9.3 Graph traversal¶
Trees represent a "one-to-many" relationship, while graphs have a higher degree of freedom and can represent any "many-to-many" relationship. Therefore, we can consider trees as a special case of graphs. Clearly, tree traversal operations are also a special case of graph traversal operations.
Both graphs and trees require the application of search algorithms to implement traversal operations. Graph traversal can be divided into two types: "Breadth-First Search (BFS)" and "Depth-First Search (DFS)".
9.3.1 Breadth-first search¶
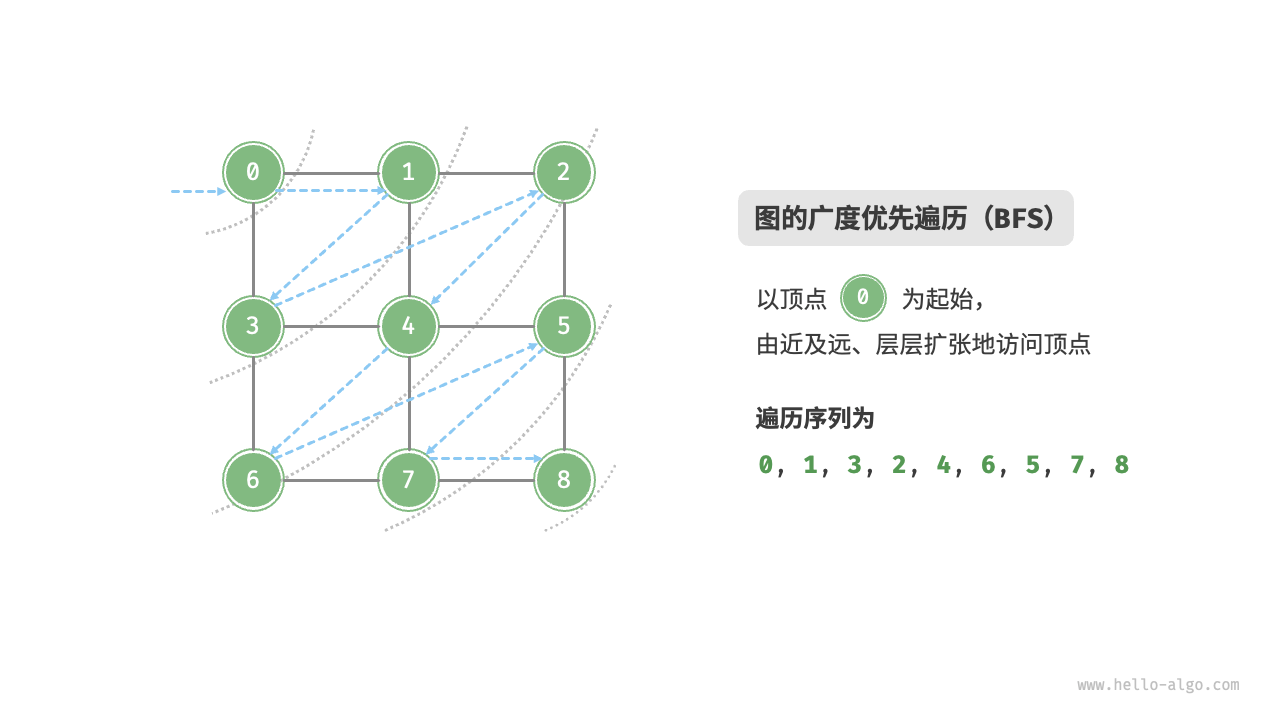
Breadth-first search is a near-to-far traversal method, starting from a certain node, always prioritizing the visit to the nearest vertices and expanding outwards layer by layer. As shown in the Figure 9-9 , starting from the top left vertex, first traverse all adjacent vertices of that vertex, then traverse all adjacent vertices of the next vertex, and so on, until all vertices have been visited.
Figure 9-9 Breadth-first traversal of a graph
1. Algorithm implementation¶
BFS is usually implemented with the help of a queue, as shown in the code below. The queue has a "first in, first out" property, which aligns with the BFS idea of traversing "from near to far".
- Add the starting vertex
startVetto the queue and start the loop. - In each iteration of the loop, pop the vertex at the front of the queue and record it as visited, then add all adjacent vertices of that vertex to the back of the queue.
- Repeat step
2.until all vertices have been visited.
To prevent revisiting vertices, we use a hash table visited to record which nodes have been visited.
def graph_bfs(graph: GraphAdjList, start_vet: Vertex) -> list[Vertex]:
"""广度优先遍历"""
# 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
# 顶点遍历序列
res = []
# 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
visited = set[Vertex]([start_vet])
# 队列用于实现 BFS
que = deque[Vertex]([start_vet])
# 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while len(que) > 0:
vet = que.popleft() # 队首顶点出队
res.append(vet) # 记录访问顶点
# 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for adj_vet in graph.adj_list[vet]:
if adj_vet in visited:
continue # 跳过已被访问的顶点
que.append(adj_vet) # 只入队未访问的顶点
visited.add(adj_vet) # 标记该顶点已被访问
# 返回顶点遍历序列
return res
/* 广度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
vector<Vertex *> graphBFS(GraphAdjList &graph, Vertex *startVet) {
// 顶点遍历序列
vector<Vertex *> res;
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
unordered_set<Vertex *> visited = {startVet};
// 队列用于实现 BFS
queue<Vertex *> que;
que.push(startVet);
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while (!que.empty()) {
Vertex *vet = que.front();
que.pop(); // 队首顶点出队
res.push_back(vet); // 记录访问顶点
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (auto adjVet : graph.adjList[vet]) {
if (visited.count(adjVet))
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
que.push(adjVet); // 只入队未访问的顶点
visited.emplace(adjVet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
}
}
// 返回顶点遍历序列
return res;
}
/* 广度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
List<Vertex> graphBFS(GraphAdjList graph, Vertex startVet) {
// 顶点遍历序列
List<Vertex> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
Set<Vertex> visited = new HashSet<>();
visited.add(startVet);
// 队列用于实现 BFS
Queue<Vertex> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(startVet);
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
Vertex vet = que.poll(); // 队首顶点出队
res.add(vet); // 记录访问顶点
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (Vertex adjVet : graph.adjList.get(vet)) {
if (visited.contains(adjVet))
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
que.offer(adjVet); // 只入队未访问的顶点
visited.add(adjVet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
}
}
// 返回顶点遍历序列
return res;
}
/* 广度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
List<Vertex> GraphBFS(GraphAdjList graph, Vertex startVet) {
// 顶点遍历序列
List<Vertex> res = [];
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
HashSet<Vertex> visited = [startVet];
// 队列用于实现 BFS
Queue<Vertex> que = new();
que.Enqueue(startVet);
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while (que.Count > 0) {
Vertex vet = que.Dequeue(); // 队首顶点出队
res.Add(vet); // 记录访问顶点
foreach (Vertex adjVet in graph.adjList[vet]) {
if (visited.Contains(adjVet)) {
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
que.Enqueue(adjVet); // 只入队未访问的顶点
visited.Add(adjVet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
}
}
// 返回顶点遍历序列
return res;
}
/* 广度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
func graphBFS(g *graphAdjList, startVet Vertex) []Vertex {
// 顶点遍历序列
res := make([]Vertex, 0)
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
visited := make(map[Vertex]struct{})
visited[startVet] = struct{}{}
// 队列用于实现 BFS, 使用切片模拟队列
queue := make([]Vertex, 0)
queue = append(queue, startVet)
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
for len(queue) > 0 {
// 队首顶点出队
vet := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
// 记录访问顶点
res = append(res, vet)
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for _, adjVet := range g.adjList[vet] {
_, isExist := visited[adjVet]
// 只入队未访问的顶点
if !isExist {
queue = append(queue, adjVet)
visited[adjVet] = struct{}{}
}
}
}
// 返回顶点遍历序列
return res
}
/* 广度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
func graphBFS(graph: GraphAdjList, startVet: Vertex) -> [Vertex] {
// 顶点遍历序列
var res: [Vertex] = []
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
var visited: Set<Vertex> = [startVet]
// 队列用于实现 BFS
var que: [Vertex] = [startVet]
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while !que.isEmpty {
let vet = que.removeFirst() // 队首顶点出队
res.append(vet) // 记录访问顶点
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for adjVet in graph.adjList[vet] ?? [] {
if visited.contains(adjVet) {
continue // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
que.append(adjVet) // 只入队未访问的顶点
visited.insert(adjVet) // 标记该顶点已被访问
}
}
// 返回顶点遍历序列
return res
}
/* 广度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
function graphBFS(graph, startVet) {
// 顶点遍历序列
const res = [];
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
const visited = new Set();
visited.add(startVet);
// 队列用于实现 BFS
const que = [startVet];
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while (que.length) {
const vet = que.shift(); // 队首顶点出队
res.push(vet); // 记录访问顶点
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (const adjVet of graph.adjList.get(vet) ?? []) {
if (visited.has(adjVet)) {
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
que.push(adjVet); // 只入队未访问的顶点
visited.add(adjVet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
}
}
// 返回顶点遍历序列
return res;
}
/* 广度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
function graphBFS(graph: GraphAdjList, startVet: Vertex): Vertex[] {
// 顶点遍历序列
const res: Vertex[] = [];
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
const visited: Set<Vertex> = new Set();
visited.add(startVet);
// 队列用于实现 BFS
const que = [startVet];
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while (que.length) {
const vet = que.shift(); // 队首顶点出队
res.push(vet); // 记录访问顶点
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (const adjVet of graph.adjList.get(vet) ?? []) {
if (visited.has(adjVet)) {
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
que.push(adjVet); // 只入队未访问
visited.add(adjVet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
}
}
// 返回顶点遍历序列
return res;
}
/* 广度优先遍历 */
List<Vertex> graphBFS(GraphAdjList graph, Vertex startVet) {
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
// 顶点遍历序列
List<Vertex> res = [];
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
Set<Vertex> visited = {};
visited.add(startVet);
// 队列用于实现 BFS
Queue<Vertex> que = Queue();
que.add(startVet);
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while (que.isNotEmpty) {
Vertex vet = que.removeFirst(); // 队首顶点出队
res.add(vet); // 记录访问顶点
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (Vertex adjVet in graph.adjList[vet]!) {
if (visited.contains(adjVet)) {
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
que.add(adjVet); // 只入队未访问的顶点
visited.add(adjVet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
}
}
// 返回顶点遍历序列
return res;
}
/* 广度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
fn graph_bfs(graph: GraphAdjList, start_vet: Vertex) -> Vec<Vertex> {
// 顶点遍历序列
let mut res = vec![];
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
let mut visited = HashSet::new();
visited.insert(start_vet);
// 队列用于实现 BFS
let mut que = VecDeque::new();
que.push_back(start_vet);
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while !que.is_empty() {
let vet = que.pop_front().unwrap(); // 队首顶点出队
res.push(vet); // 记录访问顶点
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
if let Some(adj_vets) = graph.adj_list.get(&vet) {
for &adj_vet in adj_vets {
if visited.contains(&adj_vet) {
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
que.push_back(adj_vet); // 只入队未访问的顶点
visited.insert(adj_vet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
}
}
}
// 返回顶点遍历序列
res
}
/* 节点队列结构体 */
typedef struct {
Vertex *vertices[MAX_SIZE];
int front, rear, size;
} Queue;
/* 构造函数 */
Queue *newQueue() {
Queue *q = (Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
q->front = q->rear = q->size = 0;
return q;
}
/* 判断队列是否为空 */
int isEmpty(Queue *q) {
return q->size == 0;
}
/* 入队操作 */
void enqueue(Queue *q, Vertex *vet) {
q->vertices[q->rear] = vet;
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
q->size++;
}
/* 出队操作 */
Vertex *dequeue(Queue *q) {
Vertex *vet = q->vertices[q->front];
q->front = (q->front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
q->size--;
return vet;
}
/* 检查顶点是否已被访问 */
int isVisited(Vertex **visited, int size, Vertex *vet) {
// 遍历查找节点,使用 O(n) 时间
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (visited[i] == vet)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
/* 广度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
void graphBFS(GraphAdjList *graph, Vertex *startVet, Vertex **res, int *resSize, Vertex **visited, int *visitedSize) {
// 队列用于实现 BFS
Queue *queue = newQueue();
enqueue(queue, startVet);
visited[(*visitedSize)++] = startVet;
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while (!isEmpty(queue)) {
Vertex *vet = dequeue(queue); // 队首顶点出队
res[(*resSize)++] = vet; // 记录访问顶点
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
AdjListNode *node = findNode(graph, vet);
while (node != NULL) {
// 跳过已被访问的顶点
if (!isVisited(visited, *visitedSize, node->vertex)) {
enqueue(queue, node->vertex); // 只入队未访问的顶点
visited[(*visitedSize)++] = node->vertex; // 标记该顶点已被访问
}
node = node->next;
}
}
// 释放内存
free(queue);
}
/* 广度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
fun graphBFS(graph: GraphAdjList, startVet: Vertex): MutableList<Vertex?> {
// 顶点遍历序列
val res = mutableListOf<Vertex?>()
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
val visited = HashSet<Vertex>()
visited.add(startVet)
// 队列用于实现 BFS
val que = LinkedList<Vertex>()
que.offer(startVet)
// 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
val vet = que.poll() // 队首顶点出队
res.add(vet) // 记录访问顶点
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (adjVet in graph.adjList[vet]!!) {
if (visited.contains(adjVet))
continue // 跳过已被访问的顶点
que.offer(adjVet) // 只入队未访问的顶点
visited.add(adjVet) // 标记该顶点已被访问
}
}
// 返回顶点遍历序列
return res
}
### 广度优先遍历 ###
def graph_bfs(graph, start_vet)
# 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
# 顶点遍历序列
res = []
# 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
visited = Set.new([start_vet])
# 队列用于实现 BFS
que = [start_vet]
# 以顶点 vet 为起点,循环直至访问完所有顶点
while que.length > 0
vet = que.shift # 队首顶点出队
res << vet # 记录访问顶点
# 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for adj_vet in graph.adj_list[vet]
next if visited.include?(adj_vet) # 跳过已被访问的顶点
que << adj_vet # 只入队未访问的顶点
visited.add(adj_vet) # 标记该顶点已被访问
end
end
# 返回顶点遍历序列
res
end
Code Visualization
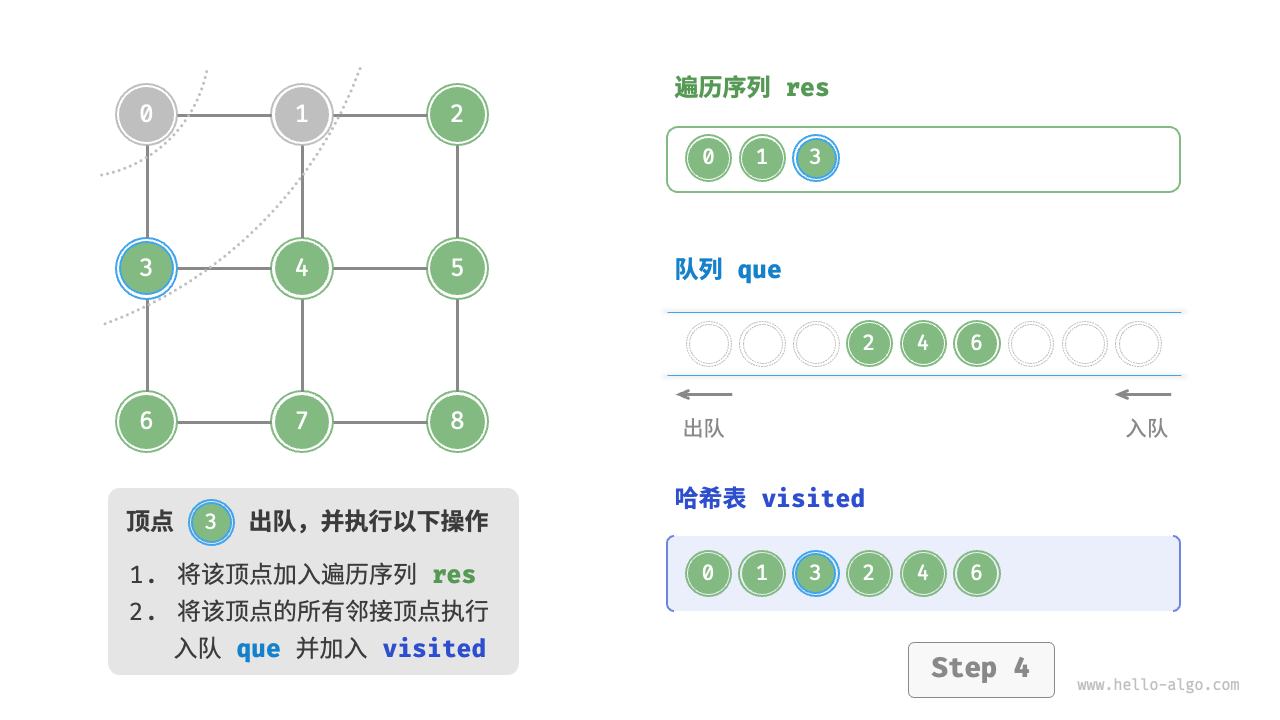
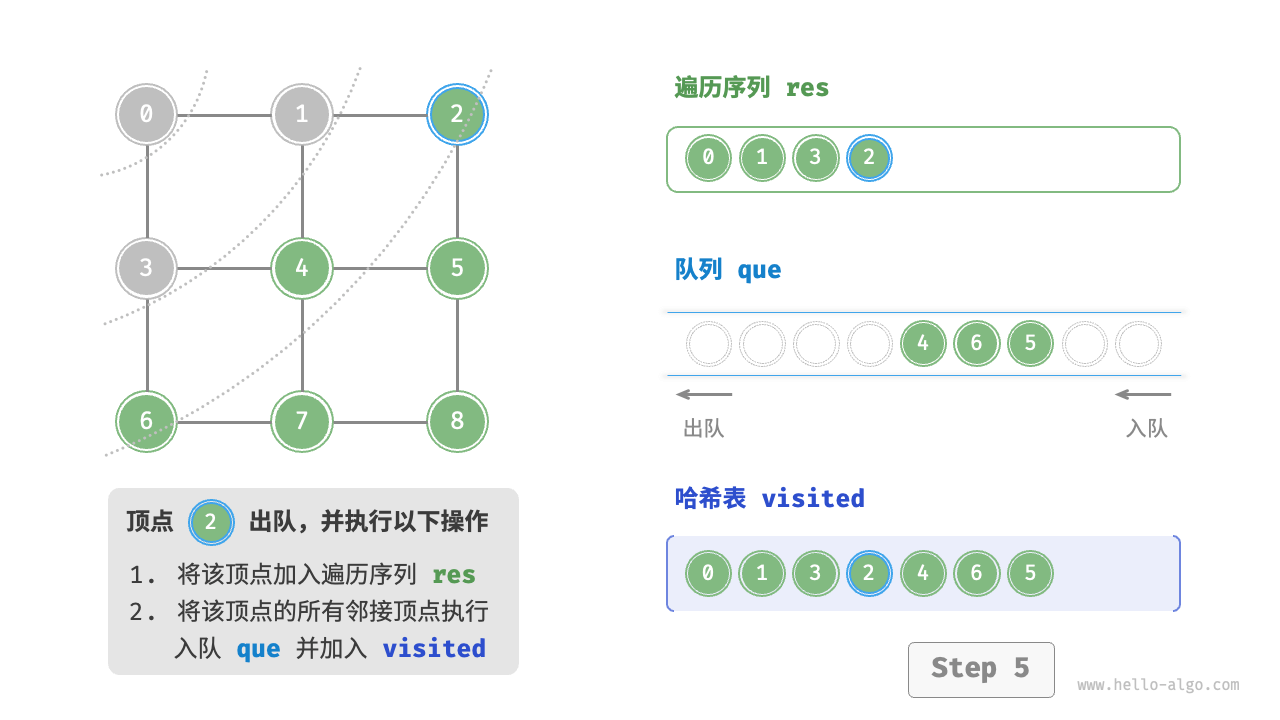
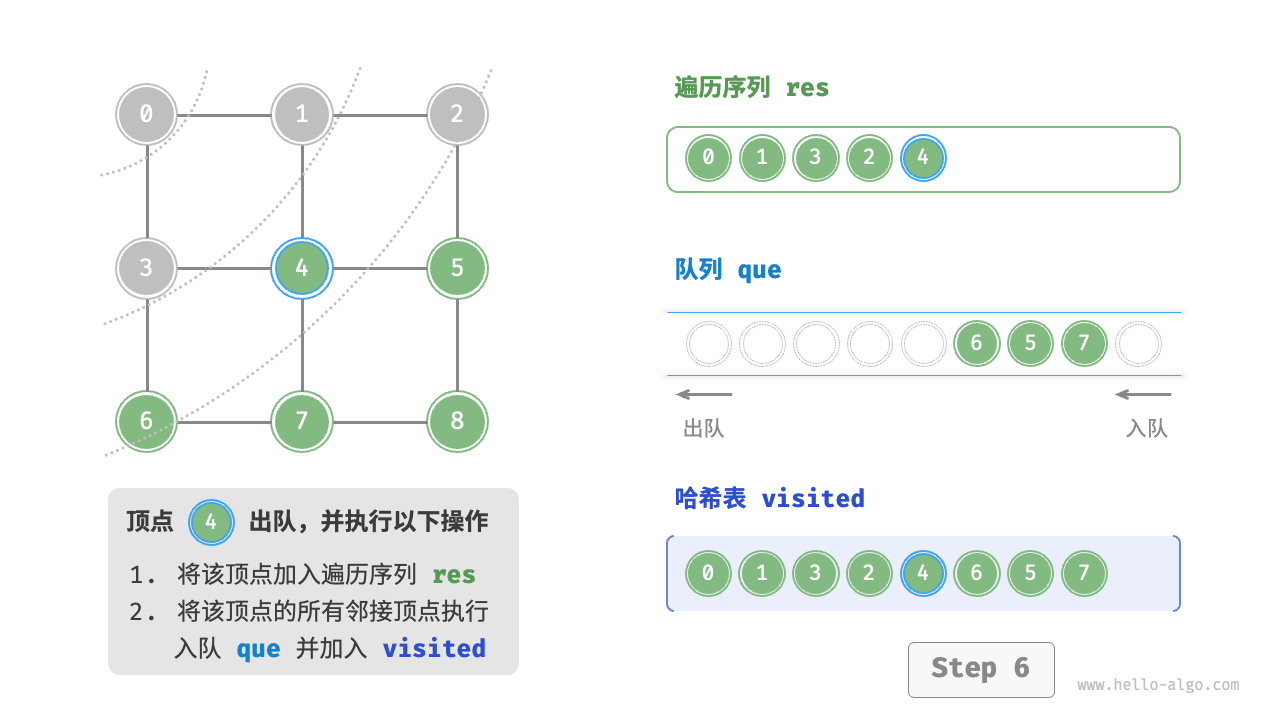
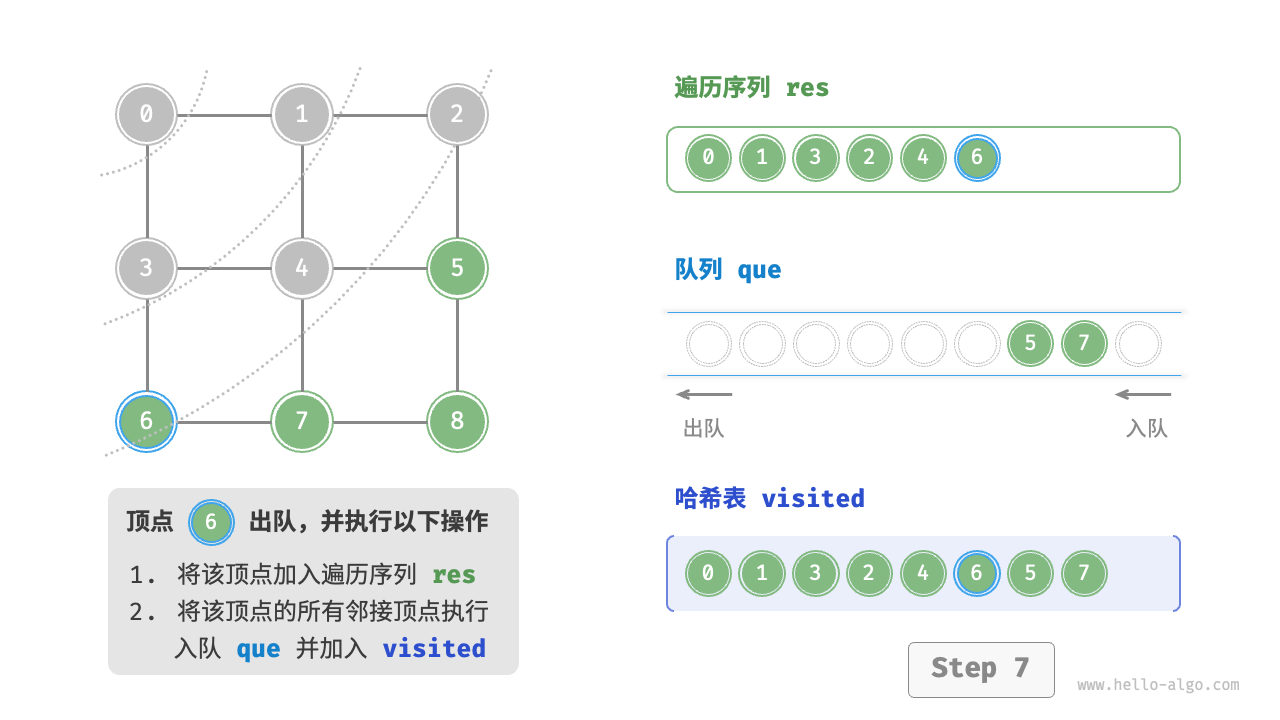
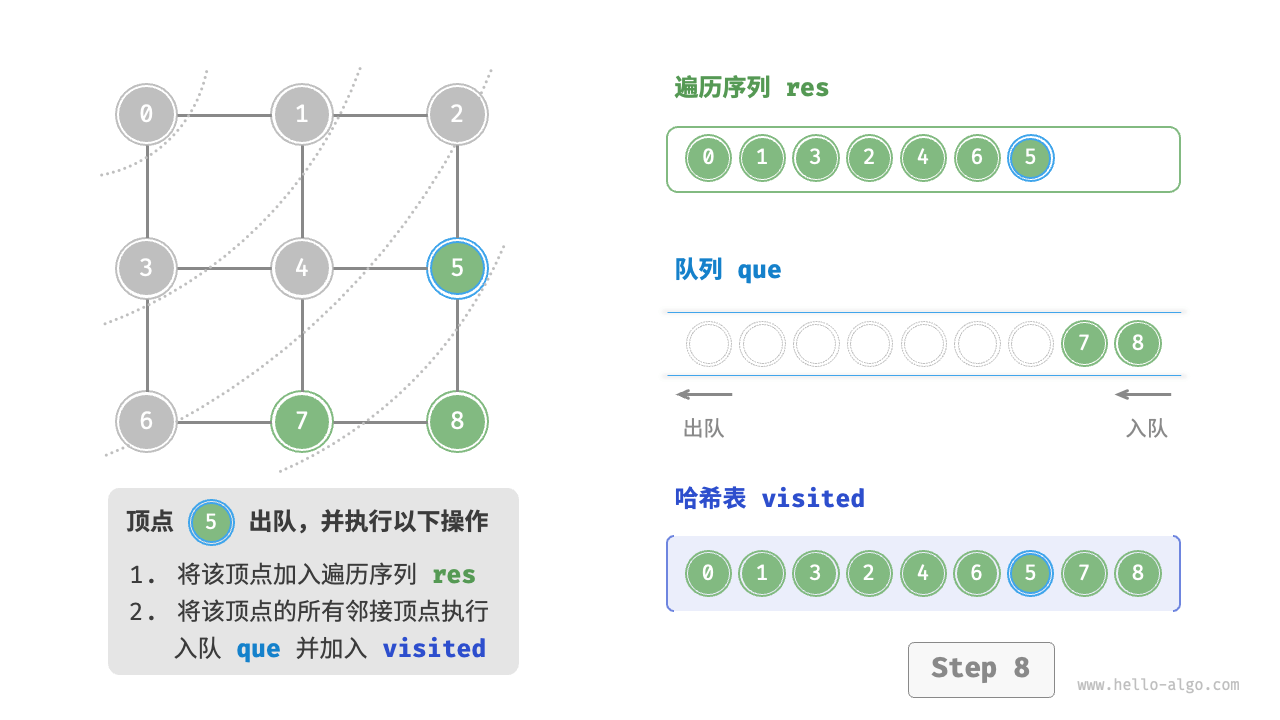
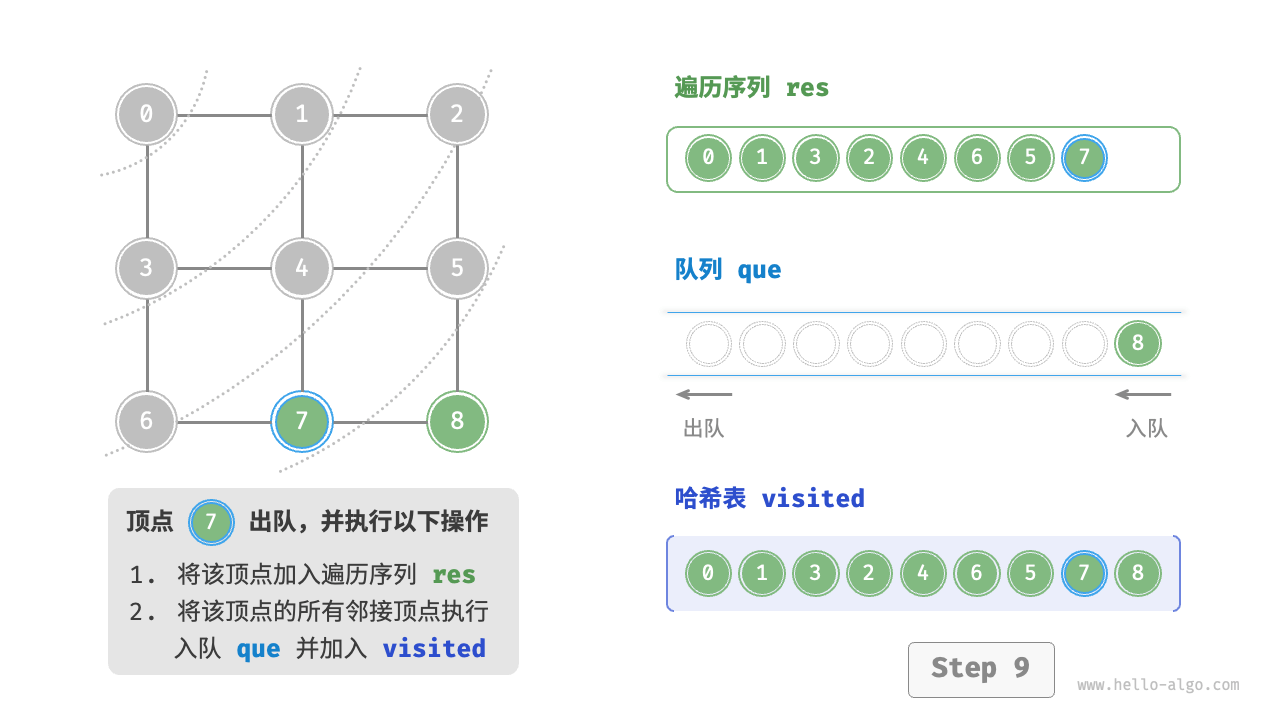
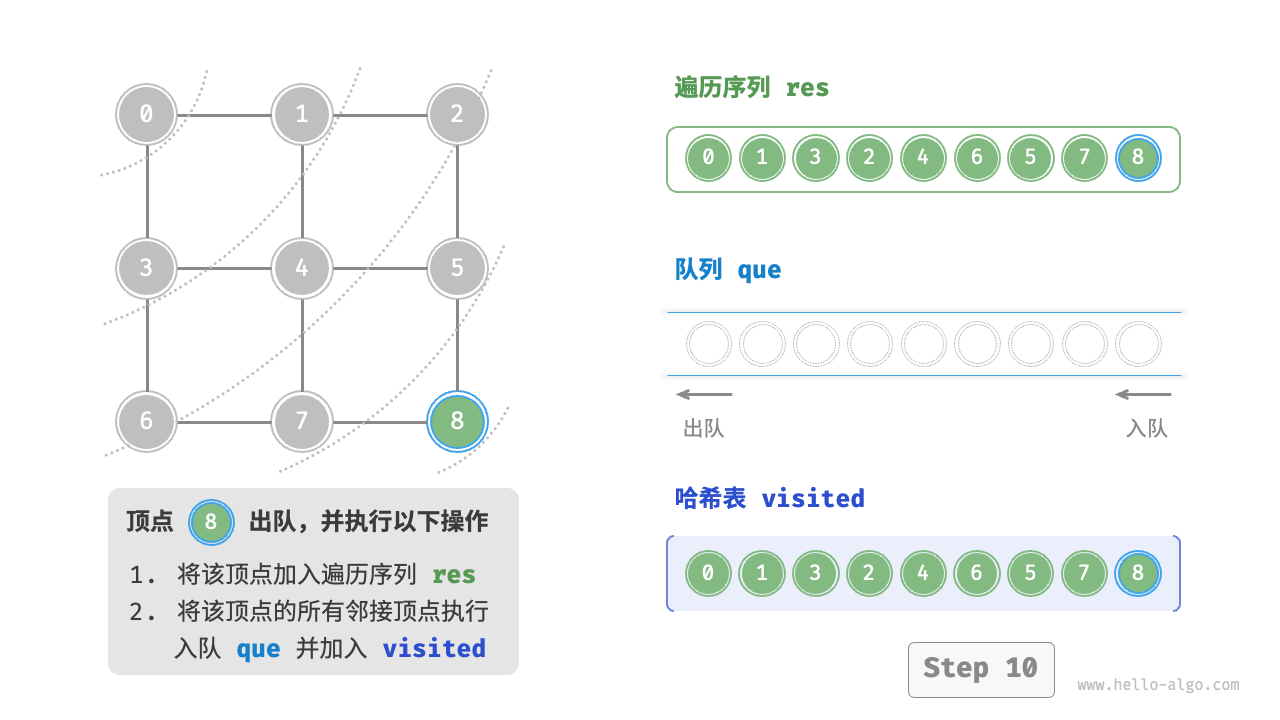
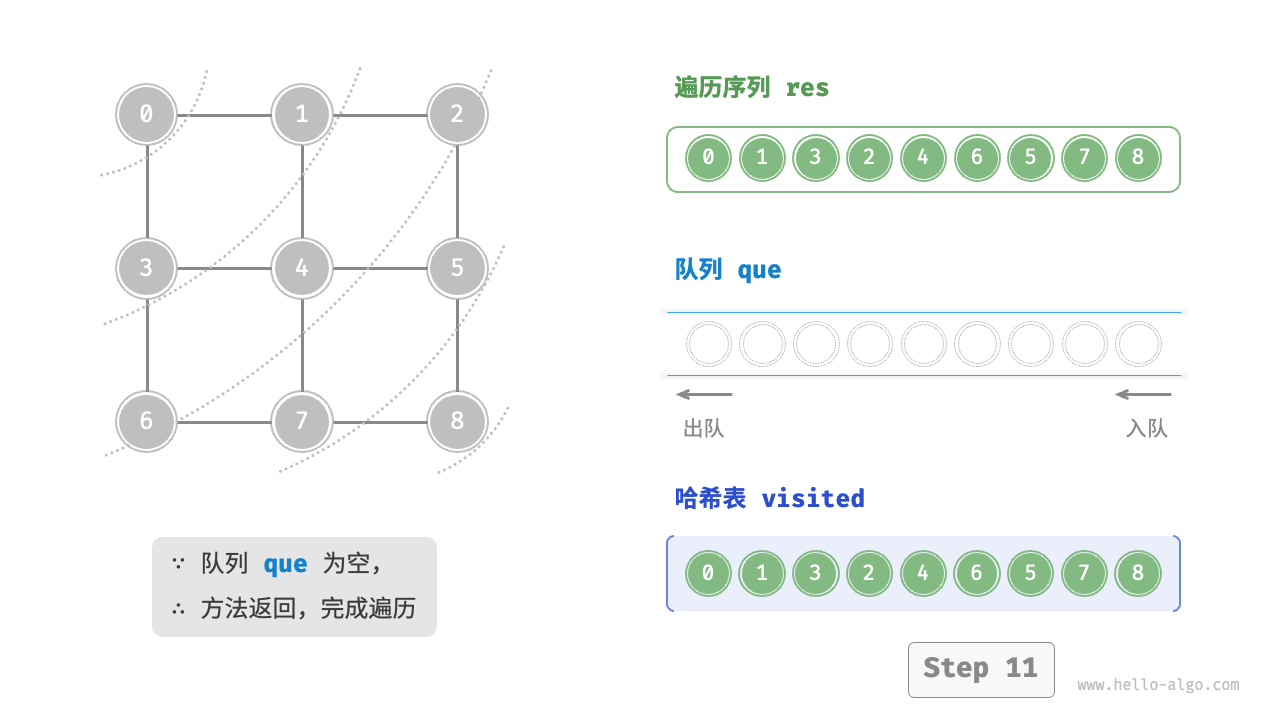
The code is relatively abstract, it is suggested to compare with the following figure to deepen the understanding.
Figure 9-10 Steps of breadth-first search of a graph
Is the sequence of breadth-first traversal unique?
Not unique. Breadth-first traversal only requires traversing in a "from near to far" order, and the traversal order of multiple vertices at the same distance can be arbitrarily shuffled. For example, in the above figure, the visitation order of vertices \(1\) and \(3\) can be switched, as can the order of vertices \(2\), \(4\), and \(6\).
2. Complexity analysis¶
Time complexity: All vertices will be enqueued and dequeued once, using \(O(|V|)\) time; in the process of traversing adjacent vertices, since it is an undirected graph, all edges will be visited \(2\) times, using \(O(2|E|)\) time; overall using \(O(|V| + |E|)\) time.
Space complexity: The maximum number of vertices in list res, hash table visited, and queue que is \(|V|\), using \(O(|V|)\) space.
9.3.2 Depth-first search¶
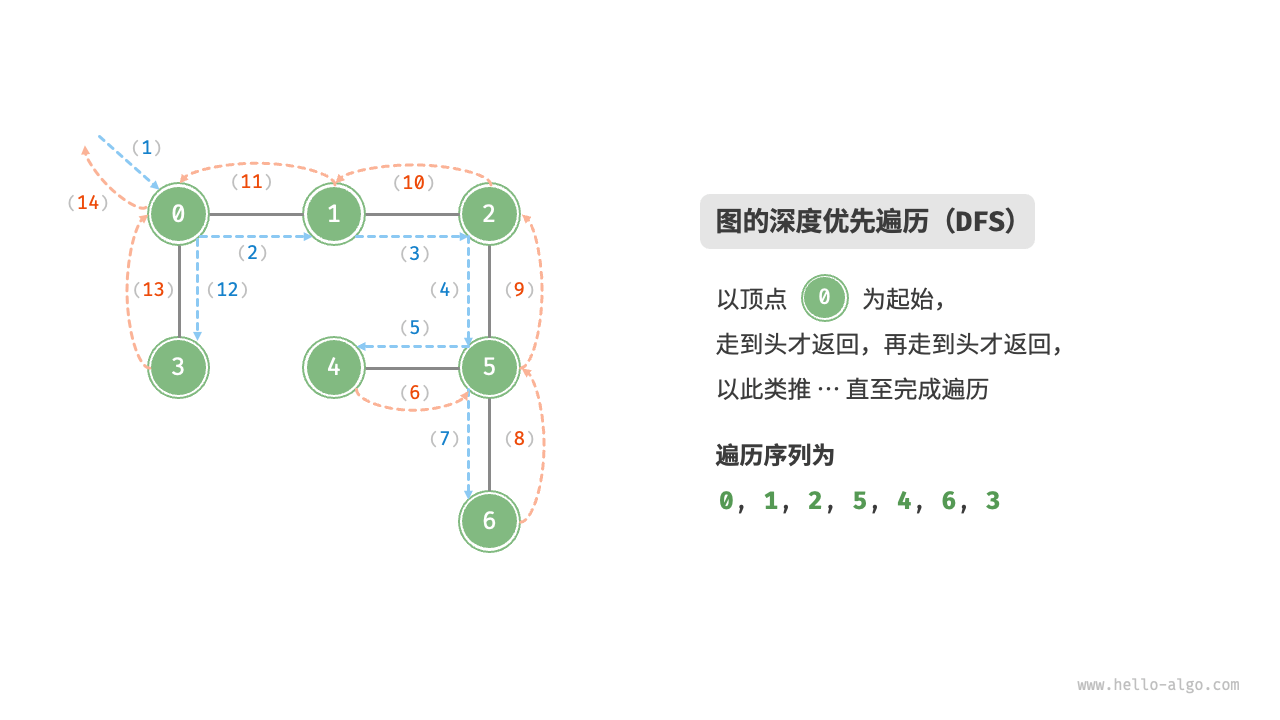
Depth-first search is a traversal method that prioritizes going as far as possible and then backtracks when no further paths are available. As shown in the Figure 9-11 , starting from the top left vertex, visit some adjacent vertex of the current vertex until no further path is available, then return and continue until all vertices are traversed.
Figure 9-11 Depth-first traversal of a graph
1. Algorithm implementation¶
This "go as far as possible and then return" algorithm paradigm is usually implemented based on recursion. Similar to breadth-first search, in depth-first search, we also need the help of a hash table visited to record the visited vertices to avoid revisiting.
def dfs(graph: GraphAdjList, visited: set[Vertex], res: list[Vertex], vet: Vertex):
"""深度优先遍历辅助函数"""
res.append(vet) # 记录访问顶点
visited.add(vet) # 标记该顶点已被访问
# 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for adjVet in graph.adj_list[vet]:
if adjVet in visited:
continue # 跳过已被访问的顶点
# 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph, visited, res, adjVet)
def graph_dfs(graph: GraphAdjList, start_vet: Vertex) -> list[Vertex]:
"""深度优先遍历"""
# 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
# 顶点遍历序列
res = []
# 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
visited = set[Vertex]()
dfs(graph, visited, res, start_vet)
return res
/* 深度优先遍历辅助函数 */
void dfs(GraphAdjList &graph, unordered_set<Vertex *> &visited, vector<Vertex *> &res, Vertex *vet) {
res.push_back(vet); // 记录访问顶点
visited.emplace(vet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (Vertex *adjVet : graph.adjList[vet]) {
if (visited.count(adjVet))
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
// 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph, visited, res, adjVet);
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
vector<Vertex *> graphDFS(GraphAdjList &graph, Vertex *startVet) {
// 顶点遍历序列
vector<Vertex *> res;
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
unordered_set<Vertex *> visited;
dfs(graph, visited, res, startVet);
return res;
}
/* 深度优先遍历辅助函数 */
void dfs(GraphAdjList graph, Set<Vertex> visited, List<Vertex> res, Vertex vet) {
res.add(vet); // 记录访问顶点
visited.add(vet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (Vertex adjVet : graph.adjList.get(vet)) {
if (visited.contains(adjVet))
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
// 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph, visited, res, adjVet);
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
List<Vertex> graphDFS(GraphAdjList graph, Vertex startVet) {
// 顶点遍历序列
List<Vertex> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
Set<Vertex> visited = new HashSet<>();
dfs(graph, visited, res, startVet);
return res;
}
/* 深度优先遍历辅助函数 */
void DFS(GraphAdjList graph, HashSet<Vertex> visited, List<Vertex> res, Vertex vet) {
res.Add(vet); // 记录访问顶点
visited.Add(vet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
foreach (Vertex adjVet in graph.adjList[vet]) {
if (visited.Contains(adjVet)) {
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
// 递归访问邻接顶点
DFS(graph, visited, res, adjVet);
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
List<Vertex> GraphDFS(GraphAdjList graph, Vertex startVet) {
// 顶点遍历序列
List<Vertex> res = [];
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
HashSet<Vertex> visited = [];
DFS(graph, visited, res, startVet);
return res;
}
/* 深度优先遍历辅助函数 */
func dfs(g *graphAdjList, visited map[Vertex]struct{}, res *[]Vertex, vet Vertex) {
// append 操作会返回新的的引用,必须让原引用重新赋值为新slice的引用
*res = append(*res, vet)
visited[vet] = struct{}{}
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for _, adjVet := range g.adjList[vet] {
_, isExist := visited[adjVet]
// 递归访问邻接顶点
if !isExist {
dfs(g, visited, res, adjVet)
}
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
func graphDFS(g *graphAdjList, startVet Vertex) []Vertex {
// 顶点遍历序列
res := make([]Vertex, 0)
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
visited := make(map[Vertex]struct{})
dfs(g, visited, &res, startVet)
// 返回顶点遍历序列
return res
}
/* 深度优先遍历辅助函数 */
func dfs(graph: GraphAdjList, visited: inout Set<Vertex>, res: inout [Vertex], vet: Vertex) {
res.append(vet) // 记录访问顶点
visited.insert(vet) // 标记该顶点已被访问
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for adjVet in graph.adjList[vet] ?? [] {
if visited.contains(adjVet) {
continue // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
// 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph: graph, visited: &visited, res: &res, vet: adjVet)
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
func graphDFS(graph: GraphAdjList, startVet: Vertex) -> [Vertex] {
// 顶点遍历序列
var res: [Vertex] = []
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
var visited: Set<Vertex> = []
dfs(graph: graph, visited: &visited, res: &res, vet: startVet)
return res
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
function dfs(graph, visited, res, vet) {
res.push(vet); // 记录访问顶点
visited.add(vet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (const adjVet of graph.adjList.get(vet)) {
if (visited.has(adjVet)) {
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
// 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph, visited, res, adjVet);
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
function graphDFS(graph, startVet) {
// 顶点遍历序列
const res = [];
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
const visited = new Set();
dfs(graph, visited, res, startVet);
return res;
}
/* 深度优先遍历辅助函数 */
function dfs(
graph: GraphAdjList,
visited: Set<Vertex>,
res: Vertex[],
vet: Vertex
): void {
res.push(vet); // 记录访问顶点
visited.add(vet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (const adjVet of graph.adjList.get(vet)) {
if (visited.has(adjVet)) {
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
// 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph, visited, res, adjVet);
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
function graphDFS(graph: GraphAdjList, startVet: Vertex): Vertex[] {
// 顶点遍历序列
const res: Vertex[] = [];
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
const visited: Set<Vertex> = new Set();
dfs(graph, visited, res, startVet);
return res;
}
/* 深度优先遍历辅助函数 */
void dfs(
GraphAdjList graph,
Set<Vertex> visited,
List<Vertex> res,
Vertex vet,
) {
res.add(vet); // 记录访问顶点
visited.add(vet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (Vertex adjVet in graph.adjList[vet]!) {
if (visited.contains(adjVet)) {
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
// 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph, visited, res, adjVet);
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
List<Vertex> graphDFS(GraphAdjList graph, Vertex startVet) {
// 顶点遍历序列
List<Vertex> res = [];
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
Set<Vertex> visited = {};
dfs(graph, visited, res, startVet);
return res;
}
/* 深度优先遍历辅助函数 */
fn dfs(graph: &GraphAdjList, visited: &mut HashSet<Vertex>, res: &mut Vec<Vertex>, vet: Vertex) {
res.push(vet); // 记录访问顶点
visited.insert(vet); // 标记该顶点已被访问
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
if let Some(adj_vets) = graph.adj_list.get(&vet) {
for &adj_vet in adj_vets {
if visited.contains(&adj_vet) {
continue; // 跳过已被访问的顶点
}
// 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph, visited, res, adj_vet);
}
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
fn graph_dfs(graph: GraphAdjList, start_vet: Vertex) -> Vec<Vertex> {
// 顶点遍历序列
let mut res = vec![];
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
let mut visited = HashSet::new();
dfs(&graph, &mut visited, &mut res, start_vet);
res
}
/* 检查顶点是否已被访问 */
int isVisited(Vertex **res, int size, Vertex *vet) {
// 遍历查找节点,使用 O(n) 时间
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (res[i] == vet) {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
/* 深度优先遍历辅助函数 */
void dfs(GraphAdjList *graph, Vertex **res, int *resSize, Vertex *vet) {
// 记录访问顶点
res[(*resSize)++] = vet;
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
AdjListNode *node = findNode(graph, vet);
while (node != NULL) {
// 跳过已被访问的顶点
if (!isVisited(res, *resSize, node->vertex)) {
// 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph, res, resSize, node->vertex);
}
node = node->next;
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
void graphDFS(GraphAdjList *graph, Vertex *startVet, Vertex **res, int *resSize) {
dfs(graph, res, resSize, startVet);
}
/* 深度优先遍历辅助函数 */
fun dfs(
graph: GraphAdjList,
visited: MutableSet<Vertex?>,
res: MutableList<Vertex?>,
vet: Vertex?
) {
res.add(vet) // 记录访问顶点
visited.add(vet) // 标记该顶点已被访问
// 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for (adjVet in graph.adjList[vet]!!) {
if (visited.contains(adjVet))
continue // 跳过已被访问的顶点
// 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph, visited, res, adjVet)
}
}
/* 深度优先遍历 */
// 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
fun graphDFS(graph: GraphAdjList, startVet: Vertex?): MutableList<Vertex?> {
// 顶点遍历序列
val res = mutableListOf<Vertex?>()
// 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
val visited = HashSet<Vertex?>()
dfs(graph, visited, res, startVet)
return res
}
### 深度优先遍历辅助函数 ###
def dfs(graph, visited, res, vet)
res << vet # 记录访问顶点
visited.add(vet) # 标记该顶点已被访问
# 遍历该顶点的所有邻接顶点
for adj_vet in graph.adj_list[vet]
next if visited.include?(adj_vet) # 跳过已被访问的顶点
# 递归访问邻接顶点
dfs(graph, visited, res, adj_vet)
end
end
### 深度优先遍历 ###
def graph_dfs(graph, start_vet)
# 使用邻接表来表示图,以便获取指定顶点的所有邻接顶点
# 顶点遍历序列
res = []
# 哈希表,用于记录已被访问过的顶点
visited = Set.new
dfs(graph, visited, res, start_vet)
res
end
Code Visualization
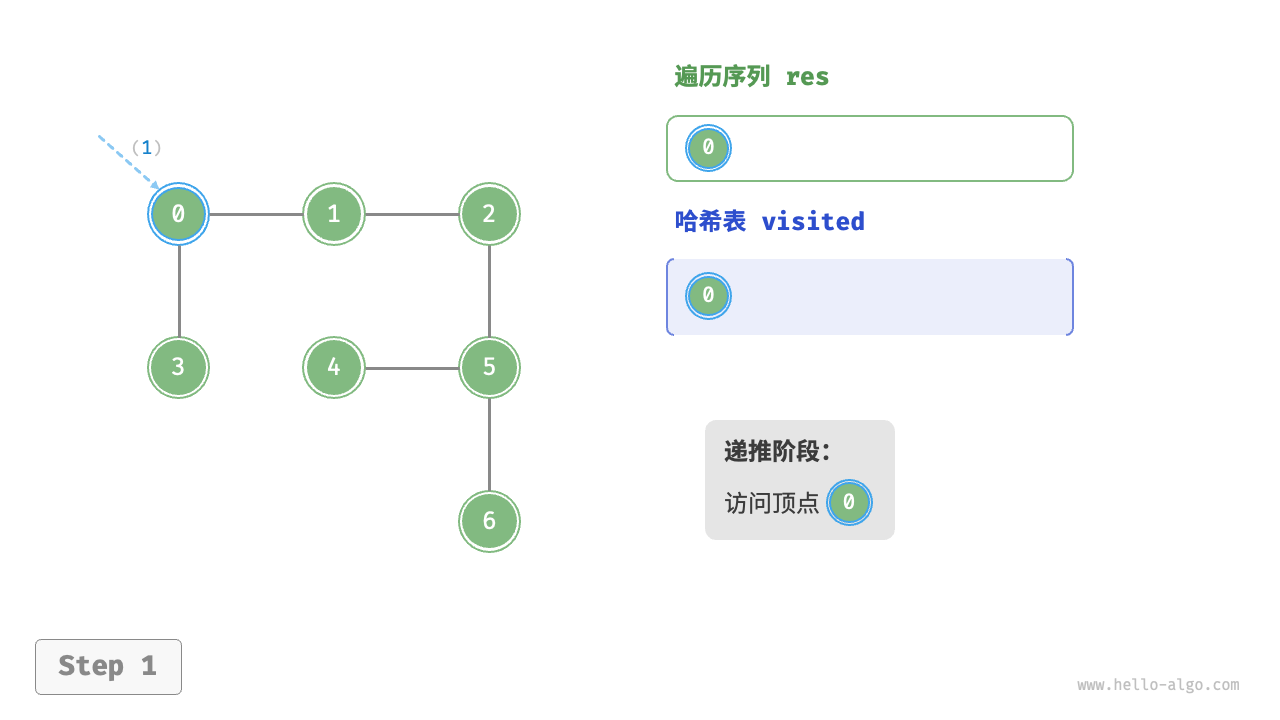
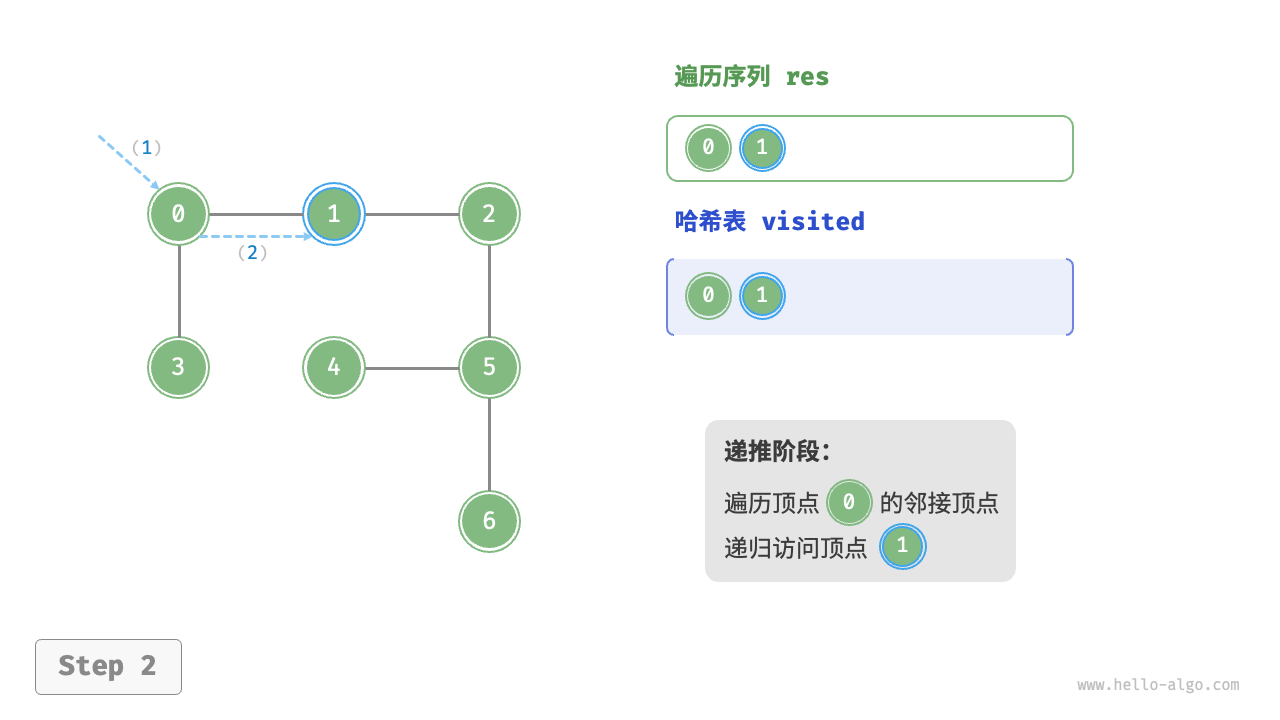
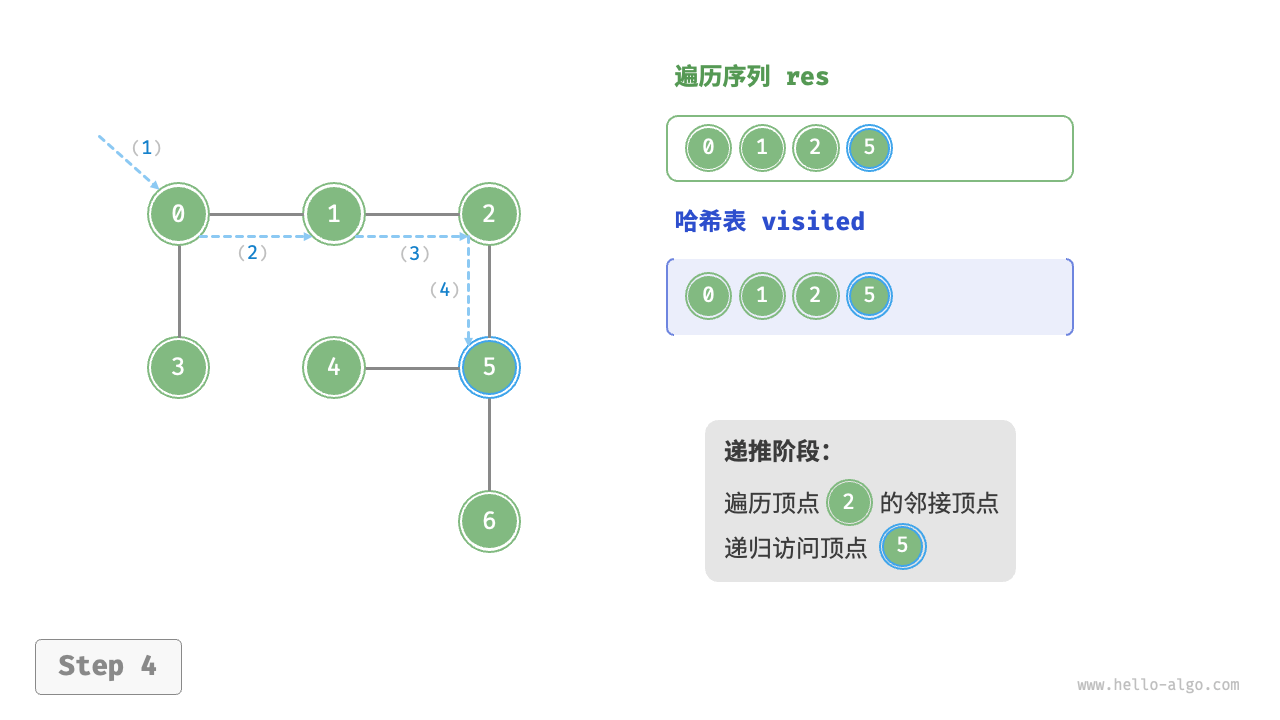
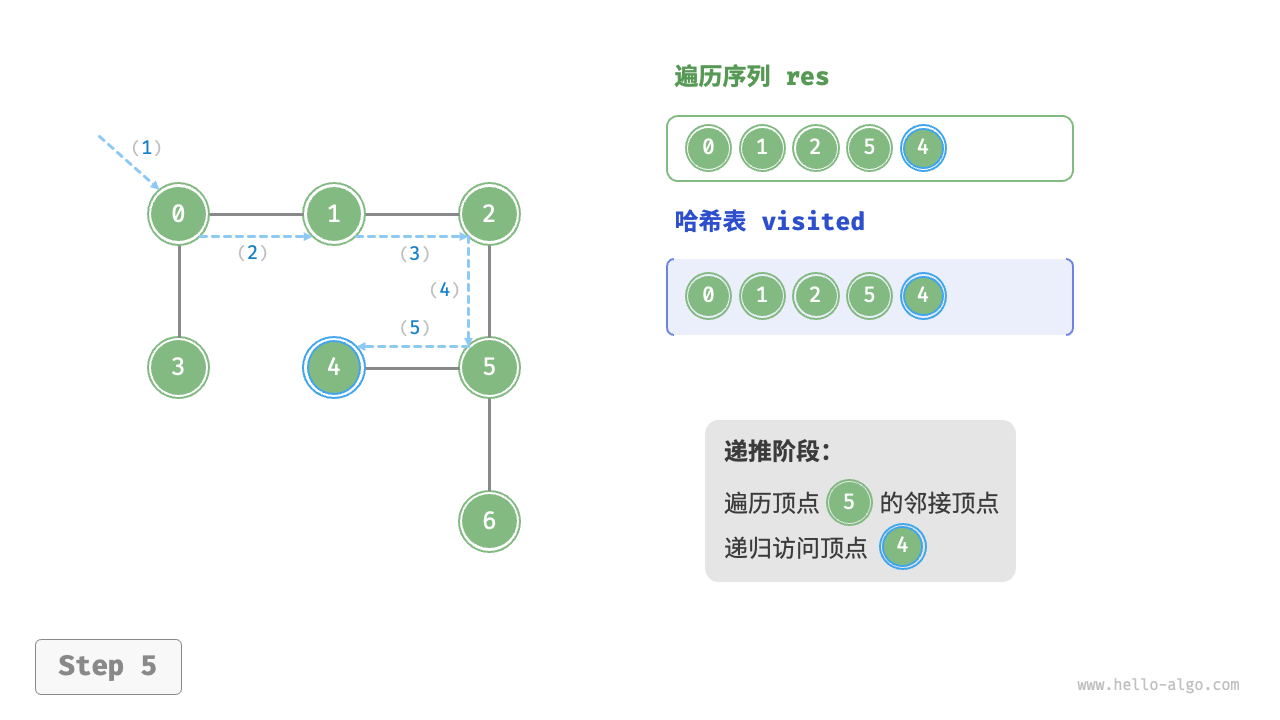
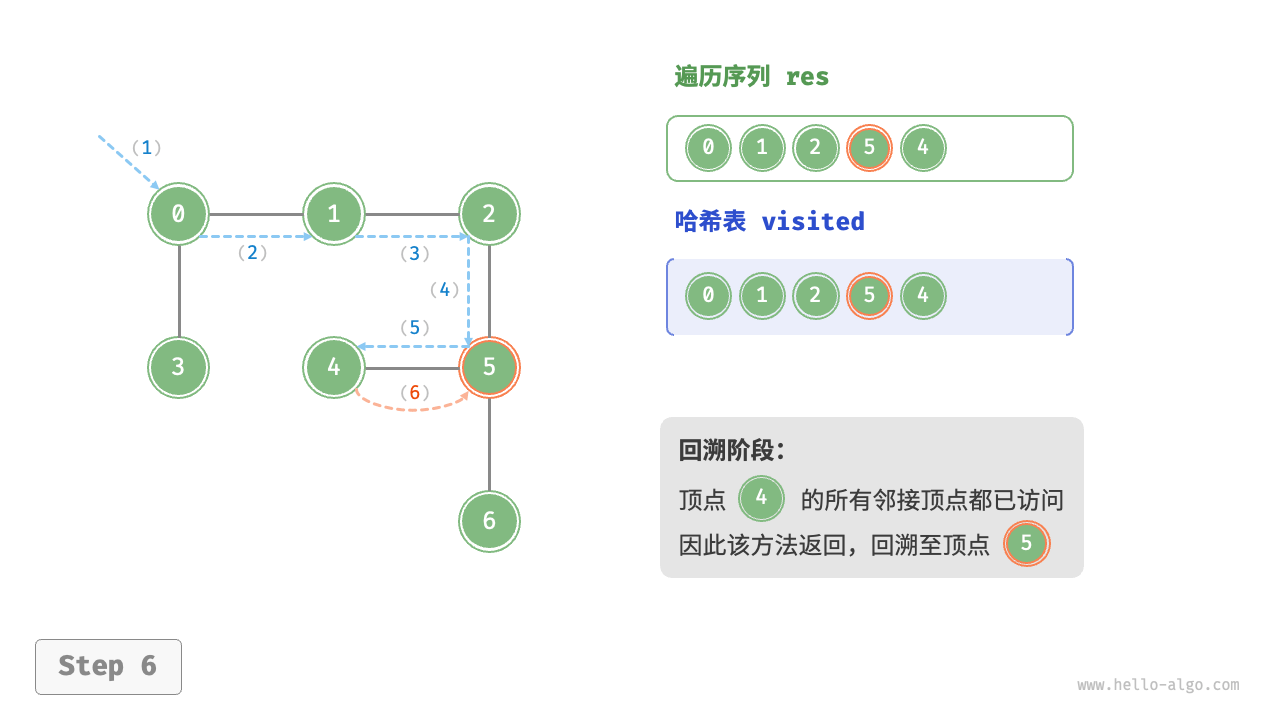
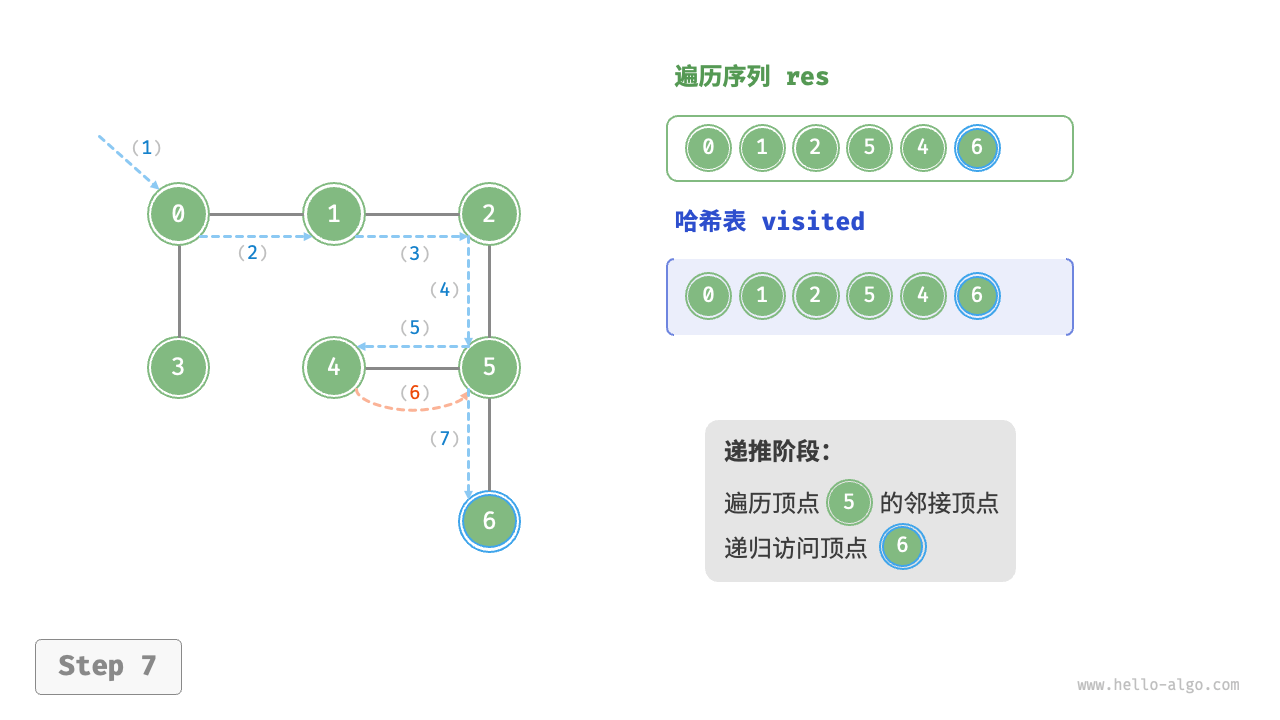
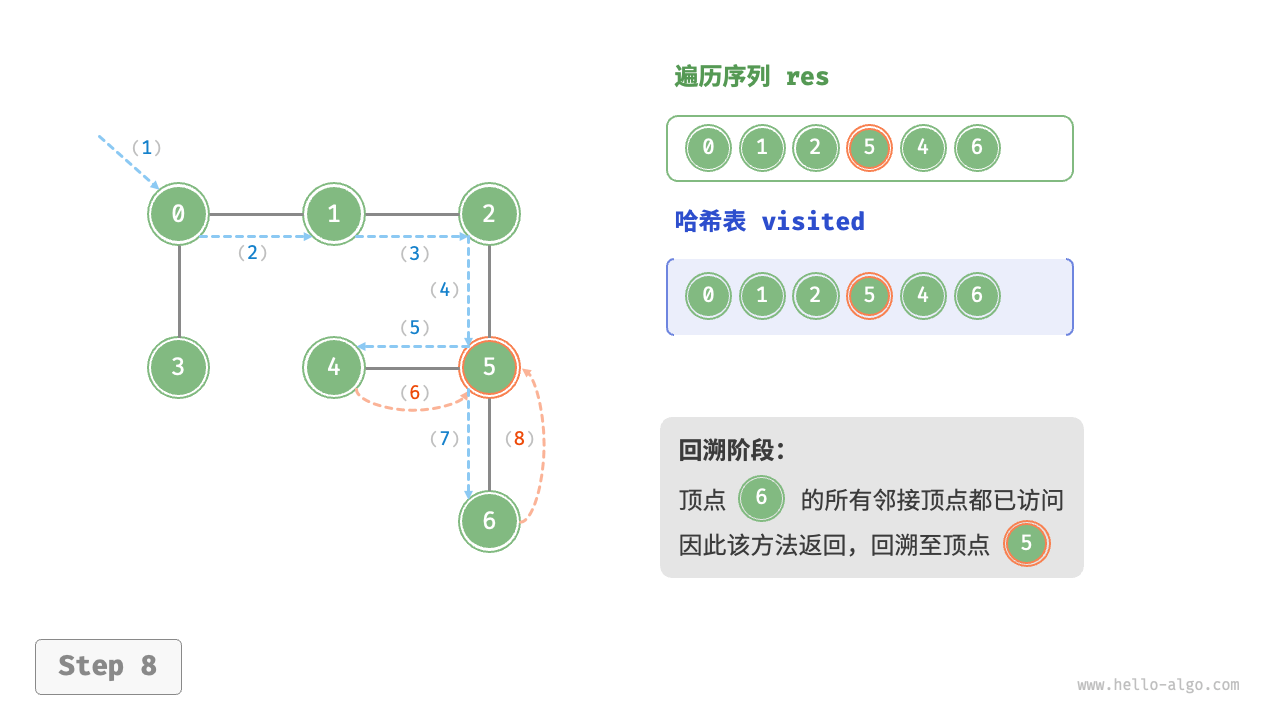
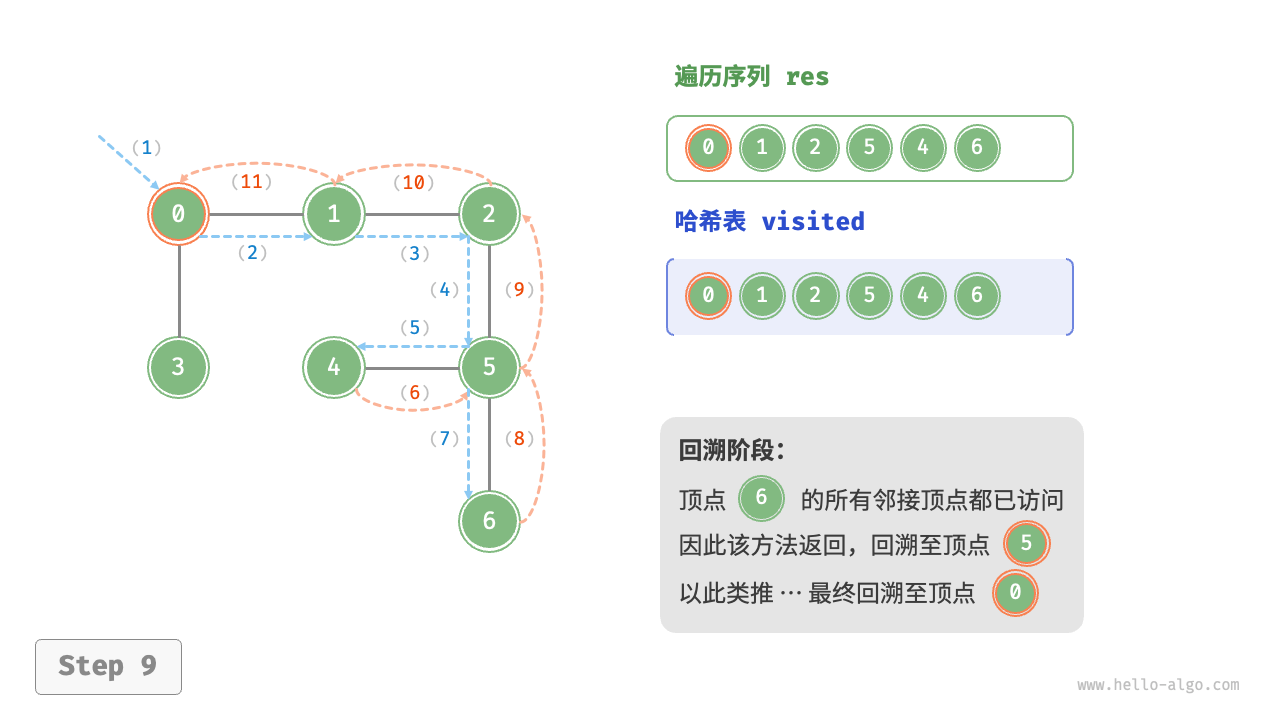
The algorithm process of depth-first search is shown in the following figure.
- Dashed lines represent downward recursion, indicating that a new recursive method has been initiated to visit a new vertex.
- Curved dashed lines represent upward backtracking, indicating that this recursive method has returned to the position where this method was initiated.
To deepen the understanding, it is suggested to combine the following figure with the code to simulate (or draw) the entire DFS process in your mind, including when each recursive method is initiated and when it returns.
Figure 9-12 Steps of depth-first search of a graph
Is the sequence of depth-first traversal unique?
Similar to breadth-first traversal, the order of the depth-first traversal sequence is also not unique. Given a certain vertex, exploring in any direction first is possible, that is, the order of adjacent vertices can be arbitrarily shuffled, all being part of depth-first traversal.
Taking tree traversal as an example, "root \(\rightarrow\) left \(\rightarrow\) right", "left \(\rightarrow\) root \(\rightarrow\) right", "left \(\rightarrow\) right \(\rightarrow\) root" correspond to preorder, inorder, and postorder traversals, respectively. They showcase three types of traversal priorities, yet all three are considered depth-first traversal.
2. Complexity analysis¶
Time complexity: All vertices will be visited once, using \(O(|V|)\) time; all edges will be visited twice, using \(O(2|E|)\) time; overall using \(O(|V| + |E|)\) time.
Space complexity: The maximum number of vertices in list res, hash table visited is \(|V|\), and the maximum recursion depth is \(|V|\), therefore using \(O(|V|)\) space.