if (node.left != null)
queue.offer(node.left); // 左子结点入队
if (node.right != null)
queue.offer(node.right); // 右子结点入队
}
return list;
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="binary_tree_bfs.cpp"
/* 层序遍历 */
vector<int> hierOrder(TreeNode* root) {
// 初始化队列,加入根结点
queue<TreeNode*> queue;
queue.push(root);
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
vector<int> vec;
while (!queue.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = queue.front();
queue.pop(); // 队列出队
vec.push_back(node->val); // 保存结点
if (node->left != nullptr)
queue.push(node->left); // 左子结点入队
if (node->right != nullptr)
queue.push(node->right); // 右子结点入队
}
return vec;
}
```
=== "Python"
```python title="binary_tree_bfs.py"
```
=== "Go"
```go title="binary_tree_bfs.go"
/* 层序遍历 */
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) []int {
// 初始化队列,加入根结点
queue := list.New()
queue.PushBack(root)
// 初始化一个切片,用于保存遍历序列
nums := make([]int, 0)
for queue.Len() > 0 {
// poll
node := queue.Remove(queue.Front()).(*TreeNode)
// 保存结点
nums = append(nums, node.Val)
if node.Left != nil {
// 左子结点入队
queue.PushBack(node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
// 右子结点入队
queue.PushBack(node.Right)
}
}
return nums
}
```
=== "JavaScript"
```js title="binary_tree_bfs.js"
/* 层序遍历 */
function hierOrder(root) {
// 初始化队列,加入根结点
let queue = [root];
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
let list = [];
while (queue.length) {
let node = queue.shift(); // 队列出队
list.push(node.val); // 保存结点
if (node.left)
queue.push(node.left); // 左子结点入队
if (node.right)
queue.push(node.right); // 右子结点入队
}
return list;
}
```
=== "TypeScript"
```typescript title="binary_tree_bfs.ts"
/* 层序遍历 */
function hierOrder(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
// 初始化队列,加入根结点
const queue = [root];
// 初始化一个列表,用于保存遍历序列
const list: number[] = [];
while (queue.length) {
let node = queue.shift() as TreeNode; // 队列出队
list.push(node.val); // 保存结点
if (node.left) {
queue.push(node.left); // 左子结点入队
}
if (node.right) {
queue.push(node.right); // 右子结点入队
}
}
return list;
}
```
=== "C"
```c title="binary_tree_bfs.c"
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title="binary_tree_bfs.cs"
```
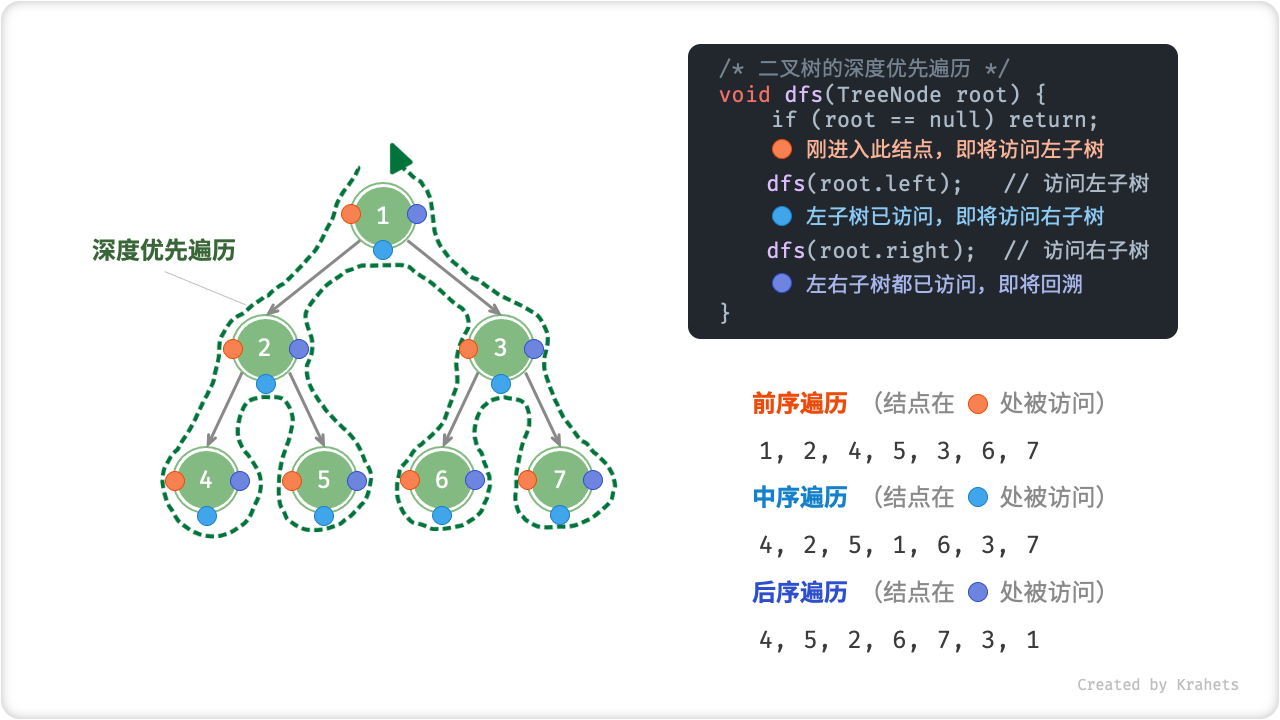
前序、中序、后序遍历
相对地,前、中、后序遍历皆属于「深度优先遍历 Depth-First Traversal」,其体现着一种“先走到尽头,再回头继续”的回溯遍历方式。
如下图所示,左侧是深度优先遍历的的示意图,右上方是对应的递归实现代码。深度优先遍历就像是绕着整个二叉树的外围“走”一圈,走的过程中,在每个结点都会遇到三个位置,分别对应前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历。
Fig. 二叉树的前 / 中 / 后序遍历
| 位置 | 含义 | 此处访问结点时对应 |
|---|---|---|
| 橙色圆圈处 | 刚进入此结点,即将访问该结点的左子树 | 前序遍历 Pre-Order Traversal |
| 蓝色圆圈处 | 已访问完左子树,即将访问右子树 | 中序遍历 In-Order Traversal |
| 紫色圆圈处 | 已访问完左子树和右子树,即将返回 | 后序遍历 Post-Order Traversal |
=== "Java"
```java title="binary_tree_dfs.java"
/* 前序遍历 */
void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
// 访问优先级:根结点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
list.add(root.val);
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根结点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root.left);
list.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
void postOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根结点
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
list.add(root.val);
}
```
=== "C++"
```cpp title="binary_tree_dfs.cpp"
/* 前序遍历 */
void preOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
// 访问优先级:根结点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
vec.push_back(root->val);
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
void inOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根结点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root->left);
vec.push_back(root->val);
inOrder(root->right);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
void postOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根结点
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
vec.push_back(root->val);
}
```
=== "Python"
```python title="binary_tree_dfs.py"
```
=== "Go"
```go title="binary_tree_dfs.go"
/* 前序遍历 */
func preOrder(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
// 访问优先级:根结点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
nums = append(nums, node.Val)
preOrder(node.Left)
preOrder(node.Right)
}
/* 中序遍历 */
func inOrder(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根结点 -> 右子树
inOrder(node.Left)
nums = append(nums, node.Val)
inOrder(node.Right)
}
/* 后序遍历 */
func postOrder(node *TreeNode) {
if node == nil {
return
}
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根结点
postOrder(node.Left)
postOrder(node.Right)
nums = append(nums, node.Val)
}
```
=== "JavaScript"
```js title="binary_tree_dfs.js"
/* 前序遍历 */
function preOrder(root){
if (root === null) return;
// 访问优先级:根结点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
list.push(root.val);
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
function inOrder(root) {
if (root === null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根结点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root.left);
list.push(root.val);
inOrder(root.right);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
function postOrder(root) {
if (root === null) return;
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根结点
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
list.push(root.val);
}
```
=== "TypeScript"
```typescript title="binary_tree_dfs.ts"
/* 前序遍历 */
function preOrder(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
// 访问优先级:根结点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
list.push(root.val);
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
/* 中序遍历 */
function inOrder(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 根结点 -> 右子树
inOrder(root.left);
list.push(root.val);
inOrder(root.right);
}
/* 后序遍历 */
function postOrder(root: TreeNode | null): void {
if (root === null) {
return;
}
// 访问优先级:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根结点
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
list.push(root.val);
}
```
=== "C"
```c title="binary_tree_dfs.c"
```
=== "C#"
```csharp title="binary_tree_dfs.cs"
```
!!! note
使用循环一样可以实现前、中、后序遍历,但代码相对繁琐,有兴趣的同学可以自行实现。