7.5 AVL tree *¶
In the "Binary Search Tree" section, we mentioned that after multiple insertions and removals, a binary search tree might degrade to a linked list. In such cases, the time complexity of all operations degrades from \(O(\log n)\) to \(O(n)\).
As shown in the Figure 7-24 , after two node removal operations, this binary search tree will degrade into a linked list.
Figure 7-24 Degradation of an AVL tree after removing nodes
For example, in the perfect binary tree shown in the Figure 7-25 , after inserting two nodes, the tree will lean heavily to the left, and the time complexity of search operations will also degrade.
Figure 7-25 Degradation of an AVL tree after inserting nodes
In 1962, G. M. Adelson-Velsky and E. M. Landis proposed the "AVL Tree" in their paper "An algorithm for the organization of information". The paper detailed a series of operations to ensure that after continuously adding and removing nodes, the AVL tree would not degrade, thus maintaining the time complexity of various operations at \(O(\log n)\) level. In other words, in scenarios where frequent additions, removals, searches, and modifications are needed, the AVL tree can always maintain efficient data operation performance, which has great application value.
7.5.1 Common terminology in AVL trees¶
An AVL tree is both a binary search tree and a balanced binary tree, satisfying all properties of these two types of binary trees, hence it is a "balanced binary search tree".
1. Node height¶
Since the operations related to AVL trees require obtaining node heights, we need to add a height variable to the node class:
/* AVL tree node */
class TreeNode {
val; // Node value
height; // Node height
left; // Left child pointer
right; // Right child pointer
constructor(val, left, right, height) {
this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val;
this.height = height === undefined ? 0 : height;
this.left = left === undefined ? null : left;
this.right = right === undefined ? null : right;
}
}
/* AVL tree node */
class TreeNode {
val: number; // Node value
height: number; // Node height
left: TreeNode | null; // Left child pointer
right: TreeNode | null; // Right child pointer
constructor(val?: number, height?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
this.val = val === undefined ? 0 : val;
this.height = height === undefined ? 0 : height;
this.left = left === undefined ? null : left;
this.right = right === undefined ? null : right;
}
}
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
/* AVL tree node */
struct TreeNode {
val: i32, // Node value
height: i32, // Node height
left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // Left child
right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, // Right child
}
impl TreeNode {
/* Constructor */
fn new(val: i32) -> Rc<RefCell<Self>> {
Rc::new(RefCell::new(Self {
val,
height: 0,
left: None,
right: None
}))
}
}
/* AVL tree node */
TreeNode struct TreeNode {
int val;
int height;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
} TreeNode;
/* Constructor */
TreeNode *newTreeNode(int val) {
TreeNode *node;
node = (TreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
node->val = val;
node->height = 0;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
The "node height" refers to the distance from that node to its farthest leaf node, i.e., the number of "edges" passed. It is important to note that the height of a leaf node is \(0\), and the height of a null node is \(-1\). We will create two utility functions for getting and updating the height of a node:
/* 获取节点高度 */
func (t *aVLTree) height(node *TreeNode) int {
// 空节点高度为 -1 ,叶节点高度为 0
if node != nil {
return node.Height
}
return -1
}
/* 更新节点高度 */
func (t *aVLTree) updateHeight(node *TreeNode) {
lh := t.height(node.Left)
rh := t.height(node.Right)
// 节点高度等于最高子树高度 + 1
if lh > rh {
node.Height = lh + 1
} else {
node.Height = rh + 1
}
}
/* 获取节点高度 */
fn height(node: OptionTreeNodeRc) -> i32 {
// 空节点高度为 -1 ,叶节点高度为 0
match node {
Some(node) => node.borrow().height,
None => -1,
}
}
/* 更新节点高度 */
fn update_height(node: OptionTreeNodeRc) {
if let Some(node) = node {
let left = node.borrow().left.clone();
let right = node.borrow().right.clone();
// 节点高度等于最高子树高度 + 1
node.borrow_mut().height = std::cmp::max(Self::height(left), Self::height(right)) + 1;
}
}
/* 获取节点高度 */
int height(TreeNode *node) {
// 空节点高度为 -1 ,叶节点高度为 0
if (node != NULL) {
return node->height;
}
return -1;
}
/* 更新节点高度 */
void updateHeight(TreeNode *node) {
int lh = height(node->left);
int rh = height(node->right);
// 节点高度等于最高子树高度 + 1
if (lh > rh) {
node->height = lh + 1;
} else {
node->height = rh + 1;
}
}
// 获取节点高度
fn height(self: *Self, node: ?*inc.TreeNode(T)) i32 {
_ = self;
// 空节点高度为 -1 ,叶节点高度为 0
return if (node == null) -1 else node.?.height;
}
// 更新节点高度
fn updateHeight(self: *Self, node: ?*inc.TreeNode(T)) void {
// 节点高度等于最高子树高度 + 1
node.?.height = @max(self.height(node.?.left), self.height(node.?.right)) + 1;
}
2. Node balance factor¶
The "balance factor" of a node is defined as the height of the node's left subtree minus the height of its right subtree, with the balance factor of a null node defined as \(0\). We will also encapsulate the functionality of obtaining the node balance factor into a function for easy use later on:
Note
Let the balance factor be \(f\), then the balance factor of any node in an AVL tree satisfies \(-1 \le f \le 1\).
7.5.2 Rotations in AVL trees¶
The characteristic feature of an AVL tree is the "rotation" operation, which can restore balance to an unbalanced node without affecting the in-order traversal sequence of the binary tree. In other words, the rotation operation can maintain the property of a "binary search tree" while also turning the tree back into a "balanced binary tree".
We call nodes with an absolute balance factor \(> 1\) "unbalanced nodes". Depending on the type of imbalance, there are four kinds of rotations: right rotation, left rotation, right-left rotation, and left-right rotation. Below, we detail these rotation operations.
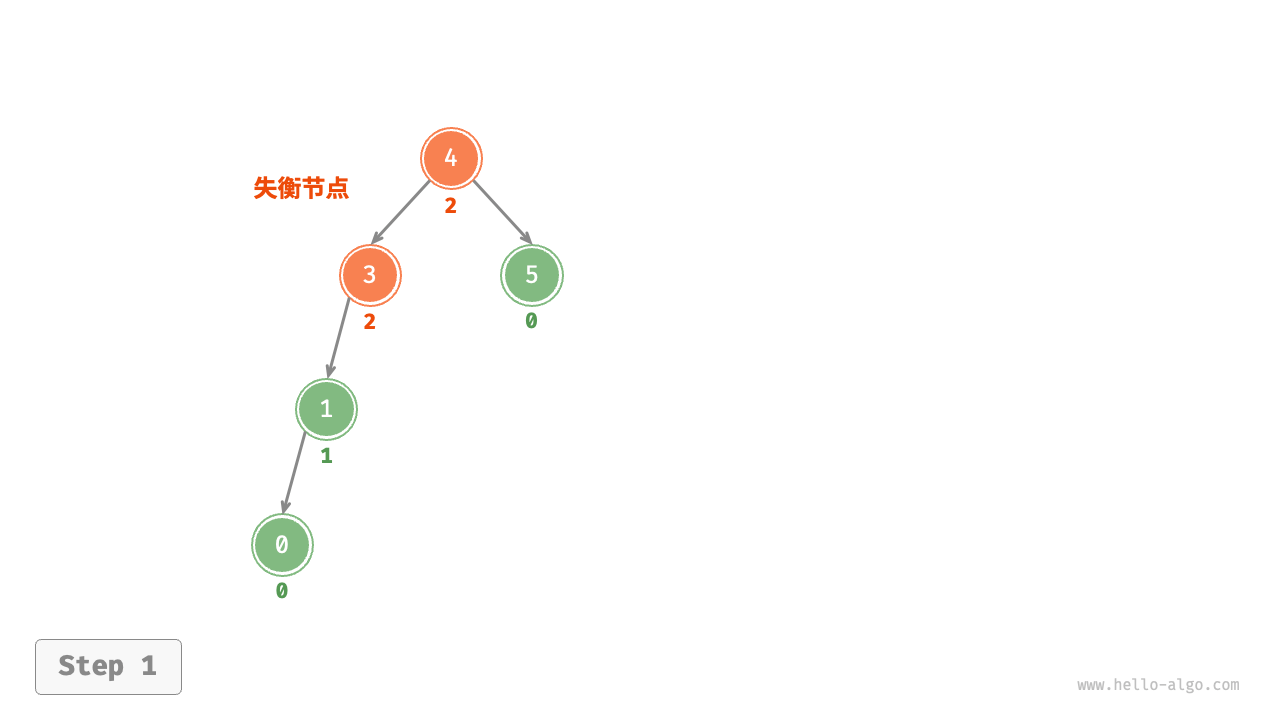
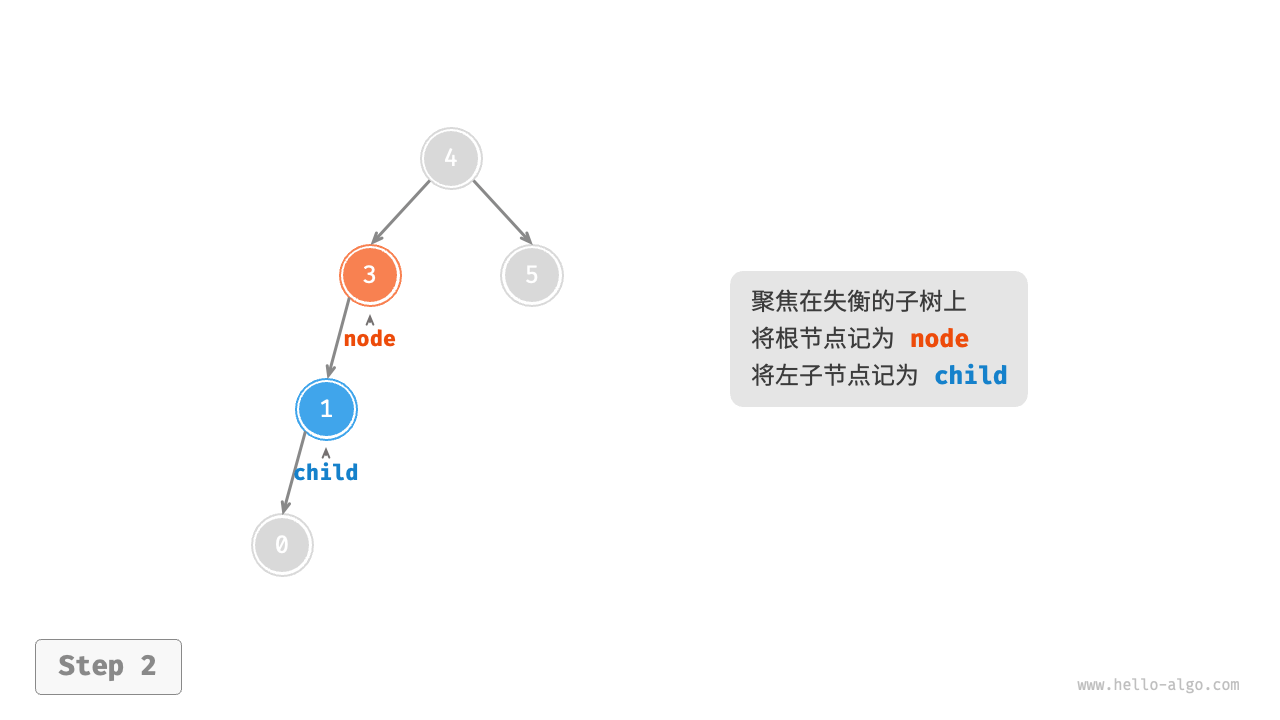
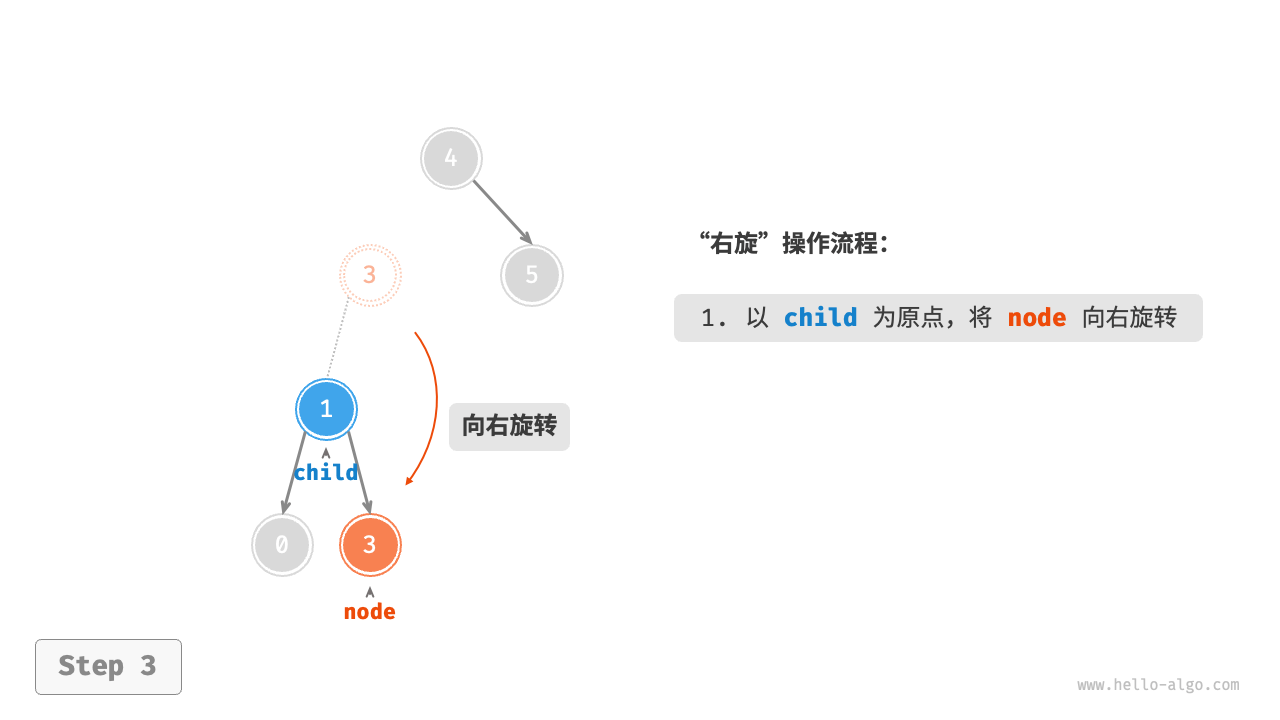
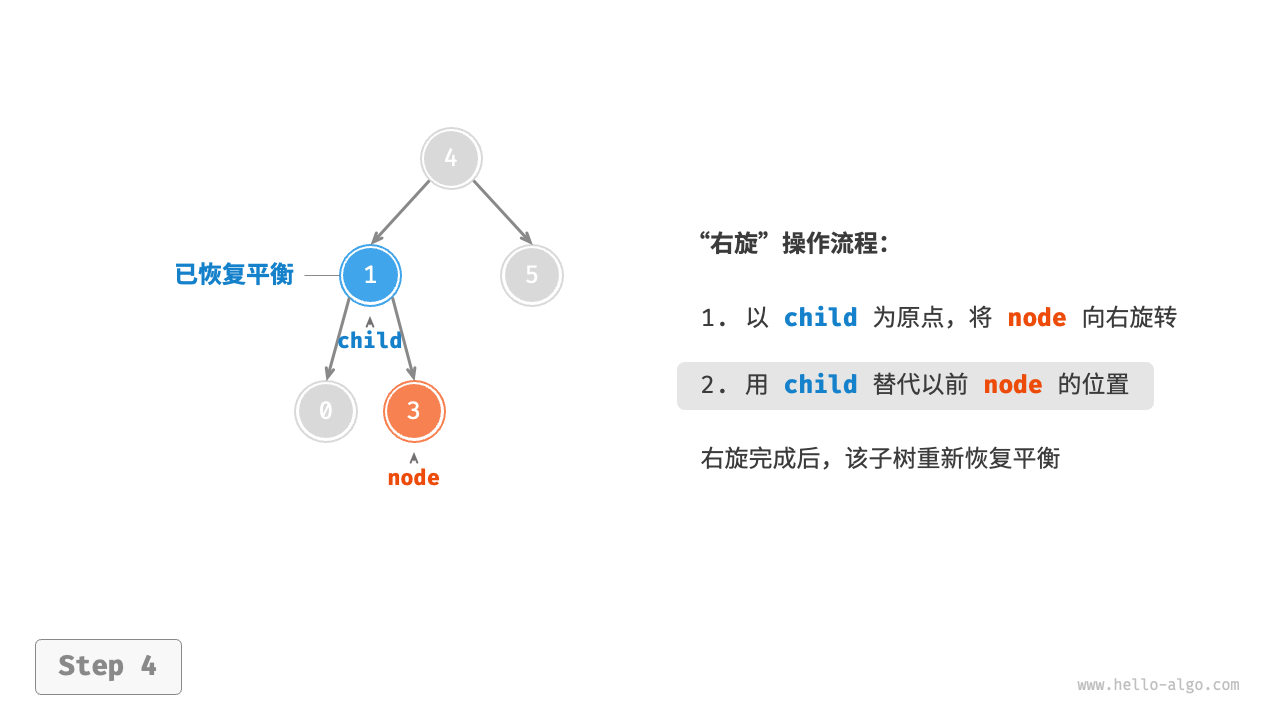
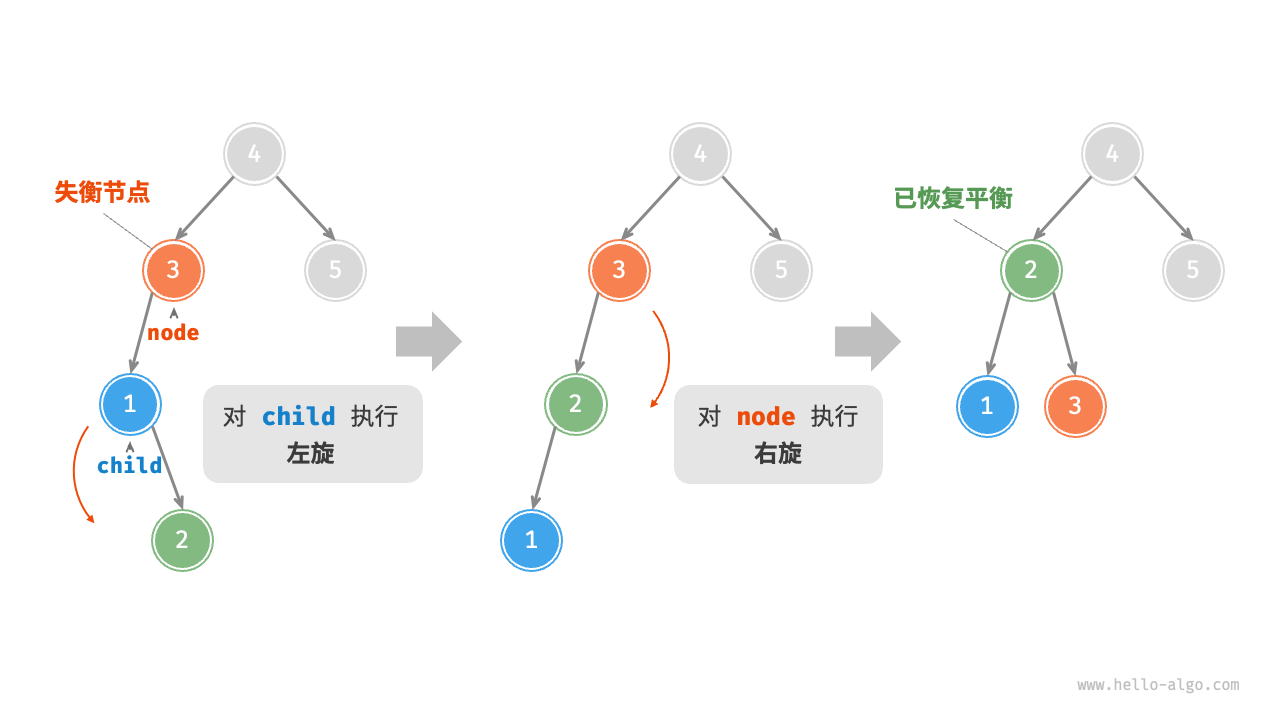
1. Right rotation¶
As shown in the Figure 7-26 , the first unbalanced node from the bottom up in the binary tree is "node 3". Focusing on the subtree with this unbalanced node as the root, denoted as node, and its left child as child, perform a "right rotation". After the right rotation, the subtree is balanced again while still maintaining the properties of a binary search tree.
Figure 7-26 Steps of right rotation
As shown in the Figure 7-27 , when the child node has a right child (denoted as grand_child), a step needs to be added in the right rotation: set grand_child as the left child of node.
Figure 7-27 Right rotation with grand_child
"Right rotation" is a figurative term; in practice, it is achieved by modifying node pointers, as shown in the following code:
/* 右旋操作 */
fn right_rotate(node: OptionTreeNodeRc) -> OptionTreeNodeRc {
match node {
Some(node) => {
let child = node.borrow().left.clone().unwrap();
let grand_child = child.borrow().right.clone();
// 以 child 为原点,将 node 向右旋转
child.borrow_mut().right = Some(node.clone());
node.borrow_mut().left = grand_child;
// 更新节点高度
Self::update_height(Some(node));
Self::update_height(Some(child.clone()));
// 返回旋转后子树的根节点
Some(child)
}
None => None,
}
}
// 右旋操作
fn rightRotate(self: *Self, node: ?*inc.TreeNode(T)) ?*inc.TreeNode(T) {
var child = node.?.left;
var grandChild = child.?.right;
// 以 child 为原点,将 node 向右旋转
child.?.right = node;
node.?.left = grandChild;
// 更新节点高度
self.updateHeight(node);
self.updateHeight(child);
// 返回旋转后子树的根节点
return child;
}
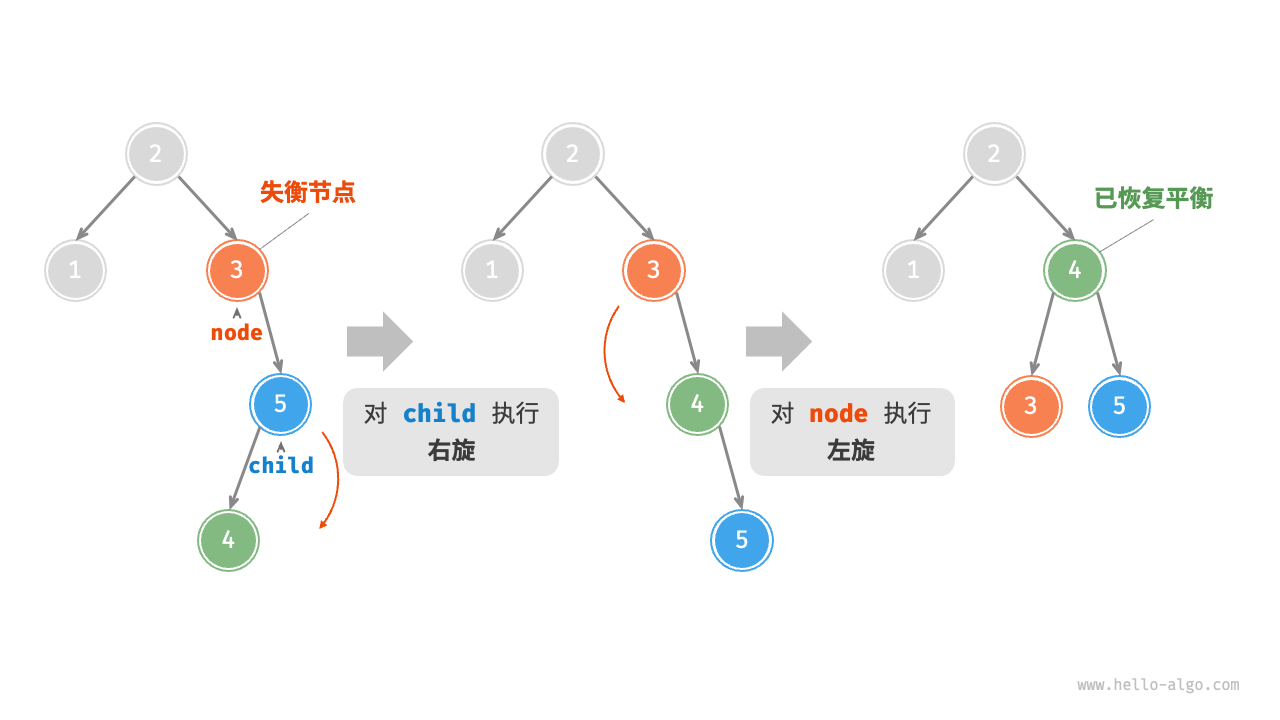
2. Left rotation¶
Correspondingly, if considering the "mirror" of the above unbalanced binary tree, the "left rotation" operation shown in the Figure 7-28 needs to be performed.
Figure 7-28 Left rotation operation
Similarly, as shown in the Figure 7-29 , when the child node has a left child (denoted as grand_child), a step needs to be added in the left rotation: set grand_child as the right child of node.
Figure 7-29 Left rotation with grand_child
It can be observed that the right and left rotation operations are logically symmetrical, and they solve two symmetrical types of imbalance. Based on symmetry, by replacing all left with right, and all right with left in the implementation code of right rotation, we can get the implementation code for left rotation:
/* 左旋操作 */
fn left_rotate(node: OptionTreeNodeRc) -> OptionTreeNodeRc {
match node {
Some(node) => {
let child = node.borrow().right.clone().unwrap();
let grand_child = child.borrow().left.clone();
// 以 child 为原点,将 node 向左旋转
child.borrow_mut().left = Some(node.clone());
node.borrow_mut().right = grand_child;
// 更新节点高度
Self::update_height(Some(node));
Self::update_height(Some(child.clone()));
// 返回旋转后子树的根节点
Some(child)
}
None => None,
}
}
// 左旋操作
fn leftRotate(self: *Self, node: ?*inc.TreeNode(T)) ?*inc.TreeNode(T) {
var child = node.?.right;
var grandChild = child.?.left;
// 以 child 为原点,将 node 向左旋转
child.?.left = node;
node.?.right = grandChild;
// 更新节点高度
self.updateHeight(node);
self.updateHeight(child);
// 返回旋转后子树的根节点
return child;
}
3. Right-left rotation¶
For the unbalanced node 3 shown in the Figure 7-30 , using either left or right rotation alone cannot restore balance to the subtree. In this case, a "left rotation" needs to be performed on child first, followed by a "right rotation" on node.
Figure 7-30 Right-left rotation
4. Left-right rotation¶
As shown in the Figure 7-31 , for the mirror case of the above unbalanced binary tree, a "right rotation" needs to be performed on child first, followed by a "left rotation" on node.
Figure 7-31 Left-right rotation
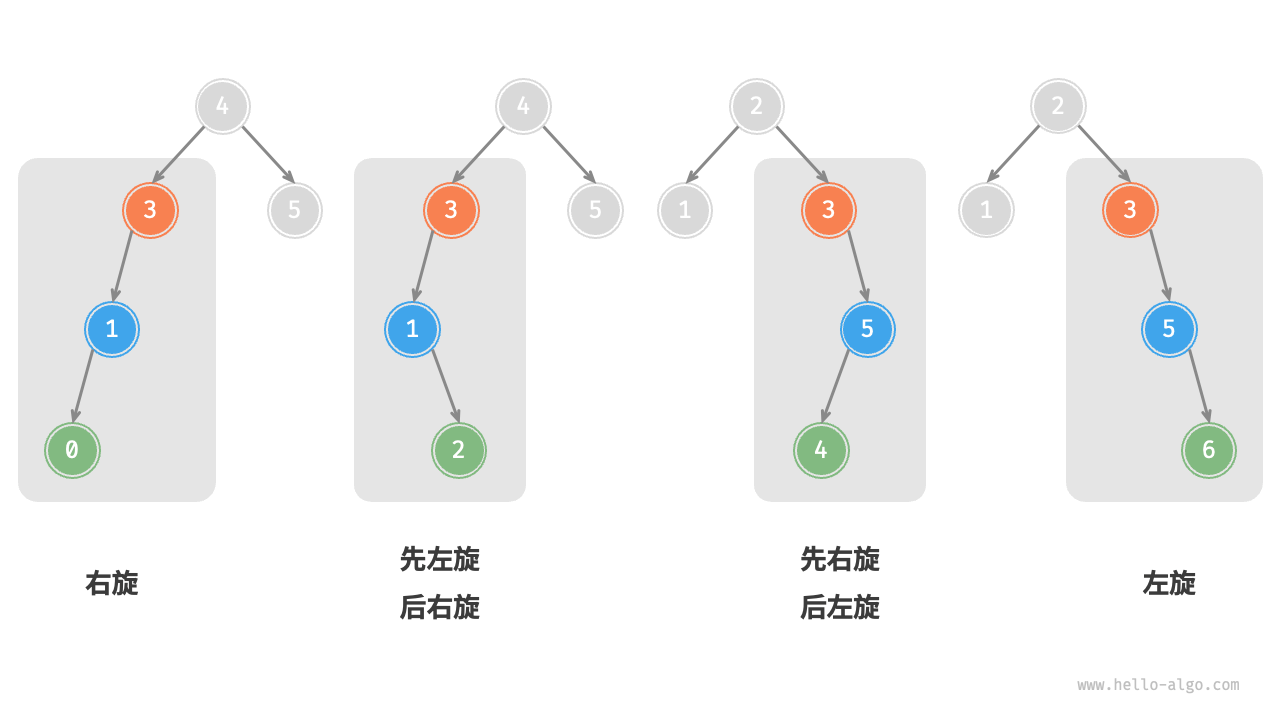
5. Choice of rotation¶
The four kinds of imbalances shown in the Figure 7-32 correspond to the cases described above, respectively requiring right rotation, left-right rotation, right-left rotation, and left rotation.
Figure 7-32 The four rotation cases of AVL tree
As shown in the Table 7-3 , we determine which of the above cases an unbalanced node belongs to by judging the sign of the balance factor of the unbalanced node and its higher-side child's balance factor.
Table 7-3 Conditions for Choosing Among the Four Rotation Cases
| Balance factor of unbalanced node | Balance factor of child node | Rotation method to use |
|---|---|---|
| \(> 1\) (Left-leaning tree) | \(\geq 0\) | Right rotation |
| \(> 1\) (Left-leaning tree) | \(<0\) | Left rotation then right rotation |
| \(< -1\) (Right-leaning tree) | \(\leq 0\) | Left rotation |
| \(< -1\) (Right-leaning tree) | \(>0\) | Right rotation then left rotation |
For convenience, we encapsulate the rotation operations into a function. With this function, we can perform rotations on various kinds of imbalances, restoring balance to unbalanced nodes. The code is as follows:
def rotate(self, node: TreeNode | None) -> TreeNode | None:
"""执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡"""
# 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
balance_factor = self.balance_factor(node)
# 左偏树
if balance_factor > 1:
if self.balance_factor(node.left) >= 0:
# 右旋
return self.right_rotate(node)
else:
# 先左旋后右旋
node.left = self.left_rotate(node.left)
return self.right_rotate(node)
# 右偏树
elif balance_factor < -1:
if self.balance_factor(node.right) <= 0:
# 左旋
return self.left_rotate(node)
else:
# 先右旋后左旋
node.right = self.right_rotate(node.right)
return self.left_rotate(node)
# 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
TreeNode *rotate(TreeNode *node) {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
int _balanceFactor = balanceFactor(node);
// 左偏树
if (_balanceFactor > 1) {
if (balanceFactor(node->left) >= 0) {
// 右旋
return rightRotate(node);
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node->left = leftRotate(node->left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
}
// 右偏树
if (_balanceFactor < -1) {
if (balanceFactor(node->right) <= 0) {
// 左旋
return leftRotate(node);
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node->right = rightRotate(node->right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node;
}
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
TreeNode rotate(TreeNode node) {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
int balanceFactor = balanceFactor(node);
// 左偏树
if (balanceFactor > 1) {
if (balanceFactor(node.left) >= 0) {
// 右旋
return rightRotate(node);
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node.left = leftRotate(node.left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
}
// 右偏树
if (balanceFactor < -1) {
if (balanceFactor(node.right) <= 0) {
// 左旋
return leftRotate(node);
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node.right = rightRotate(node.right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node;
}
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
TreeNode? Rotate(TreeNode? node) {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
int balanceFactorInt = BalanceFactor(node);
// 左偏树
if (balanceFactorInt > 1) {
if (BalanceFactor(node?.left) >= 0) {
// 右旋
return RightRotate(node);
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node!.left = LeftRotate(node!.left);
return RightRotate(node);
}
}
// 右偏树
if (balanceFactorInt < -1) {
if (BalanceFactor(node?.right) <= 0) {
// 左旋
return LeftRotate(node);
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node!.right = RightRotate(node!.right);
return LeftRotate(node);
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node;
}
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
func (t *aVLTree) rotate(node *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
// Go 推荐短变量,这里 bf 指代 t.balanceFactor
bf := t.balanceFactor(node)
// 左偏树
if bf > 1 {
if t.balanceFactor(node.Left) >= 0 {
// 右旋
return t.rightRotate(node)
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node.Left = t.leftRotate(node.Left)
return t.rightRotate(node)
}
}
// 右偏树
if bf < -1 {
if t.balanceFactor(node.Right) <= 0 {
// 左旋
return t.leftRotate(node)
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node.Right = t.rightRotate(node.Right)
return t.leftRotate(node)
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node
}
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
func rotate(node: TreeNode?) -> TreeNode? {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
let balanceFactor = balanceFactor(node: node)
// 左偏树
if balanceFactor > 1 {
if self.balanceFactor(node: node?.left) >= 0 {
// 右旋
return rightRotate(node: node)
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node?.left = leftRotate(node: node?.left)
return rightRotate(node: node)
}
}
// 右偏树
if balanceFactor < -1 {
if self.balanceFactor(node: node?.right) <= 0 {
// 左旋
return leftRotate(node: node)
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node?.right = rightRotate(node: node?.right)
return leftRotate(node: node)
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node
}
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
#rotate(node) {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
const balanceFactor = this.balanceFactor(node);
// 左偏树
if (balanceFactor > 1) {
if (this.balanceFactor(node.left) >= 0) {
// 右旋
return this.#rightRotate(node);
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node.left = this.#leftRotate(node.left);
return this.#rightRotate(node);
}
}
// 右偏树
if (balanceFactor < -1) {
if (this.balanceFactor(node.right) <= 0) {
// 左旋
return this.#leftRotate(node);
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node.right = this.#rightRotate(node.right);
return this.#leftRotate(node);
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node;
}
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
rotate(node: TreeNode): TreeNode {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
const balanceFactor = this.balanceFactor(node);
// 左偏树
if (balanceFactor > 1) {
if (this.balanceFactor(node.left) >= 0) {
// 右旋
return this.rightRotate(node);
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node.left = this.leftRotate(node.left);
return this.rightRotate(node);
}
}
// 右偏树
if (balanceFactor < -1) {
if (this.balanceFactor(node.right) <= 0) {
// 左旋
return this.leftRotate(node);
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right);
return this.leftRotate(node);
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node;
}
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
TreeNode? rotate(TreeNode? node) {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
int factor = balanceFactor(node);
// 左偏树
if (factor > 1) {
if (balanceFactor(node!.left) >= 0) {
// 右旋
return rightRotate(node);
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node.left = leftRotate(node.left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
}
// 右偏树
if (factor < -1) {
if (balanceFactor(node!.right) <= 0) {
// 左旋
return leftRotate(node);
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node.right = rightRotate(node.right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node;
}
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
fn rotate(node: OptionTreeNodeRc) -> OptionTreeNodeRc {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
let balance_factor = Self::balance_factor(node.clone());
// 左偏树
if balance_factor > 1 {
let node = node.unwrap();
if Self::balance_factor(node.borrow().left.clone()) >= 0 {
// 右旋
Self::right_rotate(Some(node))
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
let left = node.borrow().left.clone();
node.borrow_mut().left = Self::left_rotate(left);
Self::right_rotate(Some(node))
}
}
// 右偏树
else if balance_factor < -1 {
let node = node.unwrap();
if Self::balance_factor(node.borrow().right.clone()) <= 0 {
// 左旋
Self::left_rotate(Some(node))
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
let right = node.borrow().right.clone();
node.borrow_mut().right = Self::right_rotate(right);
Self::left_rotate(Some(node))
}
} else {
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
node
}
}
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
TreeNode *rotate(TreeNode *node) {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
int bf = balanceFactor(node);
// 左偏树
if (bf > 1) {
if (balanceFactor(node->left) >= 0) {
// 右旋
return rightRotate(node);
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node->left = leftRotate(node->left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
}
// 右偏树
if (bf < -1) {
if (balanceFactor(node->right) <= 0) {
// 左旋
return leftRotate(node);
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node->right = rightRotate(node->right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node;
}
/* 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
fun rotate(node: TreeNode): TreeNode {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
val balanceFactor = balanceFactor(node)
// 左偏树
if (balanceFactor > 1) {
if (balanceFactor(node.left) >= 0) {
// 右旋
return rightRotate(node)
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node.left = leftRotate(node.left)
return rightRotate(node)
}
}
// 右偏树
if (balanceFactor < -1) {
if (balanceFactor(node.right) <= 0) {
// 左旋
return leftRotate(node)
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node.right = rightRotate(node.right)
return leftRotate(node)
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node
}
// 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡
fn rotate(self: *Self, node: ?*inc.TreeNode(T)) ?*inc.TreeNode(T) {
// 获取节点 node 的平衡因子
var balance_factor = self.balanceFactor(node);
// 左偏树
if (balance_factor > 1) {
if (self.balanceFactor(node.?.left) >= 0) {
// 右旋
return self.rightRotate(node);
} else {
// 先左旋后右旋
node.?.left = self.leftRotate(node.?.left);
return self.rightRotate(node);
}
}
// 右偏树
if (balance_factor < -1) {
if (self.balanceFactor(node.?.right) <= 0) {
// 左旋
return self.leftRotate(node);
} else {
// 先右旋后左旋
node.?.right = self.rightRotate(node.?.right);
return self.leftRotate(node);
}
}
// 平衡树,无须旋转,直接返回
return node;
}
7.5.3 Common operations in AVL trees¶
1. Node insertion¶
The node insertion operation in AVL trees is similar to that in binary search trees. The only difference is that after inserting a node in an AVL tree, a series of unbalanced nodes may appear along the path from that node to the root node. Therefore, we need to start from this node and perform rotation operations upwards to restore balance to all unbalanced nodes. The code is as follows:
def insert(self, val):
"""插入节点"""
self._root = self.insert_helper(self._root, val)
def insert_helper(self, node: TreeNode | None, val: int) -> TreeNode:
"""递归插入节点(辅助方法)"""
if node is None:
return TreeNode(val)
# 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点
if val < node.val:
node.left = self.insert_helper(node.left, val)
elif val > node.val:
node.right = self.insert_helper(node.right, val)
else:
# 重复节点不插入,直接返回
return node
# 更新节点高度
self.update_height(node)
# 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡
return self.rotate(node)
/* 插入节点 */
void insert(int val) {
root = insertHelper(root, val);
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助方法) */
TreeNode *insertHelper(TreeNode *node, int val) {
if (node == nullptr)
return new TreeNode(val);
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
if (val < node->val)
node->left = insertHelper(node->left, val);
else if (val > node->val)
node->right = insertHelper(node->right, val);
else
return node; // 重复节点不插入,直接返回
updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 插入节点 */
void insert(int val) {
root = insertHelper(root, val);
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助方法) */
TreeNode insertHelper(TreeNode node, int val) {
if (node == null)
return new TreeNode(val);
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
if (val < node.val)
node.left = insertHelper(node.left, val);
else if (val > node.val)
node.right = insertHelper(node.right, val);
else
return node; // 重复节点不插入,直接返回
updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 插入节点 */
void Insert(int val) {
root = InsertHelper(root, val);
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助方法) */
TreeNode? InsertHelper(TreeNode? node, int val) {
if (node == null) return new TreeNode(val);
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
if (val < node.val)
node.left = InsertHelper(node.left, val);
else if (val > node.val)
node.right = InsertHelper(node.right, val);
else
return node; // 重复节点不插入,直接返回
UpdateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = Rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 插入节点 */
func (t *aVLTree) insert(val int) {
t.root = t.insertHelper(t.root, val)
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助函数) */
func (t *aVLTree) insertHelper(node *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
if node == nil {
return NewTreeNode(val)
}
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
if val < node.Val.(int) {
node.Left = t.insertHelper(node.Left, val)
} else if val > node.Val.(int) {
node.Right = t.insertHelper(node.Right, val)
} else {
// 重复节点不插入,直接返回
return node
}
// 更新节点高度
t.updateHeight(node)
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = t.rotate(node)
// 返回子树的根节点
return node
}
/* 插入节点 */
func insert(val: Int) {
root = insertHelper(node: root, val: val)
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助方法) */
func insertHelper(node: TreeNode?, val: Int) -> TreeNode? {
var node = node
if node == nil {
return TreeNode(x: val)
}
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
if val < node!.val {
node?.left = insertHelper(node: node?.left, val: val)
} else if val > node!.val {
node?.right = insertHelper(node: node?.right, val: val)
} else {
return node // 重复节点不插入,直接返回
}
updateHeight(node: node) // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node: node)
// 返回子树的根节点
return node
}
/* 插入节点 */
insert(val) {
this.root = this.#insertHelper(this.root, val);
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助方法) */
#insertHelper(node, val) {
if (node === null) return new TreeNode(val);
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
if (val < node.val) node.left = this.#insertHelper(node.left, val);
else if (val > node.val)
node.right = this.#insertHelper(node.right, val);
else return node; // 重复节点不插入,直接返回
this.#updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = this.#rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 插入节点 */
insert(val: number): void {
this.root = this.insertHelper(this.root, val);
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助方法) */
insertHelper(node: TreeNode, val: number): TreeNode {
if (node === null) return new TreeNode(val);
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
if (val < node.val) {
node.left = this.insertHelper(node.left, val);
} else if (val > node.val) {
node.right = this.insertHelper(node.right, val);
} else {
return node; // 重复节点不插入,直接返回
}
this.updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = this.rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 插入节点 */
void insert(int val) {
root = insertHelper(root, val);
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助方法) */
TreeNode? insertHelper(TreeNode? node, int val) {
if (node == null) return TreeNode(val);
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
if (val < node.val)
node.left = insertHelper(node.left, val);
else if (val > node.val)
node.right = insertHelper(node.right, val);
else
return node; // 重复节点不插入,直接返回
updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 插入节点 */
fn insert(&mut self, val: i32) {
self.root = Self::insert_helper(self.root.clone(), val);
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助方法) */
fn insert_helper(node: OptionTreeNodeRc, val: i32) -> OptionTreeNodeRc {
match node {
Some(mut node) => {
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
match {
let node_val = node.borrow().val;
node_val
}
.cmp(&val)
{
Ordering::Greater => {
let left = node.borrow().left.clone();
node.borrow_mut().left = Self::insert_helper(left, val);
}
Ordering::Less => {
let right = node.borrow().right.clone();
node.borrow_mut().right = Self::insert_helper(right, val);
}
Ordering::Equal => {
return Some(node); // 重复节点不插入,直接返回
}
}
Self::update_height(Some(node.clone())); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = Self::rotate(Some(node)).unwrap();
// 返回子树的根节点
Some(node)
}
None => Some(TreeNode::new(val)),
}
}
/* 插入节点 */
void insert(AVLTree *tree, int val) {
tree->root = insertHelper(tree->root, val);
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助函数) */
TreeNode *insertHelper(TreeNode *node, int val) {
if (node == NULL) {
return newTreeNode(val);
}
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
if (val < node->val) {
node->left = insertHelper(node->left, val);
} else if (val > node->val) {
node->right = insertHelper(node->right, val);
} else {
// 重复节点不插入,直接返回
return node;
}
// 更新节点高度
updateHeight(node);
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 插入节点 */
fun insert(value: Int) {
root = insertHelper(root, value)
}
/* 递归插入节点(辅助方法) */
fun insertHelper(n: TreeNode?, value: Int): TreeNode {
if (n == null)
return TreeNode(value)
var node = n
/* 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点 */
if (value < node.value) node.left = insertHelper(node.left, value)
else if (value > node.value) node.right = insertHelper(node.right, value)
else return node // 重复节点不插入,直接返回
updateHeight(node) // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node)
// 返回子树的根节点
return node
}
// 插入节点
fn insert(self: *Self, val: T) !void {
self.root = (try self.insertHelper(self.root, val)).?;
}
// 递归插入节点(辅助方法)
fn insertHelper(self: *Self, node_: ?*inc.TreeNode(T), val: T) !?*inc.TreeNode(T) {
var node = node_;
if (node == null) {
var tmp_node = try self.mem_allocator.create(inc.TreeNode(T));
tmp_node.init(val);
return tmp_node;
}
// 1. 查找插入位置并插入节点
if (val < node.?.val) {
node.?.left = try self.insertHelper(node.?.left, val);
} else if (val > node.?.val) {
node.?.right = try self.insertHelper(node.?.right, val);
} else {
return node; // 重复节点不插入,直接返回
}
self.updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
// 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡
node = self.rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
2. Node removal¶
Similarly, based on the method of removing nodes in binary search trees, rotation operations need to be performed from the bottom up to restore balance to all unbalanced nodes. The code is as follows:
def remove(self, val: int):
"""删除节点"""
self._root = self.remove_helper(self._root, val)
def remove_helper(self, node: TreeNode | None, val: int) -> TreeNode | None:
"""递归删除节点(辅助方法)"""
if node is None:
return None
# 1. 查找节点并删除
if val < node.val:
node.left = self.remove_helper(node.left, val)
elif val > node.val:
node.right = self.remove_helper(node.right, val)
else:
if node.left is None or node.right is None:
child = node.left or node.right
# 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if child is None:
return None
# 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
else:
node = child
else:
# 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
temp = node.right
while temp.left is not None:
temp = temp.left
node.right = self.remove_helper(node.right, temp.val)
node.val = temp.val
# 更新节点高度
self.update_height(node)
# 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡
return self.rotate(node)
/* 删除节点 */
void remove(int val) {
root = removeHelper(root, val);
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助方法) */
TreeNode *removeHelper(TreeNode *node, int val) {
if (node == nullptr)
return nullptr;
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if (val < node->val)
node->left = removeHelper(node->left, val);
else if (val > node->val)
node->right = removeHelper(node->right, val);
else {
if (node->left == nullptr || node->right == nullptr) {
TreeNode *child = node->left != nullptr ? node->left : node->right;
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if (child == nullptr) {
delete node;
return nullptr;
}
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
else {
delete node;
node = child;
}
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
TreeNode *temp = node->right;
while (temp->left != nullptr) {
temp = temp->left;
}
int tempVal = temp->val;
node->right = removeHelper(node->right, temp->val);
node->val = tempVal;
}
}
updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 删除节点 */
void remove(int val) {
root = removeHelper(root, val);
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助方法) */
TreeNode removeHelper(TreeNode node, int val) {
if (node == null)
return null;
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if (val < node.val)
node.left = removeHelper(node.left, val);
else if (val > node.val)
node.right = removeHelper(node.right, val);
else {
if (node.left == null || node.right == null) {
TreeNode child = node.left != null ? node.left : node.right;
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if (child == null)
return null;
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
else
node = child;
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
TreeNode temp = node.right;
while (temp.left != null) {
temp = temp.left;
}
node.right = removeHelper(node.right, temp.val);
node.val = temp.val;
}
}
updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 删除节点 */
void Remove(int val) {
root = RemoveHelper(root, val);
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助方法) */
TreeNode? RemoveHelper(TreeNode? node, int val) {
if (node == null) return null;
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if (val < node.val)
node.left = RemoveHelper(node.left, val);
else if (val > node.val)
node.right = RemoveHelper(node.right, val);
else {
if (node.left == null || node.right == null) {
TreeNode? child = node.left ?? node.right;
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if (child == null)
return null;
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
else
node = child;
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
TreeNode? temp = node.right;
while (temp.left != null) {
temp = temp.left;
}
node.right = RemoveHelper(node.right, temp.val!.Value);
node.val = temp.val;
}
}
UpdateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = Rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 删除节点 */
func (t *aVLTree) remove(val int) {
t.root = t.removeHelper(t.root, val)
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助函数) */
func (t *aVLTree) removeHelper(node *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
if node == nil {
return nil
}
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if val < node.Val.(int) {
node.Left = t.removeHelper(node.Left, val)
} else if val > node.Val.(int) {
node.Right = t.removeHelper(node.Right, val)
} else {
if node.Left == nil || node.Right == nil {
child := node.Left
if node.Right != nil {
child = node.Right
}
if child == nil {
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
return nil
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
node = child
}
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
temp := node.Right
for temp.Left != nil {
temp = temp.Left
}
node.Right = t.removeHelper(node.Right, temp.Val.(int))
node.Val = temp.Val
}
}
// 更新节点高度
t.updateHeight(node)
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = t.rotate(node)
// 返回子树的根节点
return node
}
/* 删除节点 */
func remove(val: Int) {
root = removeHelper(node: root, val: val)
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助方法) */
func removeHelper(node: TreeNode?, val: Int) -> TreeNode? {
var node = node
if node == nil {
return nil
}
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if val < node!.val {
node?.left = removeHelper(node: node?.left, val: val)
} else if val > node!.val {
node?.right = removeHelper(node: node?.right, val: val)
} else {
if node?.left == nil || node?.right == nil {
let child = node?.left ?? node?.right
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if child == nil {
return nil
}
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
else {
node = child
}
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
var temp = node?.right
while temp?.left != nil {
temp = temp?.left
}
node?.right = removeHelper(node: node?.right, val: temp!.val)
node?.val = temp!.val
}
}
updateHeight(node: node) // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node: node)
// 返回子树的根节点
return node
}
/* 删除节点 */
remove(val) {
this.root = this.#removeHelper(this.root, val);
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助方法) */
#removeHelper(node, val) {
if (node === null) return null;
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if (val < node.val) node.left = this.#removeHelper(node.left, val);
else if (val > node.val)
node.right = this.#removeHelper(node.right, val);
else {
if (node.left === null || node.right === null) {
const child = node.left !== null ? node.left : node.right;
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if (child === null) return null;
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
else node = child;
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
let temp = node.right;
while (temp.left !== null) {
temp = temp.left;
}
node.right = this.#removeHelper(node.right, temp.val);
node.val = temp.val;
}
}
this.#updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = this.#rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 删除节点 */
remove(val: number): void {
this.root = this.removeHelper(this.root, val);
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助方法) */
removeHelper(node: TreeNode, val: number): TreeNode {
if (node === null) return null;
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if (val < node.val) {
node.left = this.removeHelper(node.left, val);
} else if (val > node.val) {
node.right = this.removeHelper(node.right, val);
} else {
if (node.left === null || node.right === null) {
const child = node.left !== null ? node.left : node.right;
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if (child === null) {
return null;
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
node = child;
}
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
let temp = node.right;
while (temp.left !== null) {
temp = temp.left;
}
node.right = this.removeHelper(node.right, temp.val);
node.val = temp.val;
}
}
this.updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = this.rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 删除节点 */
void remove(int val) {
root = removeHelper(root, val);
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助方法) */
TreeNode? removeHelper(TreeNode? node, int val) {
if (node == null) return null;
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if (val < node.val)
node.left = removeHelper(node.left, val);
else if (val > node.val)
node.right = removeHelper(node.right, val);
else {
if (node.left == null || node.right == null) {
TreeNode? child = node.left ?? node.right;
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if (child == null)
return null;
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
else
node = child;
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
TreeNode? temp = node.right;
while (temp!.left != null) {
temp = temp.left;
}
node.right = removeHelper(node.right, temp.val);
node.val = temp.val;
}
}
updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 删除节点 */
fn remove(&self, val: i32) {
Self::remove_helper(self.root.clone(), val);
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助方法) */
fn remove_helper(node: OptionTreeNodeRc, val: i32) -> OptionTreeNodeRc {
match node {
Some(mut node) => {
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if val < node.borrow().val {
let left = node.borrow().left.clone();
node.borrow_mut().left = Self::remove_helper(left, val);
} else if val > node.borrow().val {
let right = node.borrow().right.clone();
node.borrow_mut().right = Self::remove_helper(right, val);
} else if node.borrow().left.is_none() || node.borrow().right.is_none() {
let child = if node.borrow().left.is_some() {
node.borrow().left.clone()
} else {
node.borrow().right.clone()
};
match child {
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
None => {
return None;
}
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
Some(child) => node = child,
}
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
let mut temp = node.borrow().right.clone().unwrap();
loop {
let temp_left = temp.borrow().left.clone();
if temp_left.is_none() {
break;
}
temp = temp_left.unwrap();
}
let right = node.borrow().right.clone();
node.borrow_mut().right = Self::remove_helper(right, temp.borrow().val);
node.borrow_mut().val = temp.borrow().val;
}
Self::update_height(Some(node.clone())); // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = Self::rotate(Some(node)).unwrap();
// 返回子树的根节点
Some(node)
}
None => None,
}
}
/* 删除节点 */
// 由于引入了 stdio.h ,此处无法使用 remove 关键词
void removeItem(AVLTree *tree, int val) {
TreeNode *root = removeHelper(tree->root, val);
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助函数) */
TreeNode *removeHelper(TreeNode *node, int val) {
TreeNode *child, *grandChild;
if (node == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if (val < node->val) {
node->left = removeHelper(node->left, val);
} else if (val > node->val) {
node->right = removeHelper(node->right, val);
} else {
if (node->left == NULL || node->right == NULL) {
child = node->left;
if (node->right != NULL) {
child = node->right;
}
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if (child == NULL) {
return NULL;
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
node = child;
}
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
TreeNode *temp = node->right;
while (temp->left != NULL) {
temp = temp->left;
}
int tempVal = temp->val;
node->right = removeHelper(node->right, temp->val);
node->val = tempVal;
}
}
// 更新节点高度
updateHeight(node);
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
/* 删除节点 */
fun remove(value: Int) {
root = removeHelper(root, value)
}
/* 递归删除节点(辅助方法) */
fun removeHelper(n: TreeNode?, value: Int): TreeNode? {
var node = n ?: return null
/* 1. 查找节点并删除 */
if (value < node.value) node.left = removeHelper(node.left, value)
else if (value > node.value) node.right = removeHelper(node.right, value)
else {
if (node.left == null || node.right == null) {
val child = if (node.left != null) node.left else node.right
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if (child == null) return null
else node = child
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
var temp = node.right
while (temp!!.left != null) {
temp = temp.left
}
node.right = removeHelper(node.right, temp.value)
node.value = temp.value
}
}
updateHeight(node) // 更新节点高度
/* 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡 */
node = rotate(node)
// 返回子树的根节点
return node
}
// 删除节点
fn remove(self: *Self, val: T) void {
self.root = self.removeHelper(self.root, val).?;
}
// 递归删除节点(辅助方法)
fn removeHelper(self: *Self, node_: ?*inc.TreeNode(T), val: T) ?*inc.TreeNode(T) {
var node = node_;
if (node == null) return null;
// 1. 查找节点并删除
if (val < node.?.val) {
node.?.left = self.removeHelper(node.?.left, val);
} else if (val > node.?.val) {
node.?.right = self.removeHelper(node.?.right, val);
} else {
if (node.?.left == null or node.?.right == null) {
var child = if (node.?.left != null) node.?.left else node.?.right;
// 子节点数量 = 0 ,直接删除 node 并返回
if (child == null) {
return null;
// 子节点数量 = 1 ,直接删除 node
} else {
node = child;
}
} else {
// 子节点数量 = 2 ,则将中序遍历的下个节点删除,并用该节点替换当前节点
var temp = node.?.right;
while (temp.?.left != null) {
temp = temp.?.left;
}
node.?.right = self.removeHelper(node.?.right, temp.?.val);
node.?.val = temp.?.val;
}
}
self.updateHeight(node); // 更新节点高度
// 2. 执行旋转操作,使该子树重新恢复平衡
node = self.rotate(node);
// 返回子树的根节点
return node;
}
3. Node search¶
The node search operation in AVL trees is consistent with that in binary search trees and will not be detailed here.
7.5.4 Typical applications of AVL trees¶
- Organizing and storing large amounts of data, suitable for scenarios with high-frequency searches and low-frequency intertions and removals.
- Used to build index systems in databases.
- Red-black trees are also a common type of balanced binary search tree. Compared to AVL trees, red-black trees have more relaxed balancing conditions, require fewer rotations for node insertion and removal, and have a higher average efficiency for node addition and removal operations.