13.4. N 皇后问题¶
Question
根据国际象棋的规则,皇后可以攻击与之处在同一行或同一列或同一斜线上的棋子。给定 \(n\) 个皇后和一个 \(n \times n\) 大小的棋盘,寻找使得所有皇后之间无法相互攻击的摆放方案。
如下图所示,当 \(n = 4\) 时,共可以找到两个解。从回溯算法的角度看,\(n \times n\) 大小的棋盘共有 \(n^2\) 个格子,给出了所有的选择 choices 。在逐个放置皇后的过程中,棋盘状态在不断地变化,每个时刻的棋盘就是状态 state 。
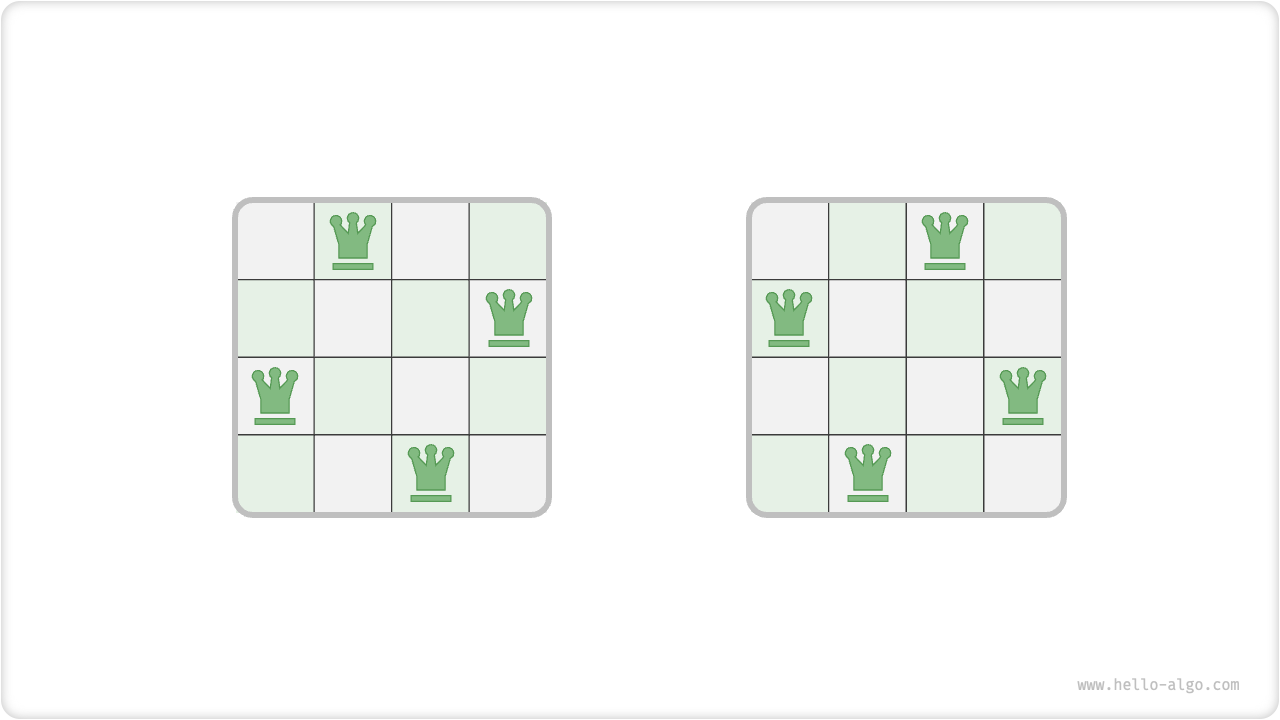
图:4 皇后问题的解
本题共包含三个约束条件:多个皇后不能在同一行、同一列、同一对角线。值得注意的是,对角线分为主对角线 \ 和次对角线 / 两种。
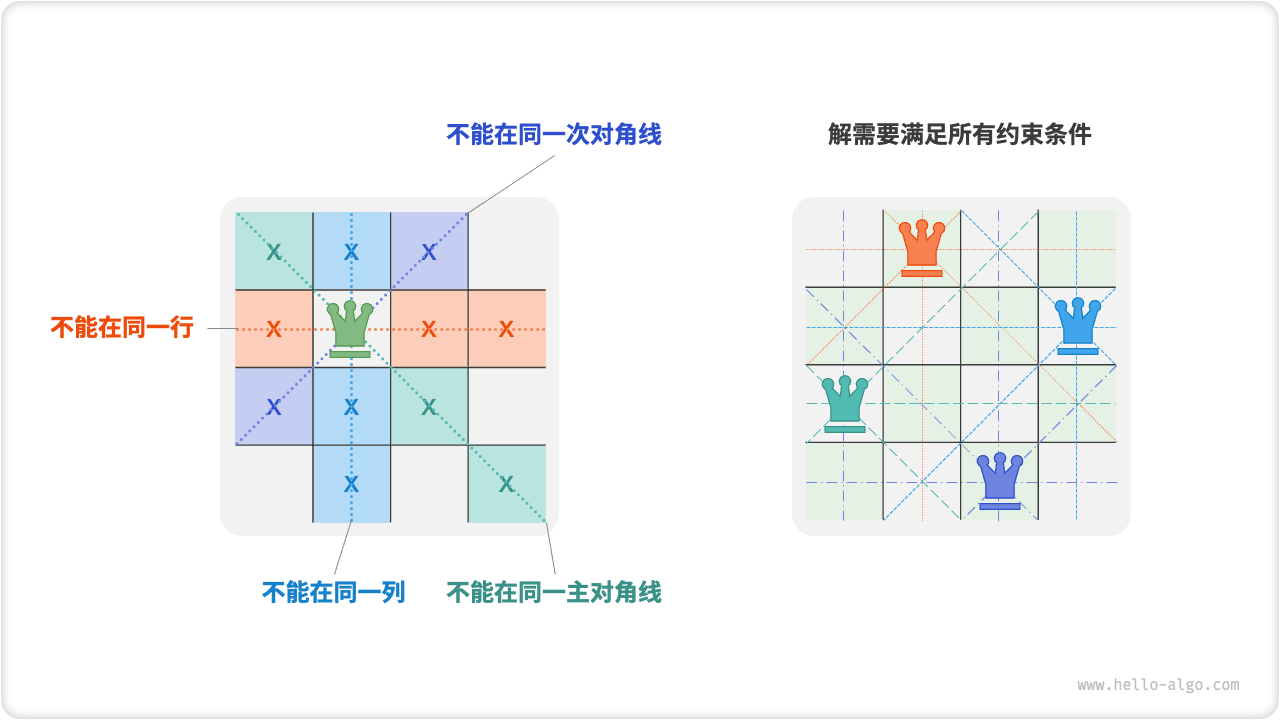
图:n 皇后问题的约束条件
逐行放置策略¶
皇后的数量和棋盘的行数都为 \(n\) ,因此我们容易得到一个推论:棋盘每行都允许且只允许放置一个皇后。
也就是说,我们可以采取逐行放置策略:从第一行开始,在每行放置一个皇后,直至最后一行结束。
如下图所示,为 \(4\) 皇后问题的逐行放置过程。受画幅限制,下图仅展开了第一行的其中一个搜索分支,并且将不满足列约束和对角线约束的方案都进行了剪枝。

图:逐行放置策略
本质上看,逐行放置策略起到了剪枝的作用,它避免了同一行出现多个皇后的所有搜索分支。
列与对角线剪枝¶
为了满足列约束,我们可以利用一个长度为 \(n\) 的布尔型数组 cols 记录每一列是否有皇后。在每次决定放置前,我们通过 cols 将已有皇后的列进行剪枝,并在回溯中动态更新 cols 的状态。
那么,如何处理对角线约束呢?设棋盘中某个格子的行列索引为 \((row, col)\) ,选定矩阵中的某条主对角线,我们发现该对角线上所有格子的行索引减列索引都相等,即对角线上所有格子的 \(row - col\) 为恒定值。
也就是说,如果两个格子满足 \(row_1 - col_1 = row_2 - col_2\) ,则它们一定处在同一条主对角线上。利用该规律,我们可以借助一个数组 diag1 来记录每条主对角线上是否有皇后。
同理,次对角线上的所有格子的 \(row + col\) 是恒定值。我们可以使用相同方法,借助数组 diag2 来处理次对角线约束。
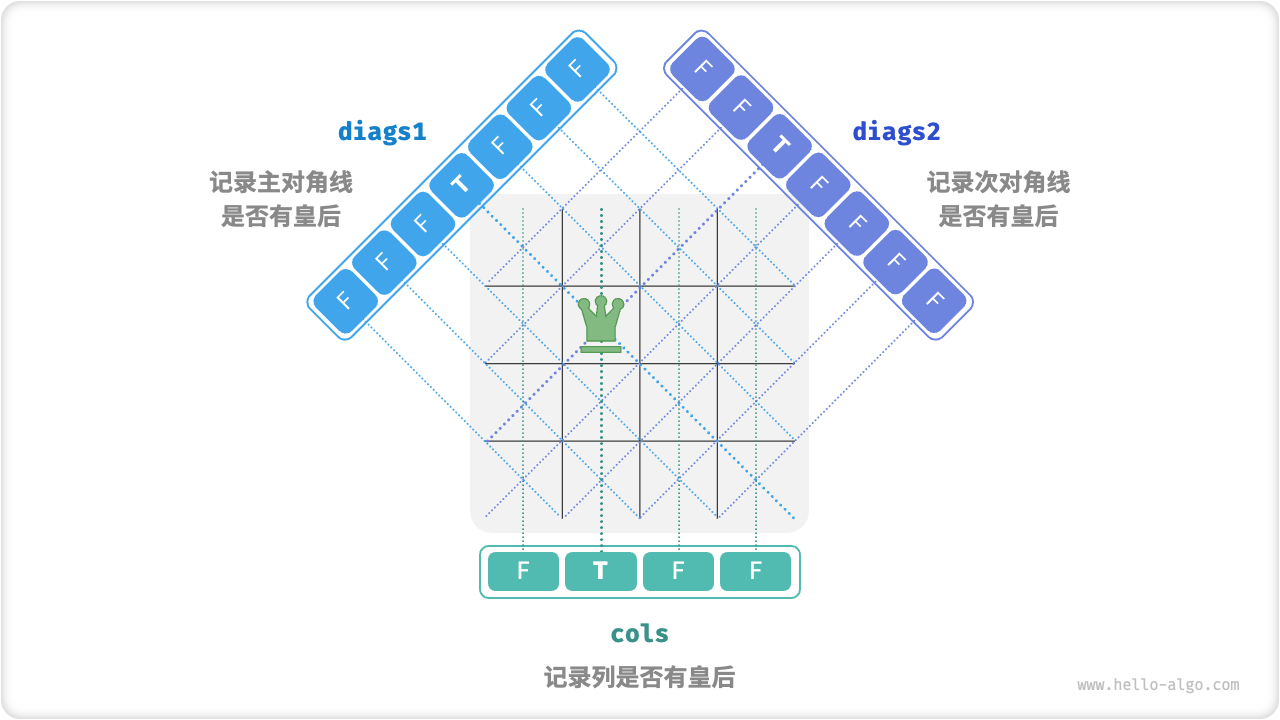
图:处理列约束和对角线约束
代码实现¶
请注意,\(n\) 维方阵中 \(row - col\) 的范围是 \([-n + 1, n - 1]\) ,\(row + col\) 的范围是 \([0, 2n - 2]\) ,所以主对角线和次对角线的数量都为 \(2n - 1\) ,即数组 diag1 和 diag2 的长度都为 \(2n - 1\) 。
/* 回溯算法:N 皇后 */
void backtrack(int row, int n, List<List<String>> state, List<List<List<String>>> res,
boolean[] cols, boolean[] diags1, boolean[] diags2) {
// 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if (row == n) {
List<List<String>> copyState = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<String> sRow : state) {
copyState.add(new ArrayList<>(sRow));
}
res.add(copyState);
return;
}
// 遍历所有列
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
// 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
int diag1 = row - col + n - 1;
int diag2 = row + col;
// 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if (!cols[col] && !diags1[diag1] && !diags2[diag2]) {
// 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
state.get(row).set(col, "Q");
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = true;
// 放置下一行
backtrack(row + 1, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
// 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
state.get(row).set(col, "#");
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = false;
}
}
}
/* 求解 N 皇后 */
List<List<List<String>>> nQueens(int n) {
// 初始化 n*n 大小的棋盘,其中 'Q' 代表皇后,'#' 代表空位
List<List<String>> state = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
List<String> row = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
row.add("#");
}
state.add(row);
}
boolean[] cols = new boolean[n]; // 记录列是否有皇后
boolean[] diags1 = new boolean[2 * n - 1]; // 记录主对角线是否有皇后
boolean[] diags2 = new boolean[2 * n - 1]; // 记录副对角线是否有皇后
List<List<List<String>>> res = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(0, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
return res;
}
/* 回溯算法:N 皇后 */
void backtrack(int row, int n, vector<vector<string>> &state, vector<vector<vector<string>>> &res, vector<bool> &cols,
vector<bool> &diags1, vector<bool> &diags2) {
// 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if (row == n) {
res.push_back(state);
return;
}
// 遍历所有列
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
// 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
int diag1 = row - col + n - 1;
int diag2 = row + col;
// 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if (!cols[col] && !diags1[diag1] && !diags2[diag2]) {
// 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
state[row][col] = "Q";
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = true;
// 放置下一行
backtrack(row + 1, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
// 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
state[row][col] = "#";
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = false;
}
}
}
/* 求解 N 皇后 */
vector<vector<vector<string>>> nQueens(int n) {
// 初始化 n*n 大小的棋盘,其中 'Q' 代表皇后,'#' 代表空位
vector<vector<string>> state(n, vector<string>(n, "#"));
vector<bool> cols(n, false); // 记录列是否有皇后
vector<bool> diags1(2 * n - 1, false); // 记录主对角线是否有皇后
vector<bool> diags2(2 * n - 1, false); // 记录副对角线是否有皇后
vector<vector<vector<string>>> res;
backtrack(0, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
return res;
}
def backtrack(
row: int,
n: int,
state: list[list[str]],
res: list[list[list[str]]],
cols: list[bool],
diags1: list[bool],
diags2: list[bool],
):
"""回溯算法:N 皇后"""
# 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if row == n:
res.append([list(row) for row in state])
return
# 遍历所有列
for col in range(n):
# 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
diag1 = row - col + n - 1
diag2 = row + col
# 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if not cols[col] and not diags1[diag1] and not diags2[diag2]:
# 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
state[row][col] = "Q"
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = True
# 放置下一行
backtrack(row + 1, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2)
# 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
state[row][col] = "#"
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = False
def n_queens(n: int) -> list[list[list[str]]]:
"""求解 N 皇后"""
# 初始化 n*n 大小的棋盘,其中 'Q' 代表皇后,'#' 代表空位
state = [["#" for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(n)]
cols = [False] * n # 记录列是否有皇后
diags1 = [False] * (2 * n - 1) # 记录主对角线是否有皇后
diags2 = [False] * (2 * n - 1) # 记录副对角线是否有皇后
res = []
backtrack(0, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2)
return res
/* 回溯算法:N 皇后 */
func backtrack(row, n int, state *[][]string, res *[][][]string, cols, diags1, diags2 *[]bool) {
// 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if row == n {
newState := make([][]string, len(*state))
for i, _ := range newState {
newState[i] = make([]string, len((*state)[0]))
copy(newState[i], (*state)[i])
}
*res = append(*res, newState)
}
// 遍历所有列
for col := 0; col < n; col++ {
// 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
diag1 := row - col + n - 1
diag2 := row + col
// 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if !(*cols)[col] && !(*diags1)[diag1] && !(*diags2)[diag2] {
// 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
(*state)[row][col] = "Q"
(*cols)[col], (*diags1)[diag1], (*diags2)[diag2] = true, true, true
// 放置下一行
backtrack(row+1, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2)
// 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
(*state)[row][col] = "#"
(*cols)[col], (*diags1)[diag1], (*diags2)[diag2] = false, false, false
}
}
}
/* 回溯算法:N 皇后 */
func backtrack(row, n int, state *[][]string, res *[][][]string, cols, diags1, diags2 *[]bool) {
// 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if row == n {
newState := make([][]string, len(*state))
for i, _ := range newState {
newState[i] = make([]string, len((*state)[0]))
copy(newState[i], (*state)[i])
}
*res = append(*res, newState)
}
// 遍历所有列
for col := 0; col < n; col++ {
// 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
diag1 := row - col + n - 1
diag2 := row + col
// 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if !(*cols)[col] && !(*diags1)[diag1] && !(*diags2)[diag2] {
// 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
(*state)[row][col] = "Q"
(*cols)[col], (*diags1)[diag1], (*diags2)[diag2] = true, true, true
// 放置下一行
backtrack(row+1, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2)
// 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
(*state)[row][col] = "#"
(*cols)[col], (*diags1)[diag1], (*diags2)[diag2] = false, false, false
}
}
}
func nQueens(n int) [][][]string {
// 初始化 n*n 大小的棋盘,其中 'Q' 代表皇后,'#' 代表空位
state := make([][]string, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
row := make([]string, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
row[i] = "#"
}
state[i] = row
}
// 记录列是否有皇后
cols := make([]bool, n)
diags1 := make([]bool, 2*n-1)
diags2 := make([]bool, 2*n-1)
res := make([][][]string, 0)
backtrack(0, n, &state, &res, &cols, &diags1, &diags2)
return res
}
/* 回溯算法:N 皇后 */
function backtrack(row, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2) {
// 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if (row === n) {
res.push(state.map((row) => row.slice()));
return;
}
// 遍历所有列
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
// 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
const diag1 = row - col + n - 1;
const diag2 = row + col;
// 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if (!cols[col] && !diags1[diag1] && !diags2[diag2]) {
// 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
state[row][col] = 'Q';
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = true;
// 放置下一行
backtrack(row + 1, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
// 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
state[row][col] = '#';
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = false;
}
}
}
/* 求解 N 皇后 */
function nQueens(n) {
// 初始化 n*n 大小的棋盘,其中 'Q' 代表皇后,'#' 代表空位
const state = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(n).fill('#'));
const cols = Array(n).fill(false); // 记录列是否有皇后
const diags1 = Array(2 * n - 1).fill(false); // 记录主对角线是否有皇后
const diags2 = Array(2 * n - 1).fill(false); // 记录副对角线是否有皇后
const res = [];
backtrack(0, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
return res;
}
/* 回溯算法:N 皇后 */
function backtrack(
row: number,
n: number,
state: string[][],
res: string[][][],
cols: boolean[],
diags1: boolean[],
diags2: boolean[]
): void {
// 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if (row === n) {
res.push(state.map((row) => row.slice()));
return;
}
// 遍历所有列
for (let col = 0; col < n; col++) {
// 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
const diag1 = row - col + n - 1;
const diag2 = row + col;
// 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if (!cols[col] && !diags1[diag1] && !diags2[diag2]) {
// 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
state[row][col] = 'Q';
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = true;
// 放置下一行
backtrack(row + 1, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
// 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
state[row][col] = '#';
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = false;
}
}
}
/* 求解 N 皇后 */
function nQueens(n: number): string[][][] {
// 初始化 n*n 大小的棋盘,其中 'Q' 代表皇后,'#' 代表空位
const state = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(n).fill('#'));
const cols = Array(n).fill(false); // 记录列是否有皇后
const diags1 = Array(2 * n - 1).fill(false); // 记录主对角线是否有皇后
const diags2 = Array(2 * n - 1).fill(false); // 记录副对角线是否有皇后
const res: string[][][] = [];
backtrack(0, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
return res;
}
/* 回溯算法:N 皇后 */
void backtrack(int row, int n, List<List<string>> state, List<List<List<string>>> res,
bool[] cols, bool[] diags1, bool[] diags2) {
// 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if (row == n) {
List<List<string>> copyState = new List<List<string>>();
foreach (List<string> sRow in state) {
copyState.Add(new List<string>(sRow));
}
res.Add(copyState);
return;
}
// 遍历所有列
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
// 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
int diag1 = row - col + n - 1;
int diag2 = row + col;
// 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if (!cols[col] && !diags1[diag1] && !diags2[diag2]) {
// 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
state[row][col] = "Q";
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = true;
// 放置下一行
backtrack(row + 1, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
// 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
state[row][col] = "#";
cols[col] = diags1[diag1] = diags2[diag2] = false;
}
}
}
/* 求解 N 皇后 */
List<List<List<string>>> nQueens(int n) {
// 初始化 n*n 大小的棋盘,其中 'Q' 代表皇后,'#' 代表空位
List<List<string>> state = new List<List<string>>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
List<string> row = new List<string>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
row.Add("#");
}
state.Add(row);
}
bool[] cols = new bool[n]; // 记录列是否有皇后
bool[] diags1 = new bool[2 * n - 1]; // 记录主对角线是否有皇后
bool[] diags2 = new bool[2 * n - 1]; // 记录副对角线是否有皇后
List<List<List<string>>> res = new List<List<List<string>>>();
backtrack(0, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
return res;
}
/* 回溯算法:N 皇后 */
func backtrack(row: Int, n: Int, state: inout [[String]], res: inout [[[String]]], cols: inout [Bool], diags1: inout [Bool], diags2: inout [Bool]) {
// 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if row == n {
res.append(state)
return
}
// 遍历所有列
for col in 0 ..< n {
// 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
let diag1 = row - col + n - 1
let diag2 = row + col
// 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if !cols[col] && !diags1[diag1] && !diags2[diag2] {
// 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
state[row][col] = "Q"
cols[col] = true
diags1[diag1] = true
diags2[diag2] = true
// 放置下一行
backtrack(row: row + 1, n: n, state: &state, res: &res, cols: &cols, diags1: &diags1, diags2: &diags2)
// 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
state[row][col] = "#"
cols[col] = false
diags1[diag1] = false
diags2[diag2] = false
}
}
}
/* 求解 N 皇后 */
func nQueens(n: Int) -> [[[String]]] {
// 初始化 n*n 大小的棋盘,其中 'Q' 代表皇后,'#' 代表空位
var state = Array(repeating: Array(repeating: "#", count: n), count: n)
var cols = Array(repeating: false, count: n) // 记录列是否有皇后
var diags1 = Array(repeating: false, count: 2 * n - 1) // 记录主对角线是否有皇后
var diags2 = Array(repeating: false, count: 2 * n - 1) // 记录副对角线是否有皇后
var res: [[[String]]] = []
backtrack(row: 0, n: n, state: &state, res: &res, cols: &cols, diags1: &diags1, diags2: &diags2)
return res
}
/* 回溯算法:N 皇后 */
void backtrack(
int row,
int n,
List<List<String>> state,
List<List<List<String>>> res,
List<bool> cols,
List<bool> diags1,
List<bool> diags2,
) {
// 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if (row == n) {
List<List<String>> copyState = [];
for (List<String> sRow in state) {
copyState.add(List.from(sRow));
}
res.add(copyState);
return;
}
// 遍历所有列
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
// 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
int diag1 = row - col + n - 1;
int diag2 = row + col;
// 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if (!cols[col] && !diags1[diag1] && !diags2[diag2]) {
// 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
state[row][col] = "Q";
cols[col] = true;
diags1[diag1] = true;
diags2[diag2] = true;
// 放置下一行
backtrack(row + 1, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
// 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
state[row][col] = "#";
cols[col] = false;
diags1[diag1] = false;
diags2[diag2] = false;
}
}
}
/* 求解 N 皇后 */
List<List<List<String>>> nQueens(int n) {
// 初始化 n*n 大小的棋盘,其中 'Q' 代表皇后,'#' 代表空位
List<List<String>> state = List.generate(n, (index) => List.filled(n, "#"));
List<bool> cols = List.filled(n, false); // 记录列是否有皇后
List<bool> diags1 = List.filled(2 * n - 1, false); // 记录主对角线是否有皇后
List<bool> diags2 = List.filled(2 * n - 1, false); // 记录副对角线是否有皇后
List<List<List<String>>> res = [];
backtrack(0, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
return res;
}
/* 回溯算法:N 皇后 */
fn backtrack(row: usize, n: usize, state: &mut Vec<Vec<String>>, res: &mut Vec<Vec<Vec<String>>>,
cols: &mut [bool], diags1: &mut [bool], diags2: &mut [bool]) {
// 当放置完所有行时,记录解
if row == n {
let mut copy_state: Vec<Vec<String>> = Vec::new();
for s_row in state.clone() {
copy_state.push(s_row);
}
res.push(copy_state);
return;
}
// 遍历所有列
for col in 0..n {
// 计算该格子对应的主对角线和副对角线
let diag1 = row + n - 1 - col;
let diag2 = row + col;
// 剪枝:不允许该格子所在列、主对角线、副对角线存在皇后
if !cols[col] && !diags1[diag1] && !diags2[diag2] {
// 尝试:将皇后放置在该格子
state.get_mut(row).unwrap()[col] = "Q".into();
(cols[col], diags1[diag1], diags2[diag2]) = (true, true, true);
// 放置下一行
backtrack(row + 1, n, state, res, cols, diags1, diags2);
// 回退:将该格子恢复为空位
state.get_mut(row).unwrap()[col] = "#".into();
(cols[col], diags1[diag1], diags2[diag2]) = (false, false, false);
}
}
}
/* 求解 N 皇后 */
fn n_queens(n: usize) -> Vec<Vec<Vec<String>>> {
// 初始化 n*n 大小的棋盘,其中 'Q' 代表皇后,'#' 代表空位
let mut state: Vec<Vec<String>> = Vec::new();
for _ in 0..n {
let mut row: Vec<String> = Vec::new();
for _ in 0..n {
row.push("#".into());
}
state.push(row);
}
let mut cols = vec![false; n]; // 记录列是否有皇后
let mut diags1 = vec![false; 2 * n - 1]; // 记录主对角线是否有皇后
let mut diags2 = vec![false; 2 * n - 1]; // 记录副对角线是否有皇后
let mut res: Vec<Vec<Vec<String>>> = Vec::new();
backtrack(0, n, &mut state, &mut res, &mut cols, &mut diags1, &mut diags2);
res
}
逐行放置 \(n\) 次,考虑列约束,则从第一行到最后一行分别有 \(n, n-1, \cdots, 2, 1\) 个选择,因此时间复杂度为 \(O(n!)\) 。实际上,根据对角线约束的剪枝也能够大幅地缩小搜索空间,因而搜索效率往往优于以上时间复杂度。
数组 state 使用 \(O(n^2)\) 空间,数组 cols , diags1 , diags2 皆使用 \(O(n)\) 空间。最大递归深度为 \(n\) ,使用 \(O(n)\) 栈帧空间。因此,空间复杂度为 \(O(n^2)\) 。