13.2 全排列問題¶
全排列問題是回溯演算法的一個典型應用。它的定義是在給定一個集合(如一個陣列或字串)的情況下,找出其中元素的所有可能的排列。
表 13-2 列舉了幾個示例資料,包括輸入陣列和對應的所有排列。
表 13-2 全排列示例
| 輸入陣列 | 所有排列 |
|---|---|
| \([1]\) | \([1]\) |
| \([1, 2]\) | \([1, 2], [2, 1]\) |
| \([1, 2, 3]\) | \([1, 2, 3], [1, 3, 2], [2, 1, 3], [2, 3, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 2, 1]\) |
13.2.1 無相等元素的情況¶
Question
輸入一個整數陣列,其中不包含重複元素,返回所有可能的排列。
從回溯演算法的角度看,我們可以把生成排列的過程想象成一系列選擇的結果。假設輸入陣列為 \([1, 2, 3]\) ,如果我們先選擇 \(1\) ,再選擇 \(3\) ,最後選擇 \(2\) ,則獲得排列 \([1, 3, 2]\) 。回退表示撤銷一個選擇,之後繼續嘗試其他選擇。
從回溯程式碼的角度看,候選集合 choices 是輸入陣列中的所有元素,狀態 state 是直至目前已被選擇的元素。請注意,每個元素只允許被選擇一次,因此 state 中的所有元素都應該是唯一的。
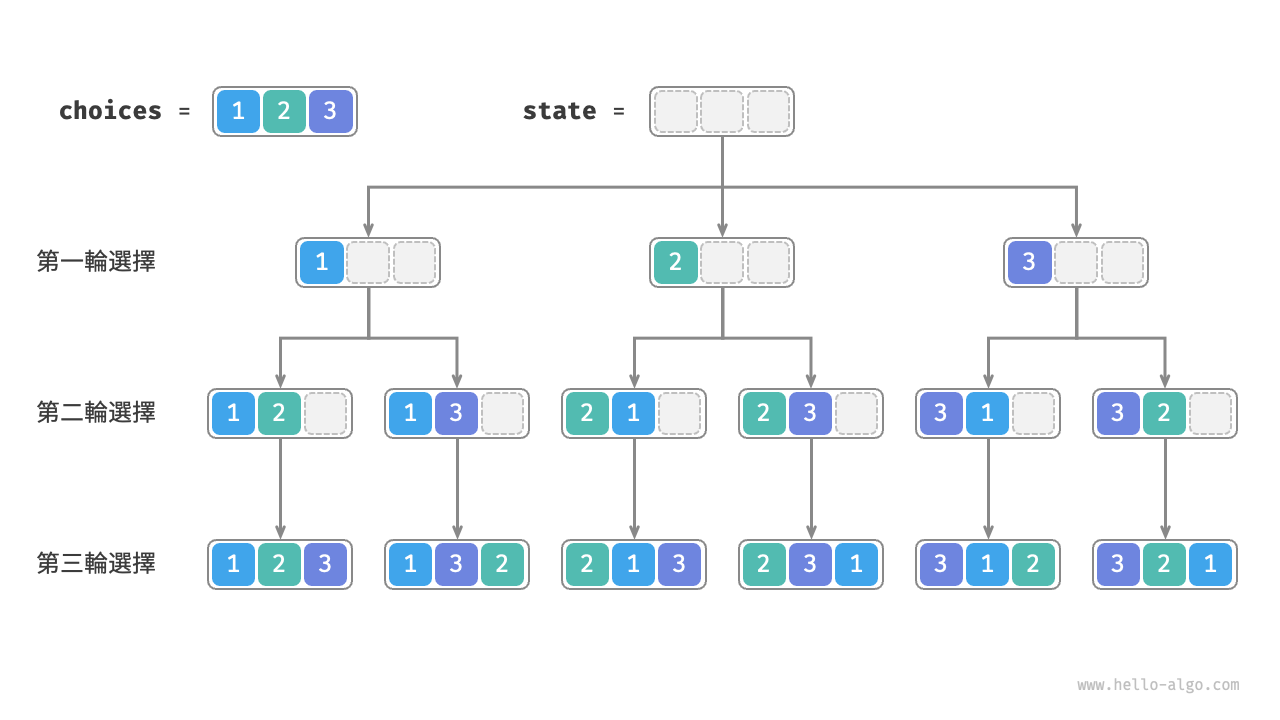
如圖 13-5 所示,我們可以將搜尋過程展開成一棵遞迴樹,樹中的每個節點代表當前狀態 state 。從根節點開始,經過三輪選擇後到達葉節點,每個葉節點都對應一個排列。
圖 13-5 全排列的遞迴樹
1. 重複選擇剪枝¶
為了實現每個元素只被選擇一次,我們考慮引入一個布林型陣列 selected ,其中 selected[i] 表示 choices[i] 是否已被選擇,並基於它實現以下剪枝操作。
- 在做出選擇
choice[i]後,我們就將selected[i]賦值為 \(\text{True}\) ,代表它已被選擇。 - 走訪選擇串列
choices時,跳過所有已被選擇的節點,即剪枝。
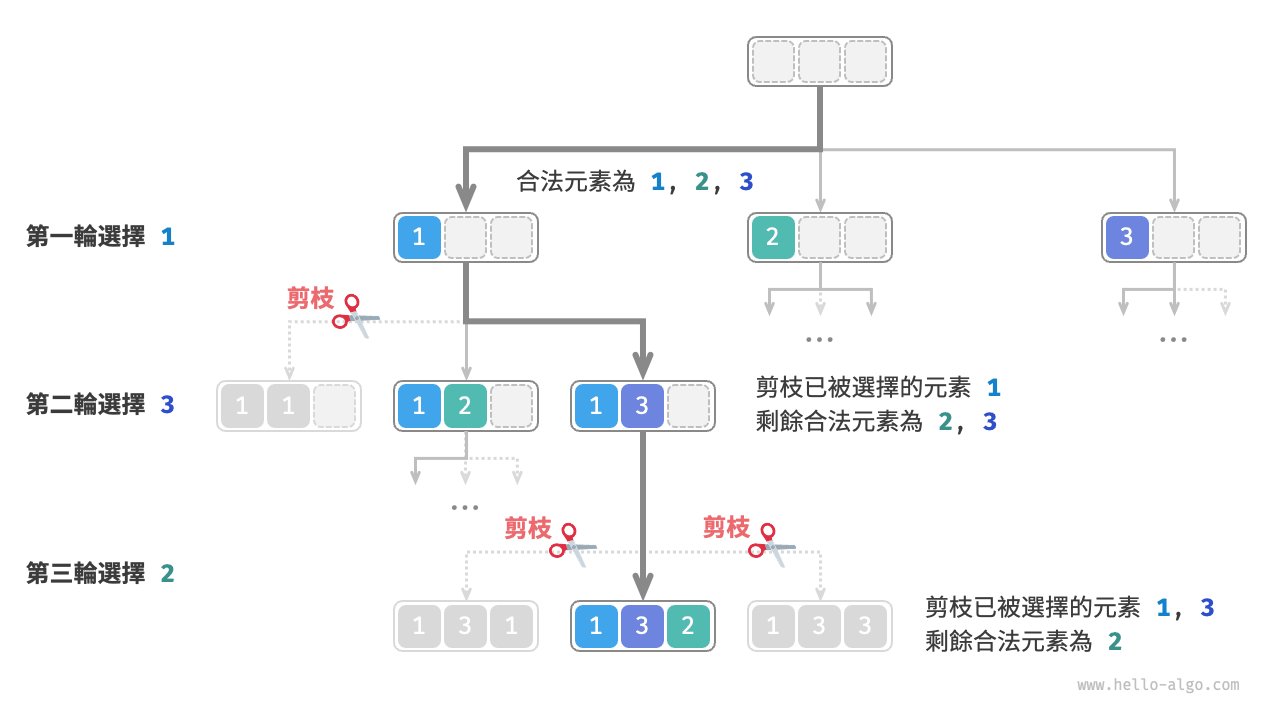
如圖 13-6 所示,假設我們第一輪選擇 1 ,第二輪選擇 3 ,第三輪選擇 2 ,則需要在第二輪剪掉元素 1 的分支,在第三輪剪掉元素 1 和元素 3 的分支。
圖 13-6 全排列剪枝示例
觀察圖 13-6 發現,該剪枝操作將搜尋空間大小從 \(O(n^n)\) 減小至 \(O(n!)\) 。
2. 程式碼實現¶
想清楚以上資訊之後,我們就可以在框架程式碼中做“完形填空”了。為了縮短整體程式碼,我們不單獨實現框架程式碼中的各個函式,而是將它們展開在 backtrack() 函式中:
def backtrack(
state: list[int], choices: list[int], selected: list[bool], res: list[list[int]]
):
"""回溯演算法:全排列 I"""
# 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if len(state) == len(choices):
res.append(list(state))
return
# 走訪所有選擇
for i, choice in enumerate(choices):
# 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if not selected[i]:
# 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = True
state.append(choice)
# 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res)
# 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = False
state.pop()
def permutations_i(nums: list[int]) -> list[list[int]]:
"""全排列 I"""
res = []
backtrack(state=[], choices=nums, selected=[False] * len(nums), res=res)
return res
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
void backtrack(vector<int> &state, const vector<int> &choices, vector<bool> &selected, vector<vector<int>> &res) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.size() == choices.size()) {
res.push_back(state);
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
for (int i = 0; i < choices.size(); i++) {
int choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if (!selected[i]) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true;
state.push_back(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.pop_back();
}
}
}
/* 全排列 I */
vector<vector<int>> permutationsI(vector<int> nums) {
vector<int> state;
vector<bool> selected(nums.size(), false);
vector<vector<int>> res;
backtrack(state, nums, selected, res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
void backtrack(List<Integer> state, int[] choices, boolean[] selected, List<List<Integer>> res) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.size() == choices.length) {
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(state));
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
for (int i = 0; i < choices.length; i++) {
int choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if (!selected[i]) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true;
state.add(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.remove(state.size() - 1);
}
}
}
/* 全排列 I */
List<List<Integer>> permutationsI(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
backtrack(new ArrayList<Integer>(), nums, new boolean[nums.length], res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
void Backtrack(List<int> state, int[] choices, bool[] selected, List<List<int>> res) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.Count == choices.Length) {
res.Add(new List<int>(state));
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
for (int i = 0; i < choices.Length; i++) {
int choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if (!selected[i]) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true;
state.Add(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
Backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.RemoveAt(state.Count - 1);
}
}
}
/* 全排列 I */
List<List<int>> PermutationsI(int[] nums) {
List<List<int>> res = [];
Backtrack([], nums, new bool[nums.Length], res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
func backtrackI(state *[]int, choices *[]int, selected *[]bool, res *[][]int) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if len(*state) == len(*choices) {
newState := append([]int{}, *state...)
*res = append(*res, newState)
}
// 走訪所有選擇
for i := 0; i < len(*choices); i++ {
choice := (*choices)[i]
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if !(*selected)[i] {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
(*selected)[i] = true
*state = append(*state, choice)
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrackI(state, choices, selected, res)
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
(*selected)[i] = false
*state = (*state)[:len(*state)-1]
}
}
}
/* 全排列 I */
func permutationsI(nums []int) [][]int {
res := make([][]int, 0)
state := make([]int, 0)
selected := make([]bool, len(nums))
backtrackI(&state, &nums, &selected, &res)
return res
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
func backtrack(state: inout [Int], choices: [Int], selected: inout [Bool], res: inout [[Int]]) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if state.count == choices.count {
res.append(state)
return
}
// 走訪所有選擇
for (i, choice) in choices.enumerated() {
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if !selected[i] {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true
state.append(choice)
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state: &state, choices: choices, selected: &selected, res: &res)
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false
state.removeLast()
}
}
}
/* 全排列 I */
func permutationsI(nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
var state: [Int] = []
var selected = Array(repeating: false, count: nums.count)
var res: [[Int]] = []
backtrack(state: &state, choices: nums, selected: &selected, res: &res)
return res
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
function backtrack(state, choices, selected, res) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.length === choices.length) {
res.push([...state]);
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
choices.forEach((choice, i) => {
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if (!selected[i]) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true;
state.push(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.pop();
}
});
}
/* 全排列 I */
function permutationsI(nums) {
const res = [];
backtrack([], nums, Array(nums.length).fill(false), res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
function backtrack(
state: number[],
choices: number[],
selected: boolean[],
res: number[][]
): void {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.length === choices.length) {
res.push([...state]);
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
choices.forEach((choice, i) => {
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if (!selected[i]) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true;
state.push(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.pop();
}
});
}
/* 全排列 I */
function permutationsI(nums: number[]): number[][] {
const res: number[][] = [];
backtrack([], nums, Array(nums.length).fill(false), res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
void backtrack(
List<int> state,
List<int> choices,
List<bool> selected,
List<List<int>> res,
) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.length == choices.length) {
res.add(List.from(state));
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
for (int i = 0; i < choices.length; i++) {
int choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if (!selected[i]) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true;
state.add(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.removeLast();
}
}
}
/* 全排列 I */
List<List<int>> permutationsI(List<int> nums) {
List<List<int>> res = [];
backtrack([], nums, List.filled(nums.length, false), res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
fn backtrack(mut state: Vec<i32>, choices: &[i32], selected: &mut [bool], res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if state.len() == choices.len() {
res.push(state);
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
for i in 0..choices.len() {
let choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if !selected[i] {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true;
state.push(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state.clone(), choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.remove(state.len() - 1);
}
}
}
/* 全排列 I */
fn permutations_i(nums: &mut [i32]) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut res = Vec::new(); // 狀態(子集)
backtrack(Vec::new(), nums, &mut vec![false; nums.len()], &mut res);
res
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
void backtrack(int *state, int stateSize, int *choices, int choicesSize, bool *selected, int **res, int *resSize) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (stateSize == choicesSize) {
res[*resSize] = (int *)malloc(choicesSize * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < choicesSize; i++) {
res[*resSize][i] = state[i];
}
(*resSize)++;
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
for (int i = 0; i < choicesSize; i++) {
int choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if (!selected[i]) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true;
state[stateSize] = choice;
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, stateSize + 1, choices, choicesSize, selected, res, resSize);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
}
}
}
/* 全排列 I */
int **permutationsI(int *nums, int numsSize, int *returnSize) {
int *state = (int *)malloc(numsSize * sizeof(int));
bool *selected = (bool *)malloc(numsSize * sizeof(bool));
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {
selected[i] = false;
}
int **res = (int **)malloc(MAX_SIZE * sizeof(int *));
*returnSize = 0;
backtrack(state, 0, nums, numsSize, selected, res, returnSize);
free(state);
free(selected);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 I */
fun backtrack(
state: MutableList<Int>,
choices: IntArray,
selected: BooleanArray,
res: MutableList<MutableList<Int>?>
) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.size == choices.size) {
res.add(state.toMutableList())
return
}
// 走訪所有選擇
for (i in choices.indices) {
val choice = choices[i]
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
if (!selected[i]) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true
state.add(choice)
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res)
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false
state.removeAt(state.size - 1)
}
}
}
/* 全排列 I */
fun permutationsI(nums: IntArray): MutableList<MutableList<Int>?> {
val res = mutableListOf<MutableList<Int>?>()
backtrack(mutableListOf(), nums, BooleanArray(nums.size), res)
return res
}
### 回溯演算法:全排列 I ###
def backtrack(state, choices, selected, res)
# 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if state.length == choices.length
res << state.dup
return
end
# 走訪所有選擇
choices.each_with_index do |choice, i|
# 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素
unless selected[i]
# 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
selected[i] = true
state << choice
# 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res)
# 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false
state.pop
end
end
end
### 全排列 I ###
def permutations_i(nums)
res = []
backtrack([], nums, Array.new(nums.length, false), res)
res
end
視覺化執行
13.2.2 考慮相等元素的情況¶
Question
輸入一個整數陣列,陣列中可能包含重複元素,返回所有不重複的排列。
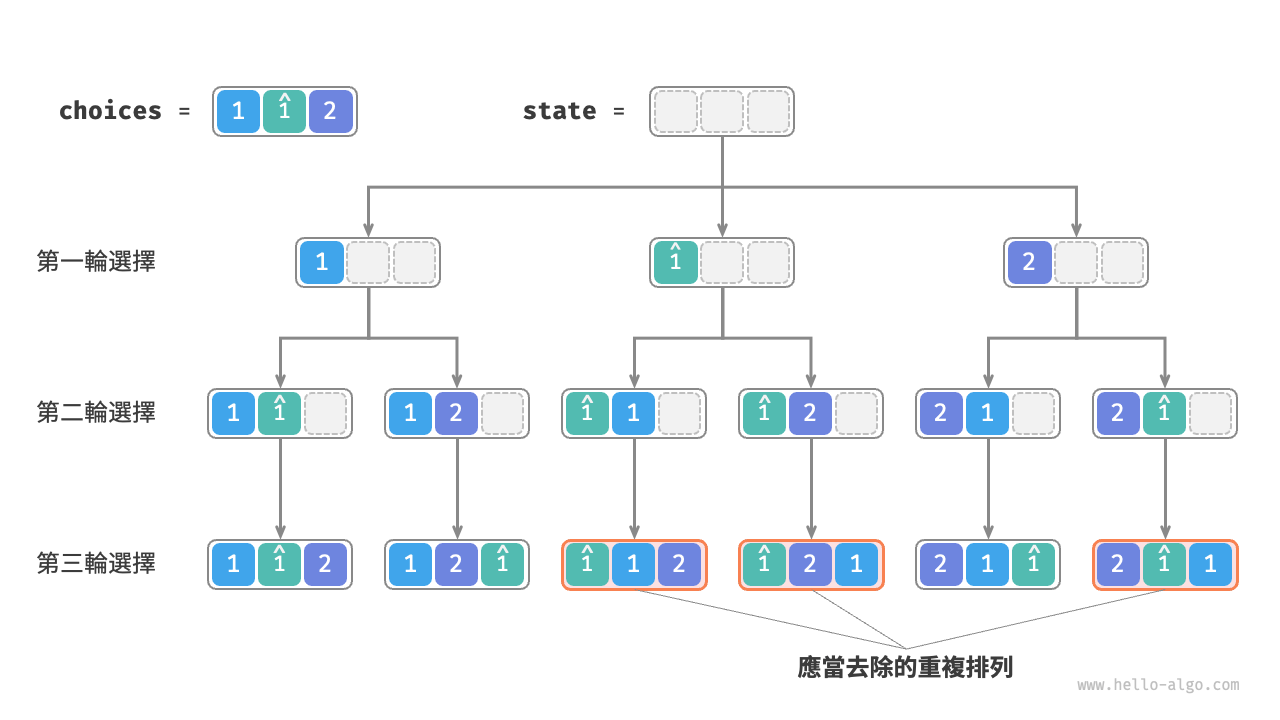
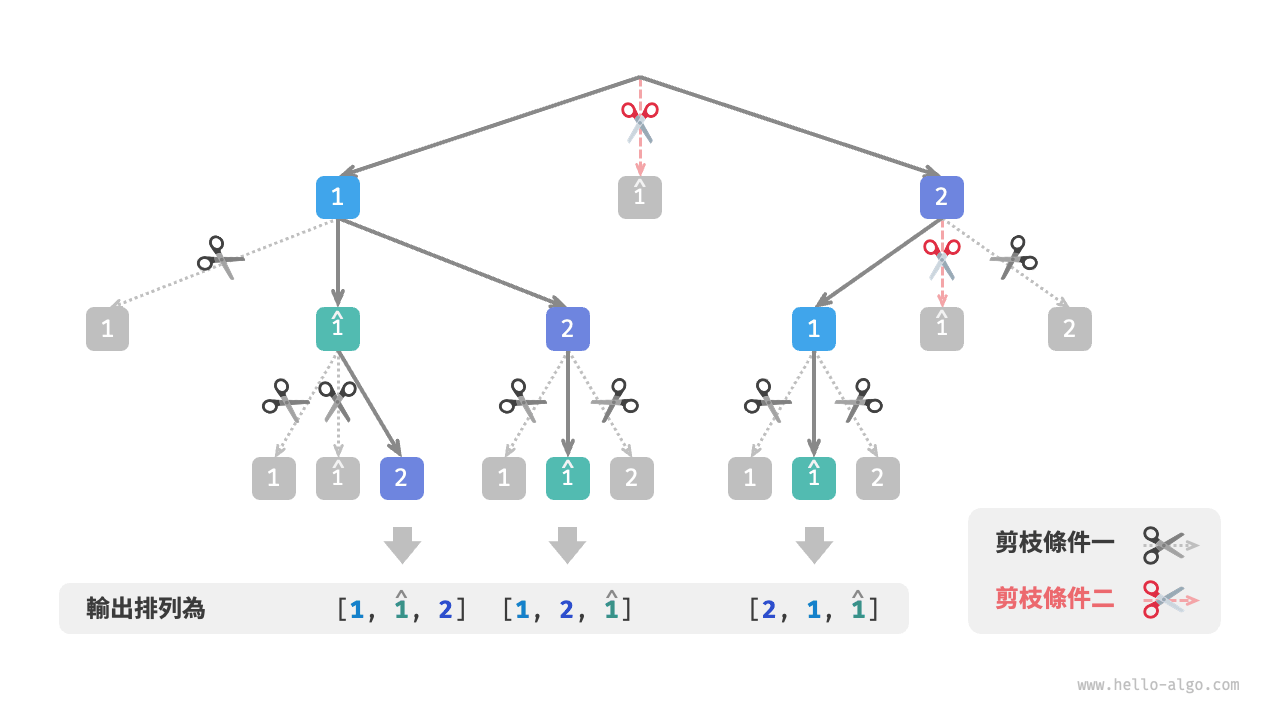
假設輸入陣列為 \([1, 1, 2]\) 。為了方便區分兩個重複元素 \(1\) ,我們將第二個 \(1\) 記為 \(\hat{1}\) 。
如圖 13-7 所示,上述方法生成的排列有一半是重複的。
圖 13-7 重複排列
那麼如何去除重複的排列呢?最直接地,考慮藉助一個雜湊集合,直接對排列結果進行去重。然而這樣做不夠優雅,因為生成重複排列的搜尋分支沒有必要,應當提前識別並剪枝,這樣可以進一步提升演算法效率。
1. 相等元素剪枝¶
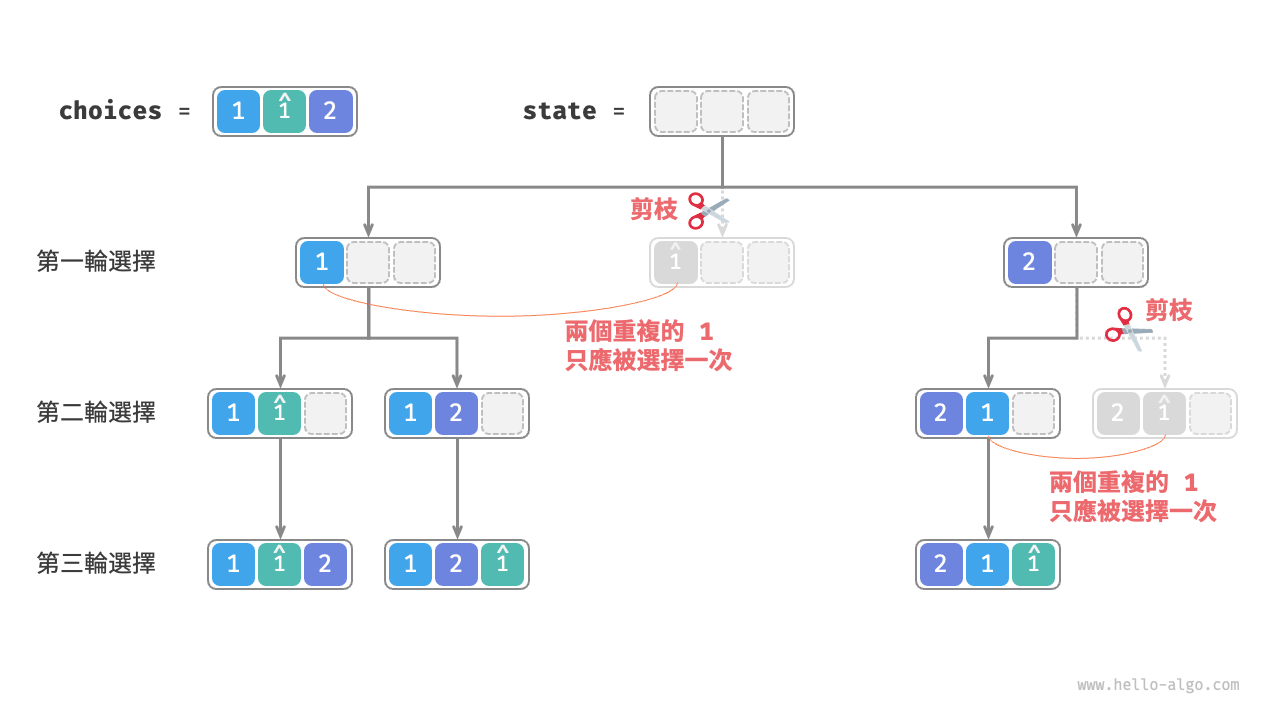
觀察圖 13-8 ,在第一輪中,選擇 \(1\) 或選擇 \(\hat{1}\) 是等價的,在這兩個選擇之下生成的所有排列都是重複的。因此應該把 \(\hat{1}\) 剪枝。
同理,在第一輪選擇 \(2\) 之後,第二輪選擇中的 \(1\) 和 \(\hat{1}\) 也會產生重複分支,因此也應將第二輪的 \(\hat{1}\) 剪枝。
從本質上看,我們的目標是在某一輪選擇中,保證多個相等的元素僅被選擇一次。
圖 13-8 重複排列剪枝
2. 程式碼實現¶
在上一題的程式碼的基礎上,我們考慮在每一輪選擇中開啟一個雜湊集合 duplicated ,用於記錄該輪中已經嘗試過的元素,並將重複元素剪枝:
def backtrack(
state: list[int], choices: list[int], selected: list[bool], res: list[list[int]]
):
"""回溯演算法:全排列 II"""
# 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if len(state) == len(choices):
res.append(list(state))
return
# 走訪所有選擇
duplicated = set[int]()
for i, choice in enumerate(choices):
# 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if not selected[i] and choice not in duplicated:
# 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.add(choice) # 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = True
state.append(choice)
# 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res)
# 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = False
state.pop()
def permutations_ii(nums: list[int]) -> list[list[int]]:
"""全排列 II"""
res = []
backtrack(state=[], choices=nums, selected=[False] * len(nums), res=res)
return res
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
void backtrack(vector<int> &state, const vector<int> &choices, vector<bool> &selected, vector<vector<int>> &res) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.size() == choices.size()) {
res.push_back(state);
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
unordered_set<int> duplicated;
for (int i = 0; i < choices.size(); i++) {
int choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if (!selected[i] && duplicated.find(choice) == duplicated.end()) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.emplace(choice); // 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = true;
state.push_back(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.pop_back();
}
}
}
/* 全排列 II */
vector<vector<int>> permutationsII(vector<int> nums) {
vector<int> state;
vector<bool> selected(nums.size(), false);
vector<vector<int>> res;
backtrack(state, nums, selected, res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
void backtrack(List<Integer> state, int[] choices, boolean[] selected, List<List<Integer>> res) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.size() == choices.length) {
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(state));
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
Set<Integer> duplicated = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < choices.length; i++) {
int choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if (!selected[i] && !duplicated.contains(choice)) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.add(choice); // 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = true;
state.add(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.remove(state.size() - 1);
}
}
}
/* 全排列 II */
List<List<Integer>> permutationsII(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
backtrack(new ArrayList<Integer>(), nums, new boolean[nums.length], res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
void Backtrack(List<int> state, int[] choices, bool[] selected, List<List<int>> res) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.Count == choices.Length) {
res.Add(new List<int>(state));
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
HashSet<int> duplicated = [];
for (int i = 0; i < choices.Length; i++) {
int choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if (!selected[i] && !duplicated.Contains(choice)) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.Add(choice); // 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = true;
state.Add(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
Backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.RemoveAt(state.Count - 1);
}
}
}
/* 全排列 II */
List<List<int>> PermutationsII(int[] nums) {
List<List<int>> res = [];
Backtrack([], nums, new bool[nums.Length], res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
func backtrackII(state *[]int, choices *[]int, selected *[]bool, res *[][]int) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if len(*state) == len(*choices) {
newState := append([]int{}, *state...)
*res = append(*res, newState)
}
// 走訪所有選擇
duplicated := make(map[int]struct{}, 0)
for i := 0; i < len(*choices); i++ {
choice := (*choices)[i]
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if _, ok := duplicated[choice]; !ok && !(*selected)[i] {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
// 記錄選擇過的元素值
duplicated[choice] = struct{}{}
(*selected)[i] = true
*state = append(*state, choice)
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrackII(state, choices, selected, res)
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
(*selected)[i] = false
*state = (*state)[:len(*state)-1]
}
}
}
/* 全排列 II */
func permutationsII(nums []int) [][]int {
res := make([][]int, 0)
state := make([]int, 0)
selected := make([]bool, len(nums))
backtrackII(&state, &nums, &selected, &res)
return res
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
func backtrack(state: inout [Int], choices: [Int], selected: inout [Bool], res: inout [[Int]]) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if state.count == choices.count {
res.append(state)
return
}
// 走訪所有選擇
var duplicated: Set<Int> = []
for (i, choice) in choices.enumerated() {
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if !selected[i], !duplicated.contains(choice) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.insert(choice) // 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = true
state.append(choice)
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state: &state, choices: choices, selected: &selected, res: &res)
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false
state.removeLast()
}
}
}
/* 全排列 II */
func permutationsII(nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
var state: [Int] = []
var selected = Array(repeating: false, count: nums.count)
var res: [[Int]] = []
backtrack(state: &state, choices: nums, selected: &selected, res: &res)
return res
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
function backtrack(state, choices, selected, res) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.length === choices.length) {
res.push([...state]);
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
const duplicated = new Set();
choices.forEach((choice, i) => {
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if (!selected[i] && !duplicated.has(choice)) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.add(choice); // 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = true;
state.push(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.pop();
}
});
}
/* 全排列 II */
function permutationsII(nums) {
const res = [];
backtrack([], nums, Array(nums.length).fill(false), res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
function backtrack(
state: number[],
choices: number[],
selected: boolean[],
res: number[][]
): void {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.length === choices.length) {
res.push([...state]);
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
const duplicated = new Set();
choices.forEach((choice, i) => {
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if (!selected[i] && !duplicated.has(choice)) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.add(choice); // 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = true;
state.push(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.pop();
}
});
}
/* 全排列 II */
function permutationsII(nums: number[]): number[][] {
const res: number[][] = [];
backtrack([], nums, Array(nums.length).fill(false), res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
void backtrack(
List<int> state,
List<int> choices,
List<bool> selected,
List<List<int>> res,
) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.length == choices.length) {
res.add(List.from(state));
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
Set<int> duplicated = {};
for (int i = 0; i < choices.length; i++) {
int choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if (!selected[i] && !duplicated.contains(choice)) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.add(choice); // 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = true;
state.add(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.removeLast();
}
}
}
/* 全排列 II */
List<List<int>> permutationsII(List<int> nums) {
List<List<int>> res = [];
backtrack([], nums, List.filled(nums.length, false), res);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
fn backtrack(mut state: Vec<i32>, choices: &[i32], selected: &mut [bool], res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if state.len() == choices.len() {
res.push(state);
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
let mut duplicated = HashSet::<i32>::new();
for i in 0..choices.len() {
let choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if !selected[i] && !duplicated.contains(&choice) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.insert(choice); // 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = true;
state.push(choice);
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state.clone(), choices, selected, res);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
state.remove(state.len() - 1);
}
}
}
/* 全排列 II */
fn permutations_ii(nums: &mut [i32]) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut res = Vec::new();
backtrack(Vec::new(), nums, &mut vec![false; nums.len()], &mut res);
res
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
void backtrack(int *state, int stateSize, int *choices, int choicesSize, bool *selected, int **res, int *resSize) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (stateSize == choicesSize) {
res[*resSize] = (int *)malloc(choicesSize * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < choicesSize; i++) {
res[*resSize][i] = state[i];
}
(*resSize)++;
return;
}
// 走訪所有選擇
bool duplicated[MAX_SIZE] = {false};
for (int i = 0; i < choicesSize; i++) {
int choice = choices[i];
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if (!selected[i] && !duplicated[choice]) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated[choice] = true; // 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = true;
state[stateSize] = choice;
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, stateSize + 1, choices, choicesSize, selected, res, resSize);
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false;
}
}
}
/* 全排列 II */
int **permutationsII(int *nums, int numsSize, int *returnSize) {
int *state = (int *)malloc(numsSize * sizeof(int));
bool *selected = (bool *)malloc(numsSize * sizeof(bool));
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {
selected[i] = false;
}
int **res = (int **)malloc(MAX_SIZE * sizeof(int *));
*returnSize = 0;
backtrack(state, 0, nums, numsSize, selected, res, returnSize);
free(state);
free(selected);
return res;
}
/* 回溯演算法:全排列 II */
fun backtrack(
state: MutableList<Int>,
choices: IntArray,
selected: BooleanArray,
res: MutableList<MutableList<Int>?>
) {
// 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if (state.size == choices.size) {
res.add(state.toMutableList())
return
}
// 走訪所有選擇
val duplicated = HashSet<Int>()
for (i in choices.indices) {
val choice = choices[i]
// 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if (!selected[i] && !duplicated.contains(choice)) {
// 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.add(choice) // 記錄選擇過的元素值
selected[i] = true
state.add(choice)
// 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res)
// 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false
state.removeAt(state.size - 1)
}
}
}
/* 全排列 II */
fun permutationsII(nums: IntArray): MutableList<MutableList<Int>?> {
val res = mutableListOf<MutableList<Int>?>()
backtrack(mutableListOf(), nums, BooleanArray(nums.size), res)
return res
}
### 回溯演算法:全排列 II ###
def backtrack(state, choices, selected, res)
# 當狀態長度等於元素數量時,記錄解
if state.length == choices.length
res << state.dup
return
end
# 走訪所有選擇
duplicated = Set.new
choices.each_with_index do |choice, i|
# 剪枝:不允許重複選擇元素 且 不允許重複選擇相等元素
if !selected[i] && !duplicated.include?(choice)
# 嘗試:做出選擇,更新狀態
duplicated.add(choice)
selected[i] = true
state << choice
# 進行下一輪選擇
backtrack(state, choices, selected, res)
# 回退:撤銷選擇,恢復到之前的狀態
selected[i] = false
state.pop
end
end
end
### 全排列 II ###
def permutations_ii(nums)
res = []
backtrack([], nums, Array.new(nums.length, false), res)
res
end
視覺化執行
假設元素兩兩之間互不相同,則 \(n\) 個元素共有 \(n!\) 種排列(階乘);在記錄結果時,需要複製長度為 \(n\) 的串列,使用 \(O(n)\) 時間。因此時間複雜度為 \(O(n!n)\) 。
最大遞迴深度為 \(n\) ,使用 \(O(n)\) 堆疊幀空間。selected 使用 \(O(n)\) 空間。同一時刻最多共有 \(n\) 個 duplicated ,使用 \(O(n^2)\) 空間。因此空間複雜度為 \(O(n^2)\) 。
3. 兩種剪枝對比¶
請注意,雖然 selected 和 duplicated 都用於剪枝,但兩者的目標不同。
- 重複選擇剪枝:整個搜尋過程中只有一個
selected。它記錄的是當前狀態中包含哪些元素,其作用是避免某個元素在state中重複出現。 - 相等元素剪枝:每輪選擇(每個呼叫的
backtrack函式)都包含一個duplicated。它記錄的是在本輪走訪(for迴圈)中哪些元素已被選擇過,其作用是保證相等元素只被選擇一次。
圖 13-9 展示了兩個剪枝條件的生效範圍。注意,樹中的每個節點代表一個選擇,從根節點到葉節點的路徑上的各個節點構成一個排列。
圖 13-9 兩種剪枝條件的作用範圍